BIOL107 Lecture 6: BIO107 – Lecture 6-Cell Transport, Cytotic Transport
BIOL107 verified notes
6/7View all
Document Summary
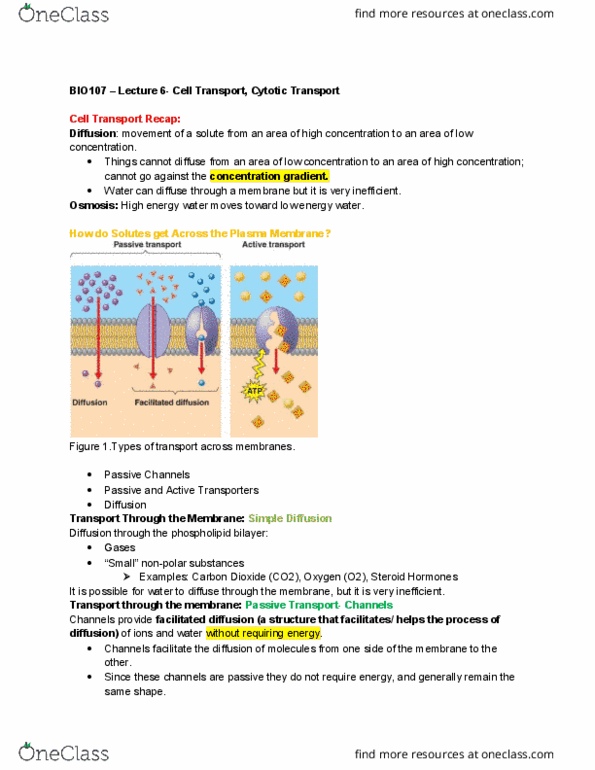
Bio107 lecture 6- cell transport, cytotic transport. Osmosis: high energy water moves toward low energy water. Figure 1. types of transport across membranes: passive channels, passive and active transporters, diffusion. Examples: carbon dioxide (co2), oxygen (o2), steroid hormones. It is possible for water to diffuse through the membrane, but it is very inefficient. Ion channels may be regulated through gating (i. e. gating means that it opens or closes, however it requires energy). Ligand-activated: water channels may require phosphorylation to open. Although, it doesn"t allow anything to move against its concentration gradient: monosaccharides. Example: glut, the human glucose transporter: amino acids. Transport through the membrane: active transport transporters. The proton pump moves h+ against their gradient: the proton pump uses atp to move h+ from the cytoplasm of the cell to the. Extracellular fluid: proton pump inhibitor: reduces acidity levels by preventing the proton pump from moving the protons (h+).