BIOL108 Lecture Notes - Lecture 29: Choanoflagellate, Choanocyte, Multicellular Organism
BIOL108 verified notes
29/41View all
Document Summary
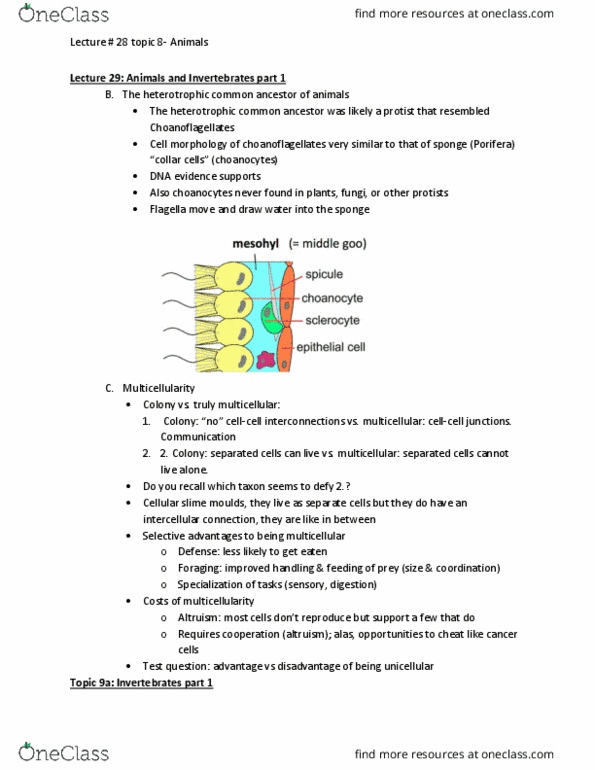
Lecture 29: animals and invertebrates part 1: the heterotrophic common ancestor of animals, the heterotrophic common ancestor was likely a protist that resembled. Choanoflagellates: cell morphology of choanoflagellates very similar to that of sponge (porifera) Collar cells (choanocytes: dna evidence supports, also choanocytes never found in plants, fungi, or other protists, flagella move and draw water into the sponge, multicellularity, colony vs. truly multicellular, colony: no cell-cell interconnections vs. multicellular: cell-cell junctions. Usually there are two separate groups: but echinodermata and hemichordata grouped as one. Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group: leaves the vertebrates out. The sponges: phylum porifera: sponge morphology, por = pore, fer = to bear, ~ 8000 extant species, 99% marine, range from a few mm to a few m in height, asymmetry (most, except for larval stage, are sessile. In the pores and out: what is causing this flow, waving back and forth of the flagella stir particles in and general flow into the pores and out.