ECON 1011 Lecture Notes - Lecture 16: Marginal Cost, Fixed Cost
ECON 1011 verified notes
16/24View all
Document Summary
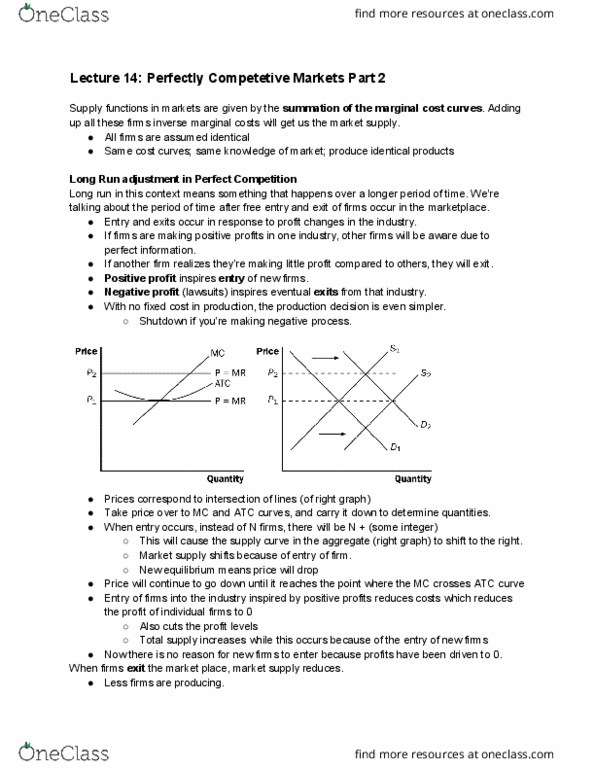
Supply functions in markets are given by the summation of the marginal cost curves. Adding up all these firms inverse marginal costs will get us the market supply. Same cost curves; same knowledge of market; produce identical products. Long run in this context means something that happens over a longer period of time. We"re talking about the period of time after free entry and exit of firms occur in the marketplace. Entry and exits occur in response to profit changes in the industry. If firms are making positive profits in one industry, other firms will be aware due to perfect information. If another firm realizes they"re making little profit compared to others, they will exit. Positive profit inspires entry of new firms. Negative profit (lawsuits) inspires eventual exits from that industry. With no fixed cost in production, the production decision is even simpler. Prices correspond to intersection of lines (of right graph)