PSYC 256 Lecture Notes - Lecture 5: Categorical Logic, Afterimage, Neural Adaptation

PERCEPTION
Sensation
• Reception of energy from environment and its initial encoding into nervous system
o Touch receptors, light waves, sound waves
• The physiological processes that underlie information intake
Perception
• Set of processes we use to recognize, organize, and make sense of sensations
received from environmental stimuli
• The psychological processes involved in organizing and interpreting of sensations
Components of Perception
• Distal stimulus: stimulus in outside world
• Proximal stimulus: stimulus as apprehended by sensory organs (e.g., eye, nose, taste
buds, etc.; interaction between stimulus’ energy and self
o Hairs in my ear disrupted by soundwaves
• Percept: internal mental representation of external stimulus; basic component in
formation of concept
Perceiving a
Stimulus
External to Internal Information
• Transduction: process of translating external messages into internal language of the
brain
• Problem of Transduction: how does external energy become internal information
(neural activity)?
find more resources at oneclass.com
find more resources at oneclass.com
Transduction in Vision
• Light waves enter eye via pupil and picked up by retina
• Retina contains light-sensitive cells that react to light by creating neural impulses
o These cells are first line of retina detection
o Transduce light energy into electrical impulses
• Retina is the only part of CNS you can see with naked eye
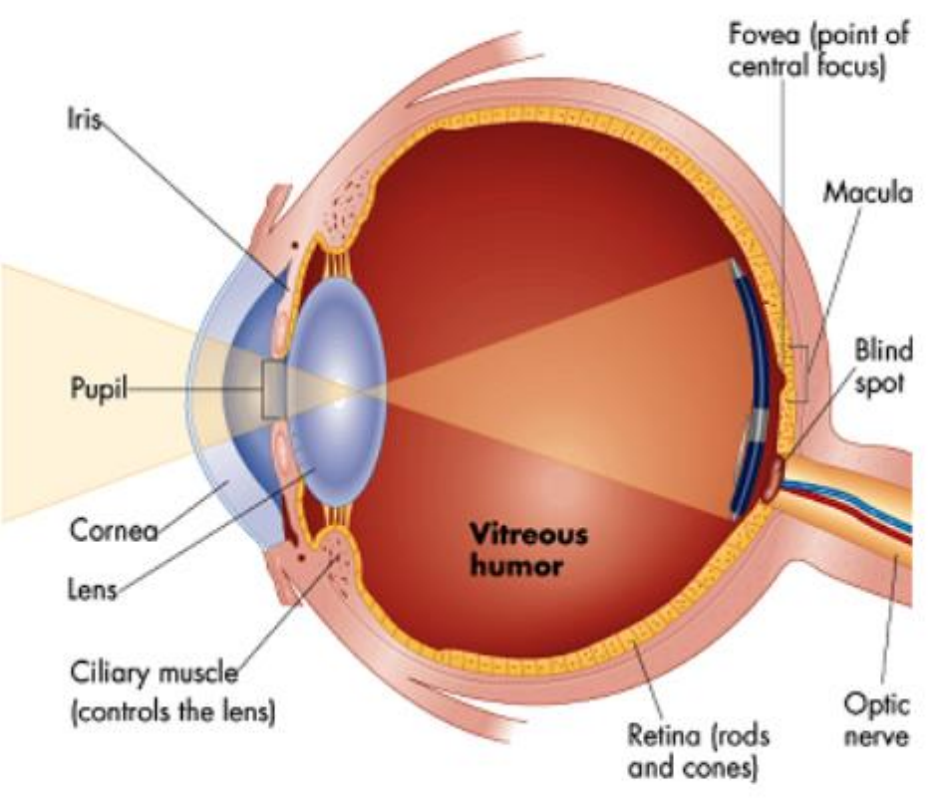
Anatomy of the Eye
• Connected to brain through optic nerve
• Blind spot doesn’t have rods and cones photoreceptor cells
• Fovea: focus
Anatomy of the Retina
find more resources at oneclass.com
find more resources at oneclass.com
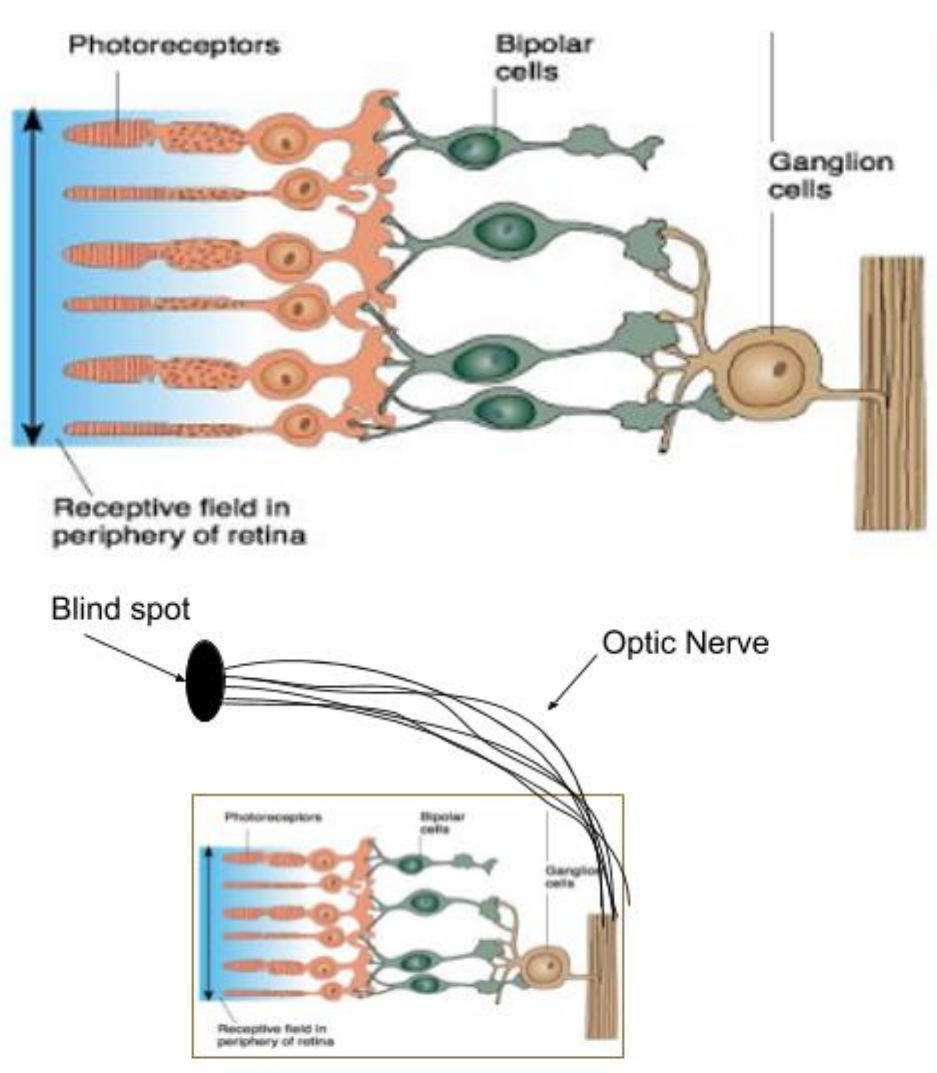
• Photoreceptors transduce light energy
• Pupil is to the right; retina is backwards
o Light has to go through ganglion and bipolar cells before reaching
photoreceptors
Transduction in Vision
• Light induces chemical reaction in photopigments in rods and cones
find more resources at oneclass.com
find more resources at oneclass.com
Document Summary
Sensation: reception of energy from environment and its initial encoding into nervous system, touch receptors, light waves, sound waves, the physiological processes that underlie information intake. Perception: set of processes we use to recognize, organize, and make sense of sensations received from environmental stimuli, the psychological processes involved in organizing and interpreting of sensations. Anatomy of the eye: connected to brain through optic nerve, blind spot doesn"t have rods and cones (cid:523)photoreceptor cells(cid:524, fovea: focus. Anatomy of the retina: photoreceptors transduce light energy, pupil is to the right; retina is backwards, light has to go through ganglion and bipolar cells before reaching photoreceptors. If the color fades because our photoreceptors get washed out: question, why doesn"t" this happen all of the time, saccadic movement of the eyes, tiny movement of the eyes is what prevents us from seeing. Proximal stimulus percept: accurate depth perception, visual illusions.

