BIOL107 Lecture Notes - Lecture 2: Proteinogenic Amino Acid, Leucine, Lysine
BIOL107 verified notes
2/7View all
Document Summary
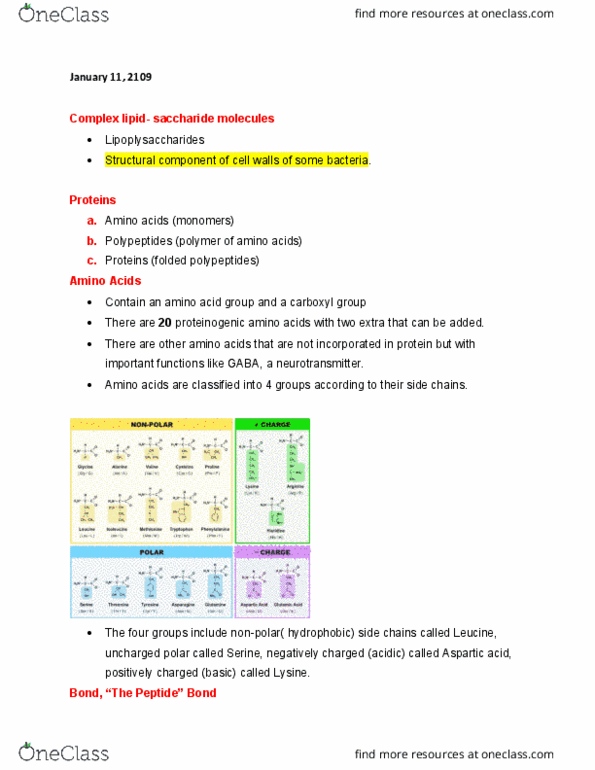
Complex lipid- saccharide molecules: lipoplysaccharides, structural component of cell walls of some bacteria. Proteins: amino acids (monomers, polypeptides (polymer of amino acids, proteins (folded polypeptides) Bond, the peptide bond: two amino acids join to form dipeptide, just like carbohydrate polymers, amino acid polymerization requires dehydration reaction. Polypeptides: sufficiently-long chains of peptides are polypeptides, the average human proteins contains 450 residues. Protein: when one or more polypeptide chains are folded in specific way, they become a protein. Polypeptide chains fold into the shape that takes the lowest possible energy. Is simply the sequence, the order of amino acids. Secondary structure (first fold) the first-order fold that forms: dominated by hydrogen bonds (h-bonds, a helix is most common (a helix is the biggest sequence, b pleated sheets can form also, and also: Tertiary structure (folding of the folding: the 3d shape, the twists and turns that the secondary structure adopts.