PSYC 256 Lecture Notes - Lecture 11: Sensory Memory, Mental Chronometry, Brute-Force Search
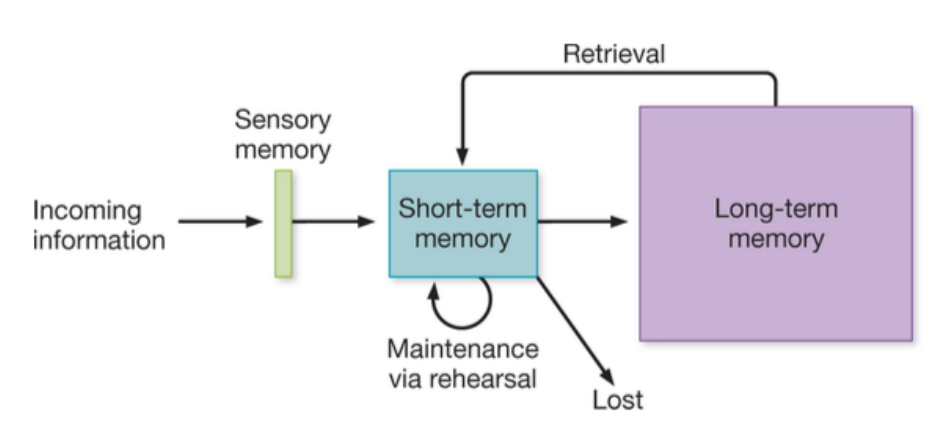
MODAL MEMORY MODEL
Storage Capacity Model
• What type of information can be stored?
• How long is that information held in storage?
• Assumption: information = information = information
•
• Short-term & long-term memories (not working memory)
• Can still lose stuff in sensory memory
Sensory Memory
• Brief storage of sensory information
• Fades quickly without deeper processing
• Separate memory store for each sense
o Iconic (visual)
o Echoic (auditory)
Sperling (1960)
• Whole report: report all rows
find more resources at oneclass.com
find more resources at oneclass.com

o
• People could only report about 4 items accurately
o Invariant over number of letters and exposure duration
• Subjects reported that the whole array was available on the screen even after it
disappeared, but it seemed to fade before they could finish reporting what they
saw
• Partial Report: tone signals subject to report one row of the display
o
Iconic Memory
• Large capacity
• Quick duration
find more resources at oneclass.com
find more resources at oneclass.com

•
Echoic Memory
• Auditory sensory memory
• Smaller capacity than iconic
• Longer duration than iconic
•
> Persistence of external environmental stimulus
find more resources at oneclass.com
find more resources at oneclass.com
Document Summary
Storage capacity model: what type of information can be stored, how long is that information held in storage, assumption: information = information = information, short-term & long-term memories (not working memory, can still lose stuff in sensory memory. Sensory memory: brief storage of sensory information, fades quickly without deeper processing, separate memory store for each sense. Sperling (1960: whole report: report all rows, people could only report about 4 items accurately. Echoic memory: auditory sensory memory, smaller capacity than iconic, longer duration than iconic. Modal model: stm: processes used to hold and rehearse information in current awareness, longer than sensory memory, but shorter than long-term memory. Capacity of stm: george miller (1956, 7 +/- 2 chunks of information, chunk = integrated piece of information. Duration of stm: how could we measure duration of stm, seems to be unlimited in some cases and as brief as sensory store in others. Introduce a constant distraction to prevent maintenance rehearsal.

