CISC 102 Lecture Notes - Lecture 37: Propositional Function, Universal Quantification, Complex Instruction Set Computing
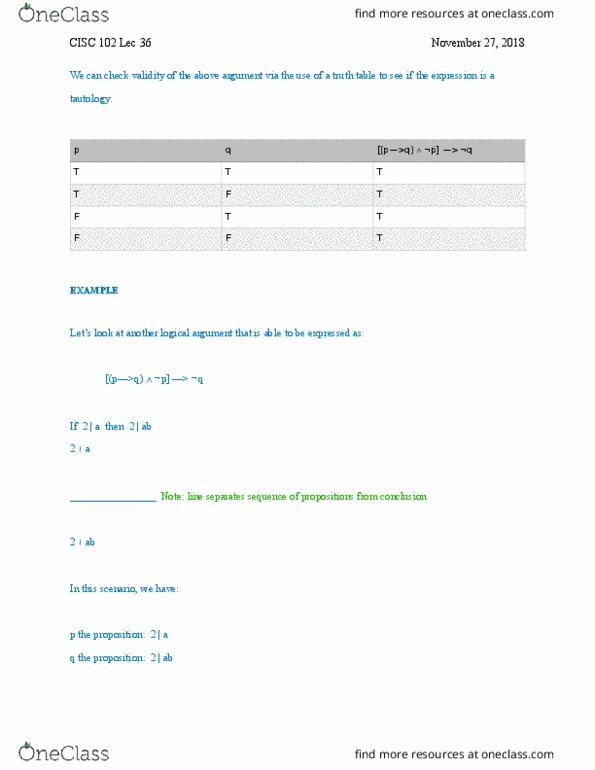
CISC 102 Lecture Notes - Lecture 36: Complex Instruction Set Computing, Propositional Function

CISC 102 Lecture Notes - Lecture 37: Propositional Function, Universal Quantification, Complex Instruction Set Computing

CISC 102 Lecture Notes - Lecture 38: Complex Instruction Set Computing, Rule Of Inference, Modus Ponens
Document Summary
Get access


Related Documents
Related Questions
1. You are given only three quarterly seasonal indices and quarterly seasonally adjusted data for the entire year. What is the raw data value for Q4? Raw data is not adjusted for seasonality.
Quarter Seasonal Index Seasonally Adjusted Data
Q1 .80 295
Q2 .85 299
Q3 1.15 270
Q4 --- 271
2. One model of exponential smoothing will provide almost the same forecast as a liner trend method. What are linear trend intercept and slope counterparts for exponential smoothing?
A. Alpha and Delta
B. Delta and Gamma
C. Alpha and Gamma
D. Standard Deviation and Mean
3. When performing correlation analysis what is the null hypothesis? What measure in Minitab is used to test it and to be 95% confident in the significance of correlation coefficient.
A. Ho: r = .05 p < .5
B. Ho: r = 0 p >.05
C. Ho: r ? 0 p?.05
D. Ho: r = 0 p?.05
| In decomposition what does the cycle factor (CF) of .80 represent for a monthly forecast estimate of a Y variable? |
A. The estimated value is 80% of the average monthly seasonal estimate.
B. The estimate is .80 of the forecasted Y trend value.
C. The estimated value is .80 of the historical average CMA values.
D. The estimated value has 20% more variation than the average historical Y data values.
| 5. A Wendy's franchise owner notes that the sales per store has fallen below the stated national Wendy's outlet average of $1,368,000. He asserts a change has occurred that reduced the fast food eating habits of Americans. What is his hypothesis (H1) and what type of test for significance must be applied? |
A. H1: u ? $1,368,000 A one-tailed t-test to the left.
B. H1: u = $1,368,000 A two-tailed t-test.
C. H1: u < $1,368,000 A one-tailed t-test to the left.
D. H1: p < $1,368,000 A one-tailed test to the right
A. The rejection region and the t-table value generally gets smaller for sample size below 31. |
A. Yes. The data are significantly correlated through the 12th lag. C. No. Only the 12 lag period is not correlated. D. You cannot tell since the number of sample observations is not provided. E. The p-value is above .05 so the data is correlated. |
A. Type 2 error |
A. Yes. They move in the same direction as statistical significance. |
A. The weight cannot be calculated since the data observation is not given. |
A. Yes. The correlation coefficient is .873 that is greater than .05. |
A. Yes, since the residuals randomly vary in magnitude. |
A. -101.0 |
|
1. Suppose that there is a tax of $1 per unit, and the elasticity of supply is 3 and the elasticity of demand is 2 (in absolute value). How much of the $1 tax is paid by sellers?
| $0.60 | ||
| $0.40 | ||
| $0.75 | ||
| $0.67 |
2. In Market X, the external benefit of consumption is $5. In Market Y, the external cost of consumption is $10. Efficiency in both markets could be achieved by:
| a tax of $5 in Market X and a subsidy of $10 in Market Y. | ||
| subsidizing both markets. | ||
| taxing Market Y and subsidizing Market X. | ||
| taxing both markets. |
3.Economic theory suggests that a natural monopoly should be:
| eliminated whenever it arises. | ||
| regulated to take advantage of economies of scale. | ||
| left alone to operate with excess capacity. | ||
| taken over by the government. |
4.When the size of the production is the most efficient:
| total cost is at the minimum. | ||
| average cost is at the minimum. | ||
| marginal cost is at the minimum. | ||
| fixed cost is at the minimum. |
5.A firm should exit the industry if which of the following conditions apply?
| TR > TC | ||
| P < AC | ||
| Lifetime expected profit is positive. | ||
| Prices are low now but expected to rise. |
6.Figure: Costs
Reference: Ref 11-6
(Figure: Costs) Use the figure. At a price of $20, the firm earns profit of:
| $75. | ||
| $300. | ||
| $225. | ||
| $0, because P = MC at P = $20. |
7.When external benefits are present, the market price is ________, however when external costs are present, the market price is ________.
| too low; too high | ||
| equal to the efficient price; too low | ||
| too high; too low | ||
| equal to the efficient price; too high |
8.Which of the following statements is TRUE?
I. The EPA's tradeable allowances program for sulfur dioxide establishes property rights to pollute and helps reduce transaction costs by distributing allowances, maintaining databases, and monitoring emissions.
II. One criticism of tradeable allowances is that they prohibit non-businesses and environmental groups from purchasing the allowances.
III. The tradeable allowances for sulfur dioxide have performed poorly because electricity output has increased, causing a rise in sulfur dioxide levels.
| I only | ||
| II and III only | ||
| I, II, and III | ||
| III only |
9.Price floors make it illegal to compete for more customers by lowering prices, so firms compete by offering customers:
| various options. | ||
| more quantity. | ||
| more discount. | ||
| higher quality. |
10.Figure: Government Price Controls
Reference: Ref 8-3
(Figure: Government Price Controls) Refer to the figure. If the government sets the price ceiling at $31, there will be:
| a shortage of 15 units. | ||
| a surplus of 15 units. | ||
| a supply of 20 units. | ||
| no effect on the market. |
11.In which of these instances does price function as a signal in the market?
| Suppliers invest more in exploration when the price of oil increases. | ||
| Consumers complain of price gouging as the price of oil skyrockets. | ||
| Government imposes price controls on the skyrocketing price of oil. | ||
| All of the answers are correct. |
12.Ethanol and sugar are both made from sugar cane, and ethanol can be used as substitute fuel for oil. Increasing oil prices cause the demand for ethanol to increase. This will cause the ______ sugar to ______ and its price to ______.
| demand for; decrease; decrease | ||
| supply of; increase; increase | ||
| supply of; decrease; increase | ||
| demand for; increase; increase |
13.Why do cotton growers spend billions of dollars to dam rivers and transport water hundreds of miles to grow cotton in California deserts?
| Cotton growers in California don't pay payroll taxes. | ||
| The water used to grow California cotton is highly subsidized by the government. | ||
| Cotton growers in California are mostly operated as nonprofit enterprises. | ||
| The water used to grow California cotton is high in mineral contents, making for a bigger cotton yield. |
14.Suppose that the equilibrium price in the market is $10. If the current market price is $7.50:
| the equilibrium price will fall to $7.50. | ||
| competition among buyers will increase the current price. | ||
| the current price will fall below $7.50 as sellers compete for market share. | ||
| There is not enough information provided to answer the question. |
15.Which of the following would increase the demand for beef?
| lower pork prices | ||
| higher consumer income | ||
| higher prices of feed grains used to feed beef cattle | ||
| an increase in the price of beef |
16.A change in quantity supplied is reflected by a movement along the same supply curve while a change in supply refers to a shift in the entire supply curve.
True
False
17.Table: Production in the United States and Germany
| Labor units required to produce: |
| One Clock | One Sofa |
| United States | 2 | 5 | |
| Germany | 3 | 9 |
Reference: Ref 2-8
(Table: Production in the United States and Germany) According to the table, the opportunity cost of producing one sofa in the United States is _________, and the opportunity cost of producing one sofa in Germany is _______.
| two clocks; three clocks | ||
| 10 clocks; 27 clocks | ||
| 0.4 clocks; 0.33 clocks | ||
| 2.5 clocks; three clocks |
18.Mark values his drum set at $800 and Ella values her guitar at $1,000. Suppose that Mark trades his drum set for Ella's guitar.
| This trade makes Ella worse off by $200. | ||
| This trade makes Mark better off by $200. | ||
| Mark must value Ella's guitar for at least $1,000, and Ella must value Mark's drum set for at least $800. | ||
| This trade creates value by moving the guitar and drum set to people who value them more. |
1. Suppose that there is a tax of $1 per unit, and the elasticity of supply is 3 and the elasticity of demand is 2 (in absolute value). How much of the $1 tax is paid by sellers?
| $0.60 | ||
| $0.40 | ||
| $0.75 | ||
| $0.67 |
2. In Market X, the external benefit of consumption is $5. In Market Y, the external cost of consumption is $10. Efficiency in both markets could be achieved by:
| a tax of $5 in Market X and a subsidy of $10 in Market Y. | ||
| subsidizing both markets. | ||
| taxing Market Y and subsidizing Market X. | ||
| taxing both markets. |
3.Economic theory suggests that a natural monopoly should be:
| eliminated whenever it arises. | ||
| regulated to take advantage of economies of scale. | ||
| left alone to operate with excess capacity. | ||
| taken over by the government. |
4.When the size of the production is the most efficient:
| total cost is at the minimum. | ||
| average cost is at the minimum. | ||
| marginal cost is at the minimum. | ||
| fixed cost is at the minimum. |
5.A firm should exit the industry if which of the following conditions apply?
| TR > TC | ||
| P < AC | ||
| Lifetime expected profit is positive. | ||
| Prices are low now but expected to rise. |
6.Figure: Costs
Reference: Ref 11-6
(Figure: Costs) Use the figure. At a price of $20, the firm earns profit of:
| $75. | ||
| $300. | ||
| $225. | ||
| $0, because P = MC at P = $20. |
7.When external benefits are present, the market price is ________, however when external costs are present, the market price is ________.
| too low; too high | ||
| equal to the efficient price; too low | ||
| too high; too low | ||
| equal to the efficient price; too high |
8.Which of the following statements is TRUE?
I. The EPA's tradeable allowances program for sulfur dioxide establishes property rights to pollute and helps reduce transaction costs by distributing allowances, maintaining databases, and monitoring emissions.
II. One criticism of tradeable allowances is that they prohibit non-businesses and environmental groups from purchasing the allowances.
III. The tradeable allowances for sulfur dioxide have performed poorly because electricity output has increased, causing a rise in sulfur dioxide levels.
| I only | ||
| II and III only | ||
| I, II, and III | ||
| III only |
9.Price floors make it illegal to compete for more customers by lowering prices, so firms compete by offering customers:
| various options. | ||
| more quantity. | ||
| more discount. | ||
| higher quality. |
10.Figure: Government Price Controls
Reference: Ref 8-3
(Figure: Government Price Controls) Refer to the figure. If the government sets the price ceiling at $31, there will be:
| a shortage of 15 units. | ||
| a surplus of 15 units. | ||
| a supply of 20 units. | ||
| no effect on the market. |
11.In which of these instances does price function as a signal in the market?
| Suppliers invest more in exploration when the price of oil increases. | ||
| Consumers complain of price gouging as the price of oil skyrockets. | ||
| Government imposes price controls on the skyrocketing price of oil. | ||
| All of the answers are correct. |
12.Ethanol and sugar are both made from sugar cane, and ethanol can be used as substitute fuel for oil. Increasing oil prices cause the demand for ethanol to increase. This will cause the ______ sugar to ______ and its price to ______.
| demand for; decrease; decrease | ||
| supply of; increase; increase | ||
| supply of; decrease; increase | ||
| demand for; increase; increase |
13.Why do cotton growers spend billions of dollars to dam rivers and transport water hundreds of miles to grow cotton in California deserts?
| Cotton growers in California don't pay payroll taxes. | ||
| The water used to grow California cotton is highly subsidized by the government. | ||
| Cotton growers in California are mostly operated as nonprofit enterprises. | ||
| The water used to grow California cotton is high in mineral contents, making for a bigger cotton yield. |
14.Suppose that the equilibrium price in the market is $10. If the current market price is $7.50:
| the equilibrium price will fall to $7.50. | ||
| competition among buyers will increase the current price. | ||
| the current price will fall below $7.50 as sellers compete for market share. | ||
| There is not enough information provided to answer the question. |
15.Which of the following would increase the demand for beef?
| lower pork prices | ||
| higher consumer income | ||
| higher prices of feed grains used to feed beef cattle | ||
| an increase in the price of beef |
16.A change in quantity supplied is reflected by a movement along the same supply curve while a change in supply refers to a shift in the entire supply curve.
True
False
17.Table: Production in the United States and Germany
| Labor units required to produce: |
| One Clock | One Sofa |
| United States | 2 | 5 | |
| Germany | 3 | 9 |
Reference: Ref 2-8
(Table: Production in the United States and Germany) According to the table, the opportunity cost of producing one sofa in the United States is _________, and the opportunity cost of producing one sofa in Germany is _______.
| two clocks; three clocks | ||
| 10 clocks; 27 clocks | ||
| 0.4 clocks; 0.33 clocks | ||
| 2.5 clocks; three clocks |
18.Mark values his drum set at $800 and Ella values her guitar at $1,000. Suppose that Mark trades his drum set for Ella's guitar.
| This trade makes Ella worse off by $200. | ||
| This trade makes Mark better off by $200. | ||
| Mark must value Ella's guitar for at least $1,000, and Ella must value Mark's drum set for at least $800. | ||
| This trade creates value by moving the guitar and drum set to people who value them more. |