CHEM 101 Lecture Notes - Lecture 38: Metal, Intermolecular Force, Network Covalent Bonding
CHEM 101 verified notes
38/40View all
Document Summary
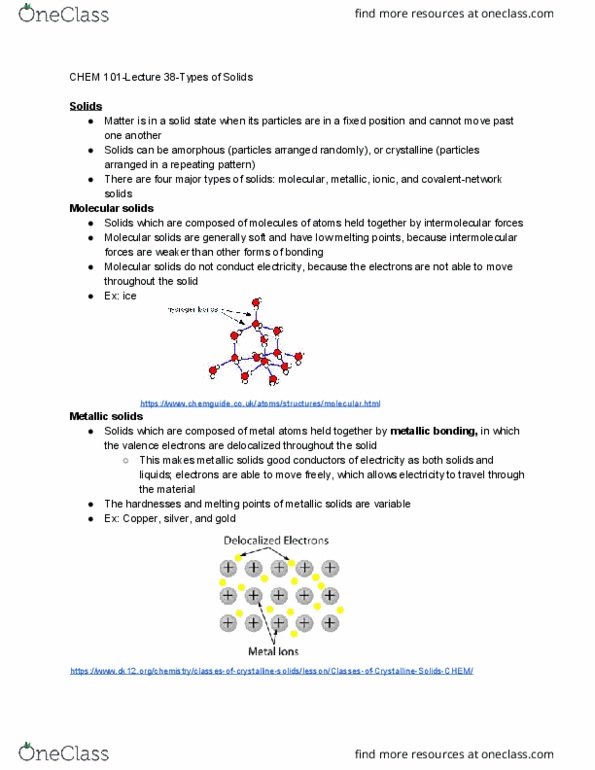
Matter is in a solid state when its particles are in a fixed position and cannot move past one another. Solids can be amorphous (particles arranged randomly), or crystalline (particles arranged in a repeating pattern) There are four major types of solids: molecular, metallic, ionic, and covalent-network solids. Solids which are composed of molecules of atoms held together by intermolecular forces. Molecular solids are generally soft and have low melting points, because intermolecular forces are weaker than other forms of bonding. Molecular solids do not conduct electricity, because the electrons are not able to move throughout the solid. Solids which are composed of metal atoms held together by metallic bonding, the valence electrons are delocalized throughout the solid. This makes metallic solids good conductors of electricity as both solids and liquids; electrons are able to move freely, which allows electricity to travel through the material. The hardnesses and melting points of metallic solids are variable.