CHM136H1 Lecture Notes - Lecture 32: Rate-Determining Step, Racemic Mixture, Carbocation
CHM136H1 verified notes
32/39View all
Document Summary
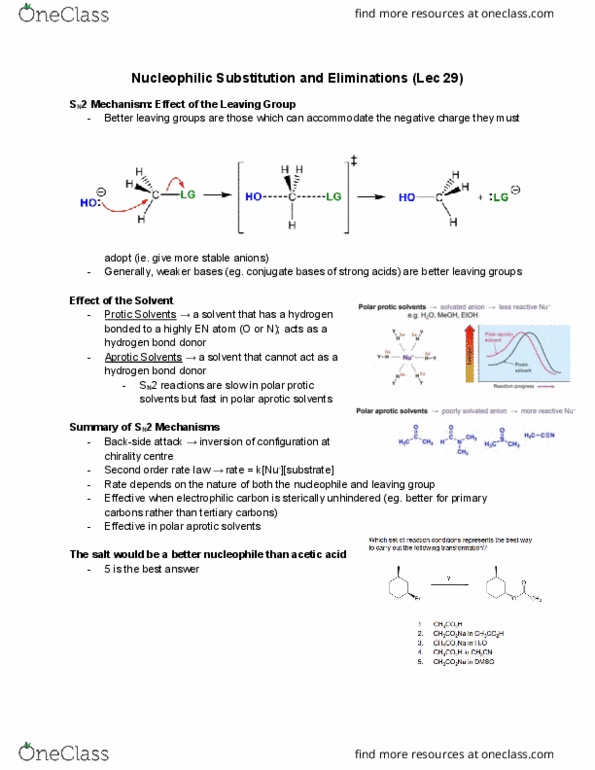
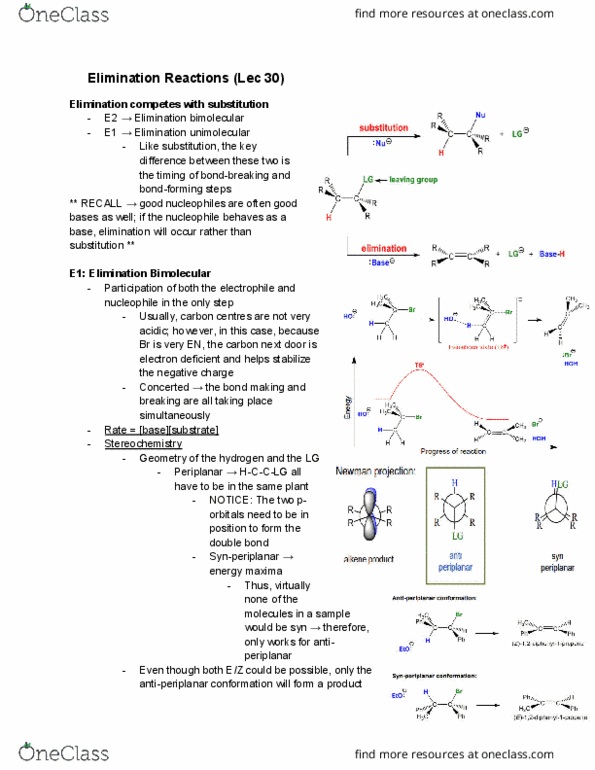
A pure sn1 reaction should give a racemic mixture. When the leaving group leaves, a planar carbocation is formed substrate can attack from either face. A small excess (0-20%) of inverted product can form when the lg leaves, one side of the face is shielded (reaction with an ion-pair) The faster the rate limiting step, the faster the sn1 reaction. Hammond postulate the most stable carbocation forms the fastest (however, increasing the size of the r-groups, like substituting methyl groups for t-butyl groups, doesn"t really have the big of an impact) Resonance stabilized primary carbocations are about as stable as secondary alkyl carbocations. Resonance stabilized secondary carbocations are about as stable as tertiary carbocations. The overall rate of the reaction does not depend on the nucleophile (does not participate in the rate determining step) Although an aggressive nucleophile leads to a fast sn2 reaction, it has not. Effect of the lg effect on an sn1 reaction.