CHEM101 Lecture Notes - Lecture 3: Electron Density, Bohr Radius, Resultant Force
17 views7 pages
Verified Note
5 Oct 2018
School
Department
Course
Professor
CHEM101 verified notes
3/14View all
Document Summary
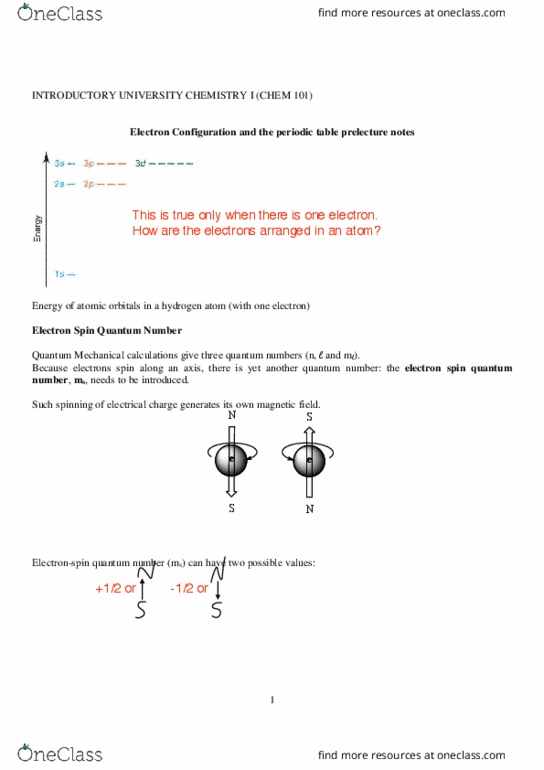
Electron configuration and the periodic table prelecture notes. This is true only when there is one electron. Energy of atomic orbitals in a hydrogen atom (with one electron) Quantum mechanical calculations give three quantum numbers (n, l and ml). Because electrons spin along an axis, there is yet another quantum number: the electron spin quantum number, ms, needs to be introduced. Such spinning of electrical charge generates its own magnetic field. Electron-spin quantum number (ms) can have two possible values: Thus, it takes three quantum numbers to define an atomic orbital but we need four quantum numbers to identify an electron in an atom. 0,1,2,3, (n-1) orbital shape (s, p, d, f) +1/2, -1/2 direction of electron spin an atom. Although the electron density is highest around the nucleus, it does not mean it has the greatest probability of being found around the nucleus. Recall: electron density of the orbital (s orbitals as shown below):
Get access
Grade+20% off
$8 USD/m$10 USD/m
Billed $96 USD annually

Homework Help
Study Guides
Textbook Solutions
Class Notes
Textbook Notes
Booster Class
40 Verified Answers
Class+
$8 USD/m
Billed $96 USD annually

Homework Help
Study Guides
Textbook Solutions
Class Notes
Textbook Notes
Booster Class
30 Verified Answers
Related textbook solutions
Chemistry: Structure and Properties
2 Edition,
Tro
ISBN: 9780134293936
Basic Chemistry
5 Edition,
Timberlake
ISBN: 9780134138046
Principles of Chemistry Molecular Approach
4th Edition,
Tro
ISBN: 9780134112831
Chemistry: Structure and Properties
2nd Edition,
Tro
ISBN: 9780134293936
Principles of Chemistry Molecular Approach
3rd Edition, 2014
Tro
ISBN: 9780321971944
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach
3rd Edition,
Tro
ISBN: 9780321809247
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach
5th Edition,
Tro
ISBN: 9780134874371
Principles of Chemistry: A Molecular Approach
4th Edition,
Tro
ISBN: 9780134895741
Chemistry: The Central Science
14th Edition, 2017
Brown
ISBN: 9780134414232