MATH 1ZA3 Lecture Notes - Lecture 5: Intermediate Value Theorem
MATH 1ZA3 verified notes
5/39View all
Document Summary
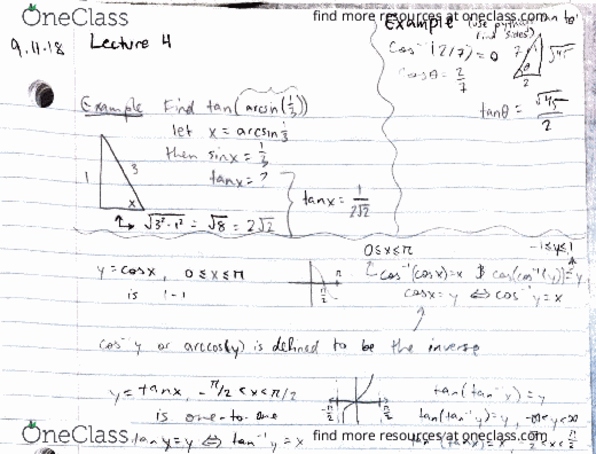
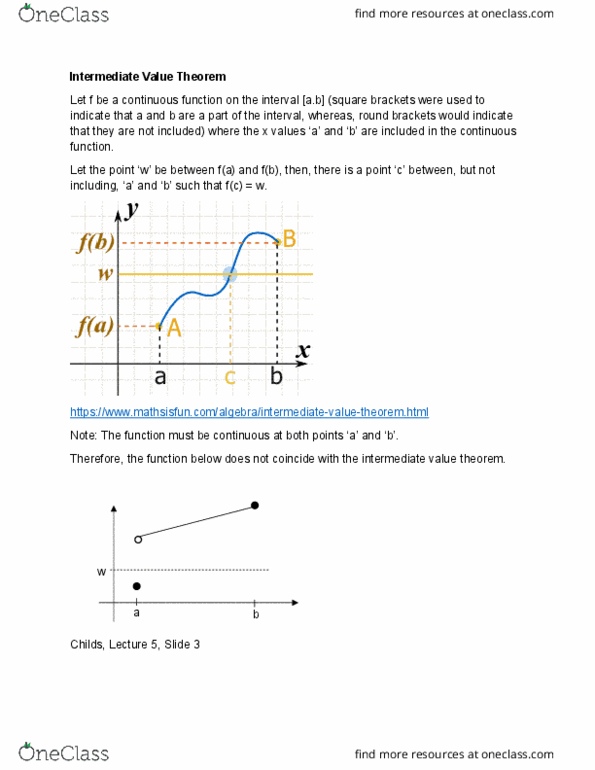
Let the point w" be between f(a) and f(b), then, there is a point c" between, but not including, a" and b" such that f(c) = w. https://www. mathsisfun. com/algebra/intermediate-value-theorem. html. Note: the function must be continuous at both points a" and b". Therefore, the function below does not coincide with the intermediate value theorem. w a b. Show that 4x3 6x2 = 2 3x has at least one root. Note: a function like this is impossible to solve without the aid of technology as the root(s) are decimal values. f(x) = 4x3 6x2 + 3x 2. A method for solving this problem time using the intermediate values theorem. Since 0 is between f(0) = -2 and f(2) = 12, and f is continuous on, and including the interval [0,2], by the intermediate value theorem, there is a value c in the interval (0,2) where f(c) = 0.