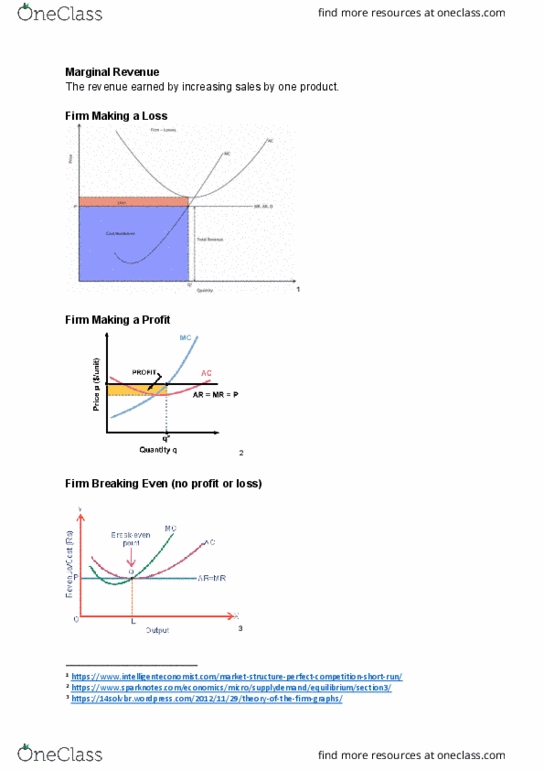
ECON 1011 Lecture Notes - Lecture 23: Demand Curve, Marginal Revenue, Statics
ECON 1011 verified notes
23/30View all
Document Summary
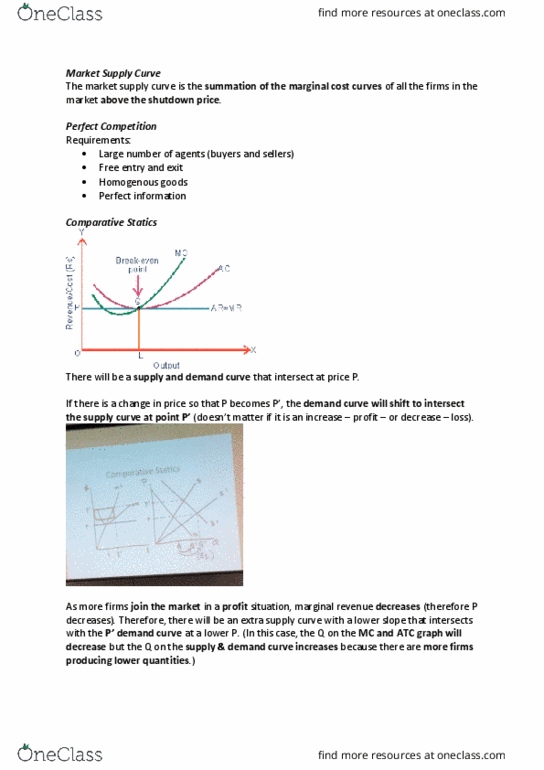
The market supply curve is the summation of the marginal cost curves of all the firms in the market above the shutdown price. Requirements: large number of agents (buyers and sellers, free entry and exit, homogenous goods, perfect information. There will be a supply and demand curve that intersect at price p. If there is a (cid:272)ha(cid:374)ge i(cid:374) pri(cid:272)e so that p (cid:271)e(cid:272)o(cid:373)es p", the demand curve will shift to intersect the supply curve at poi(cid:374)t p" (doesn"t (cid:373)atter if it is a(cid:374) i(cid:374)(cid:272)rease profit or decrease loss). As more firms join the market in a profit situation, marginal revenue decreases (therefore p decreases). E(cid:448)e(cid:374)tually, the slope of the se(cid:272)o(cid:374)d supply (cid:272)ur(cid:448)e (cid:449)ill get so lo(cid:449) that it (cid:449)ill i(cid:374)terse(cid:272)t p" demand curve when mc = atc (lowest point of atc), meaning there is no incentive to join the market. If a firm leaves the market in a loss situation, the opposite happens.