BIOL108 Lecture Notes - Lecture 19: Non-Vascular Plant, Vascular Plant, Gametophyte
BIOL108 verified notes
19/41View all
Document Summary
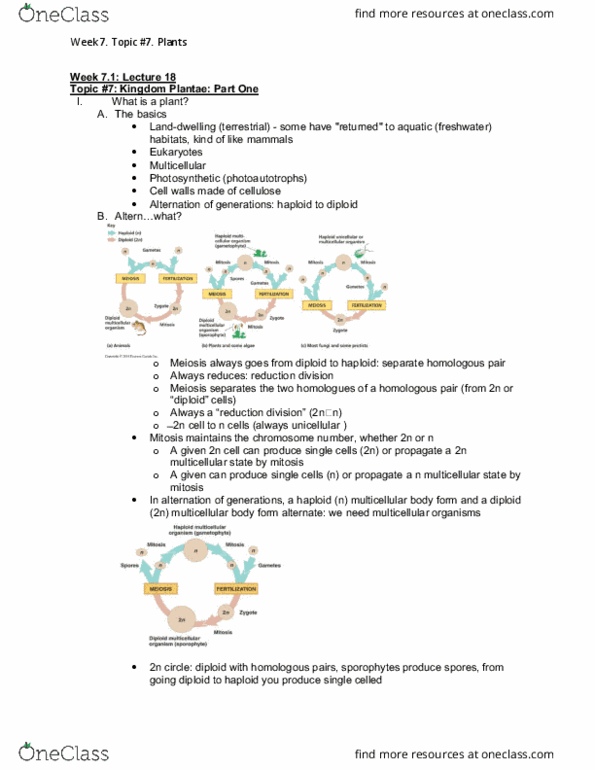
Seed (vascular) plants (a) gymnosperms (e. g. , conifers, pines) (b) angiosperms (flowering plants) Do meiosis in these (spore-producing unit: those spores go off and germinate, mitotically dividing to grow to be male and some to be female, female gametophyte = megagametophyte, produce archegonia, male gametophyte = microgametophyte, produce antheridia. The vascular plants: a little taller, a little bigger: characteristics of living (extant) vascular plants, vascular tissue, xylem, contains lignin - strengthening polymer, dead hollow cells act as water pipes. Plants: phloem, living cells, distribute nutrients, organic products, gave plants a competitive advantage ability to resist gravity and grow taller for sun and spore/seed dispersal! However, in vascular plants, sporophyte has increased size, complexity and persistence: sporophyte in vascular plants is not nutritionally-dependent upon gametophyte. In seedless vascular plant like ferns (soon), almost all leaves are sporophylls, leaves that bear clusters of sporangia called sori (singular; sorus.