MAT 1339 Lecture 2: MAT1339-Lecture2 Secant lines & Rate of change
MAT 1339 verified notes
2/27View all
Document Summary
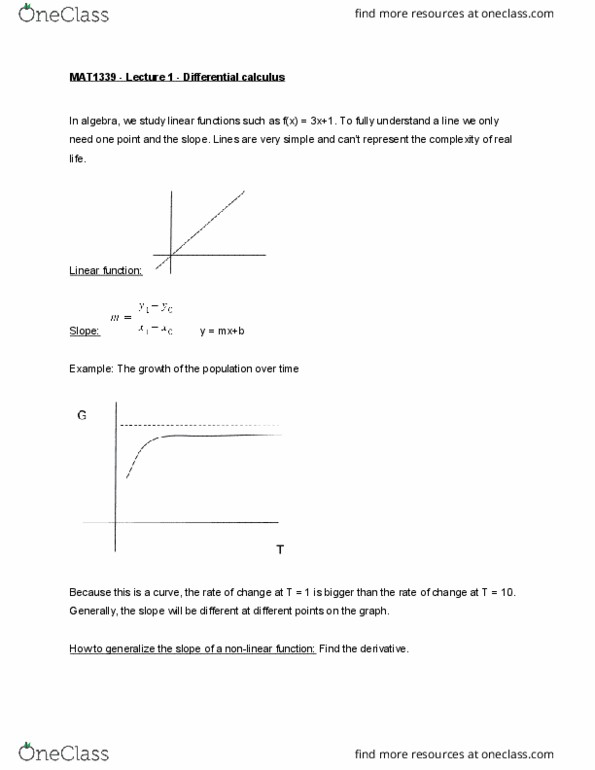
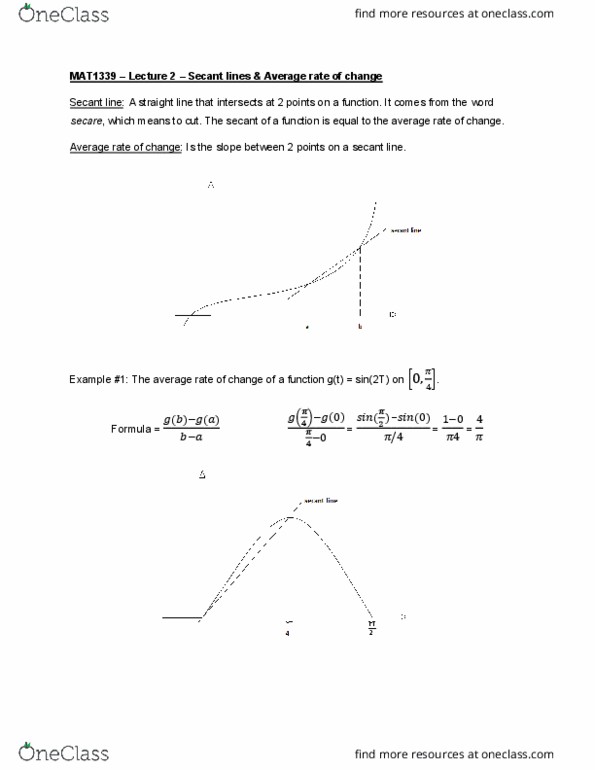
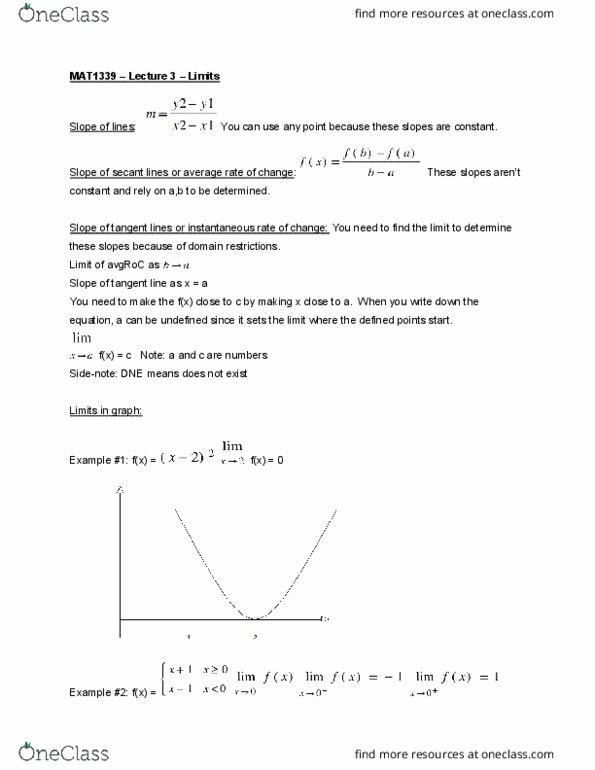
Mat1339 lecture 2 secant lines & average rate of change. Secant line: a straight line that intersects at 2 points on a function. It comes from the word secare, which means to cut. The secant of a function is equal to the average rate of change. Average rate of change: is the slope between 2 points on a secant line. Example #1: the average rate of change of a function g(t) = sin(2t) on [(cid:882),(cid:2872)]. Example #2: the average rate of change of a function f(x) = 4-(cid:2870) on : Note: the rate of change gets shallower as you get closer to 0. The secant line will become horizontal once you reach it. Tangent line: a straight line that touches a function at only one point. It comes from the word tangere, which means to kiss. The tangent of a function represents the instantaneous rate of change for its particular point on the slope.