SOCSCI 2J03 Lecture Notes - Lecture 15: Random Variable, Probability Distribution, Mutual Exclusivity
SOCSCI 2J03 verified notes
15/27View all
Document Summary
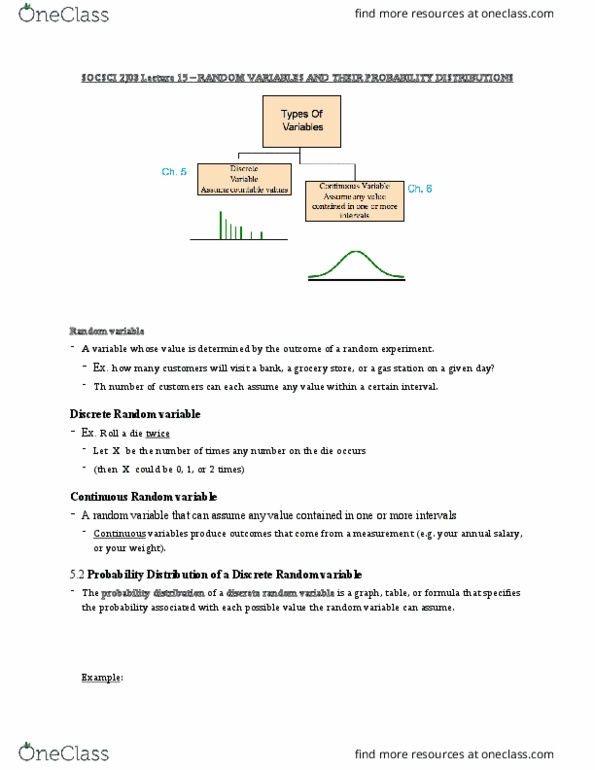
Socsci 2j03 lecture 15 random variables and their probability distributions. A variable whose value is determined by the outcome of a random experiment. Th number of customers can each assume any value within a certain interval. Let x be the number of times any number on the die occurs. (then x could be 0, 1, or 2 times) A random variable that can assume any value contained in one or more intervals. Continuous variables produce outcomes that come from a measurement (e. g. your annual salary, or your weight). 5. 2 probability distribution of a discrete random variable. The probability distribution of a discrete random variable is a graph, table, or formula that specifies the probability associated with each possible value the random variable can assume. The probability distribution of the number showing on top is: You win (+4) if you roll a 5 or a 6. You lose (-5) if you roll a 1.