CHM 2211L Lecture Notes - Lecture 9: Dichloromethane, Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, Wavenumber
Eric Aalo
CHM 2211L Section 1
Group 1 Members:
Benedicte
Danielle
Capstone Research Project: Optimization of Imine Synthesis Reaction- Influence of Water Trapping
Reagents
Abstract:
Three reactions of p-chlorobenzaldehyde and p-bromoaniline were conducted simultaneously
under different conditions in order to produce and later isolate 4-bromo-N-[(4-
chlorophenyl)methylene]-benzenamine. The first reaction condition was conducted without any water
trapping agents, and then visualized on a TLC plate. The second reaction condition was conducted using
300mg of sodium sulfate as the water trapping agent. The third reaction condition was conducted using
300mg of molecular sieves as the water trapping agent. Our crude products were then filtered using
Hirsch filtration with methanol as the solvent. Upon analyzing our product using reaction yields, TLC, 1H
NMR spectroscopy, IR spectroscopy, and melting point analysis we were able to conclude that the
molecular sieves were the most successful.
Introduction:
4Imines make up a class of biological reactive intermediates that are able to form C-C, C-N, and
C-X(heteroatom) bonds. Imines are typically synthesized from the condensation reaction of an aldehyde
or ketone with a primary amine. Imine formation is similar to nucleophilic addition to a carbonyl group,
where the amine is the nucleophile. The result is a carbon double bonded to an amine group attached to
an R group, similar to a carbonyl. Successful imine synthesis needs water to be separated or removed.
6This is because water left in the reaction can actually reverse imine formation, causing the reactants to
not properly interact and no product being formed. Because of this, water removing agents like
molecular sieves and sodium sulfate are used to remove the water that is produced. 4Schiff bases are a
subclass of imines that contain an azomethine group (-CH=N-). Schiff bases are known for their
important antitumor, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial activity. The human body uses
decarboxylation mechanisms, similar to the mechanism of Schiff base formation, in order to synthesize a
number of catalysts, neurotransmitters, and hormones. The purpose of this experiment was to
synthesize imines in the most efficient manner. By using water trapping agents compared to a
control(reaction 1), we are able to determine which method was most successful in yielding our imine
product, 4-bromo-N-[(4-chlorophenyl)methylene]-benzenamine. The water trapping agents used were
molecular sieves(reaction 3) and sodium sulfate(reaction 2). No water trapping agent was used for
reaction 1. Our product was then analyzed and characterized using reaction yields, TLC, 1H NMR
spectroscopy, IR spectroscopy, and melting point analysis in order to determine how each experimental
condition effected the success of the reaction.
Materials and Methods:
IUPAC Name
(structure)
CAS #
Molecul
ar Mass
(g/mol)
Meltin
g
Point
(⁰C)
Boilin
g
Point
(⁰C)
Solubili
ty in
Water
Densit
y
(g/mL
)
Amount Used
Role of
Reagen
t
p-
chlorobenzaldeh
yde
104-
88-1
140.56
117
214
No
1.196
1mmol=0.140
57g
Reacta
nt
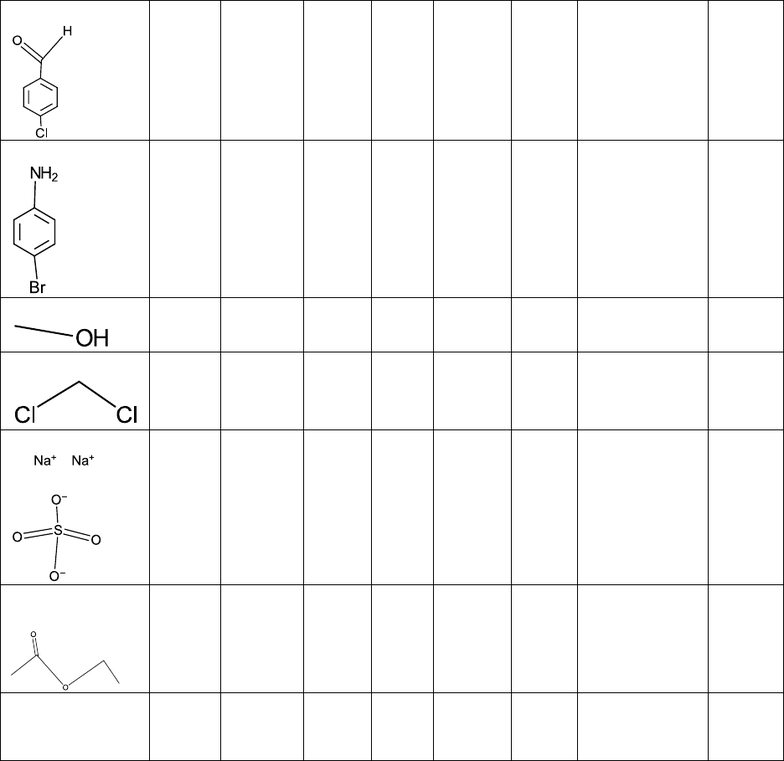
p- bromoaniline
106-
40-1
172.02
64
223
No
1.5
1mmol=.1720
2g
Reacta
nt
Methanol
67-56-
1
32.04
-97.6
64.7
Yes
.791
10-20 drops
Solvent
Dichloromethane
75-09-
2
84.93
-96.7
39.6
No
1.33
4mL
Solvent
Sodium Sulfate
7757-
82-6
142.04
884
1429
Yes
2.66
304.69mg
Water-
trappin
g agent
20% Ethyl
Acetate
11292
6-00-8
174.28
-83.6
77.1
Yes
.902
~1mL
Solvent
Molecular Sieves
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
No
N/A
300mg
Water-
trappin
g agent
Instrumentation:
- All weighing happened at scale #9
- Hotplate stirrer (120V, Corning) used to mix reaction
- Benchtop 42.5MHz Spinsolve Carbon NMR Spectrometer (Magritek, New Zealand) used for 1H NMR
analysis of reactants and product
- Melting Point Analysis conducted using MPA 160 Digimelt apparatus (SRS, USA)
- Reactant and Product IR analysis conducted using Nicolet is5 FT-IR spectrometer (ThermoFischer
Scientific, USA)
Document Summary
Capstone research project: optimization of imine synthesis reaction- influence of water trapping. Three reactions of p-chlorobenzaldehyde and p-bromoaniline were conducted simultaneously under different conditions in order to produce and later isolate 4-bromo-n-[(4- chlorophenyl)methylene]-benzenamine. The first reaction condition was conducted without any water trapping agents, and then visualized on a tlc plate. 300mg of sodium sulfate as the water trapping agent. 300mg of molecular sieves as the water trapping agent. Upon analyzing our product using reaction yields, tlc, 1h. Nmr spectroscopy, ir spectroscopy, and melting point analysis we were able to conclude that the molecular sieves were the most successful. 4imines make up a class of biological reactive intermediates that are able to form c-c, c-n, and. Imines are typically synthesized from the condensation reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with a primary amine. Imine formation is similar to nucleophilic addition to a carbonyl group, where the amine is the nucleophile.


