MAT136H1 Lecture 4: Antiderivatives
36 views3 pages
Verified Note
MAT136H1 verified notes
4/4View all
Document Summary
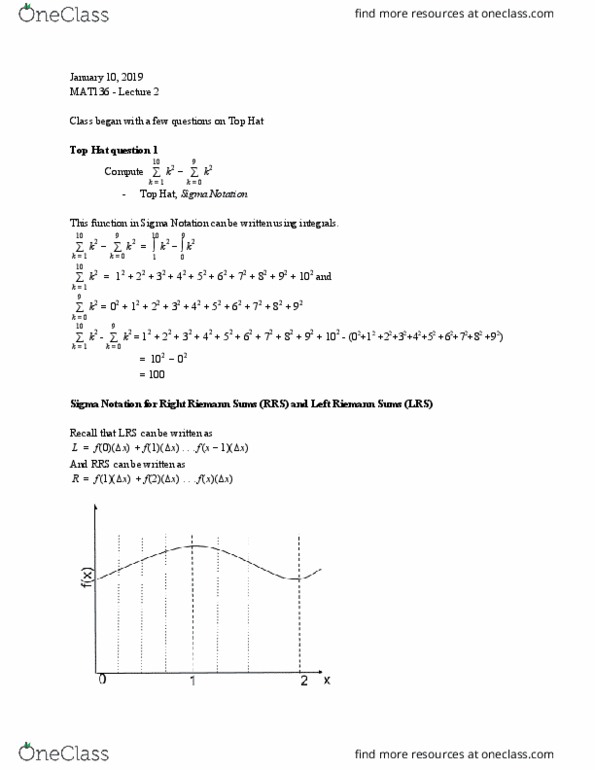
C is a equation for an antiderivative of the function f(x) = x . Key word is an example for a specific antiderivative. This means there are more other possible equations. x2 + ( 2. It is important to note the differences between b a f (x)dx and f (x)dx. The first is a number, the second is a family of functions. If f"(x) = 0 on an interval, then f(x) = c on this interval, for some constant c. If f(x) is a derivative of a constant function, it will always equal 0. Remember the antiderivative includes another aspect: c . F f(x) = 0 (a constant function), and f(x) is an antiderivative with f (0) = 1. F x f(x) = 1 (a constant function), and f(x) is an antiderivative with f (0) = 0. = f: find any function f , (x, general form of the antiderivative, plug in a .
Get access
Grade+20% off
$8 USD/m$10 USD/m
Billed $96 USD annually

Homework Help
Study Guides
Textbook Solutions
Class Notes
Textbook Notes
Booster Class
40 Verified Answers
Class+
$8 USD/m
Billed $96 USD annually

Homework Help
Study Guides
Textbook Solutions
Class Notes
Textbook Notes
Booster Class
30 Verified Answers