CHEM 101 Lecture Notes - Lecture 40: Polyvinyl Chloride, Chain-Growth Polymerization, Polystyrene
CHEM 101 verified notes
40/40View all
Document Summary
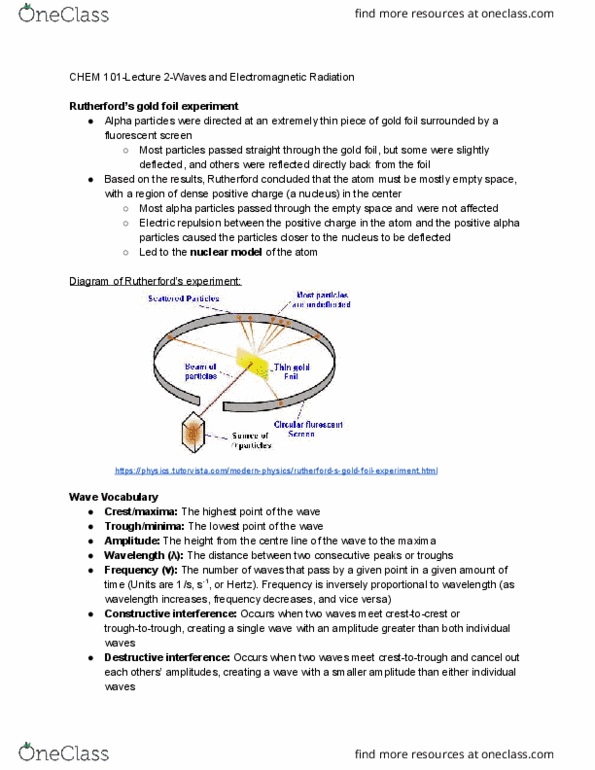
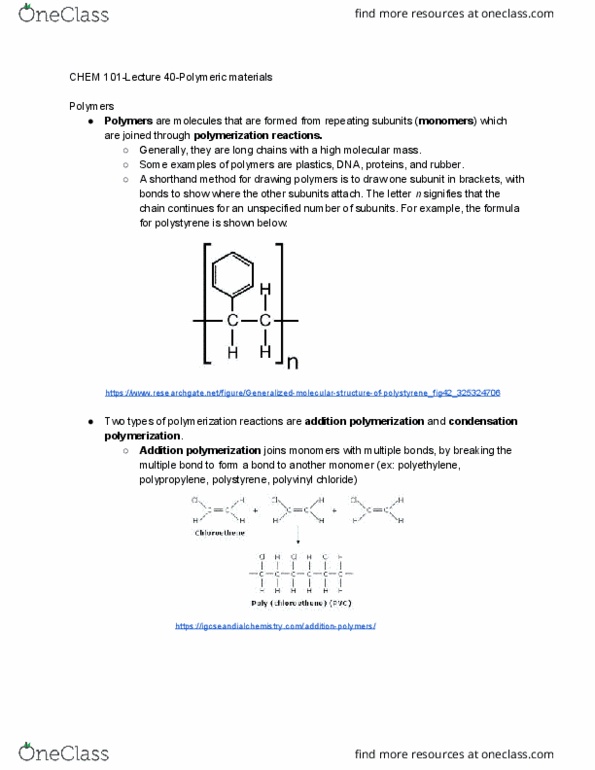
Are molecules that are formed from repeating subunits ( monomers . Generally, they are long chains with a high molecular mass. Some examples of polymers are plastics, dna, proteins, and rubber. A shorthand method for drawing polymers is to draw one subunit in brackets, with bonds to show where the other subunits attach. The letter n signifies that the chain continues for an unspecified number of subunits. For example, the formula for polystyrene is shown below: https://www. researchgate. net/figure/generalized-molecular-structure-of-polystyrene_fig42_325324706. Two types of polymerization reactions are addition polymerization . Joins monomers with multiple bonds, by breaking the polymerization . Addition polymerization multiple bond to form a bond to another monomer (ex: polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene, polyvinyl chloride) https://igcseandialchemistry. com/addition-polymers/ Joins monomers through the removal of a small molecule such as water, methane, or hydrogen chloride (ex: polyamides, polyesters, proteins) In the example shown below, a large number of diacids (carboxylic acids with two.