PHYSICS 1A03 Lecture Notes - Lecture 7: Kick 2
PHYSICS 1A03 verified notes
7/26View all
Document Summary
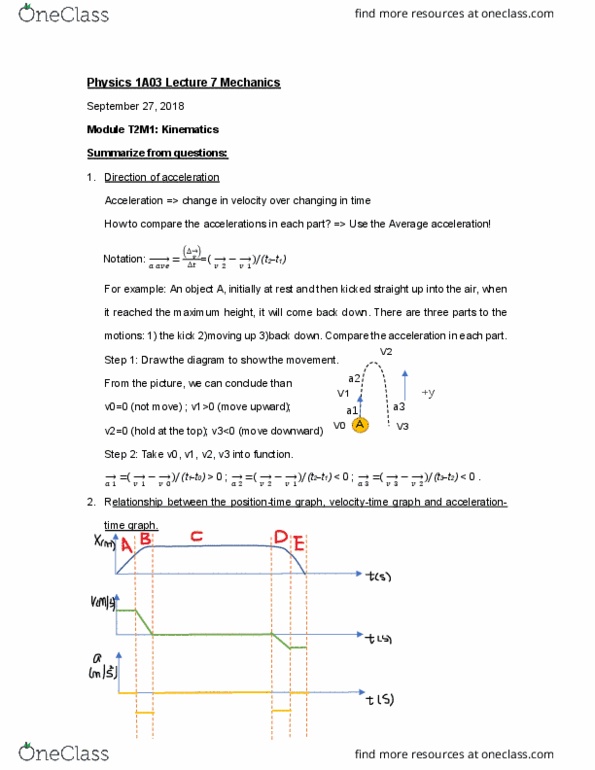
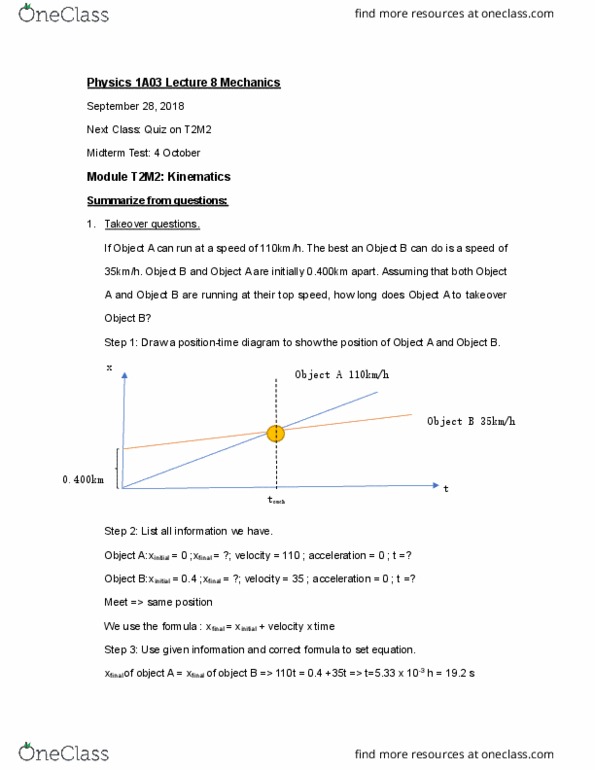
Acceleration => change in velocity over changing in time. Notation: =(cid:4672) (cid:4673) =( (cid:2870) (cid:2869) )/(t2-t1) For example: an object a, initially at rest and then kicked straight up into the air, when it reached the maximum height, it will come back down. There are three parts to the motions: 1) the kick 2)moving up 3)back down. Step 1: draw the diagram to show the movement. From the picture, we can conclude than v0=0 (not move) ; v1>0 (move upward); v2=0 (hold at the top); v3<0 (move downward) a2. For part a: the slope of the position-time graph is constant, it means the velocity is constant, so the slope of velocity has slope zero, which implies the acceleration of part. For part d and e: it seems like part b and a respect, however, the velocity is negative because it towards negative direction.