PSYC 256 Lecture Notes - Lecture 16: Episodic Memory, Spreading Activation, Subset

Unit 3 (Includes 16-22)
CONCEPTS & GENERAL KNOWLEDGE
Semantic Memory
• A mental thesaurus, organized knowledge a person possesses about words and
other verbal symbols, their meanings and referents, about relations among them,
and about rules, formulas, and algorithms for the manipulation of the symbols,
concepts, and relations.
Concept Formation
• Traditional research on concept formation
o Show S a series of arbitrary patterns
o S determines which patterns belong or do not belong to a given
category/concept
• Know which factors influence performance but do not know how these effects relate
to real world concepts
Common Concepts
• Categories that occur in the real world of our experience
o Have a complex internal structure
o Well established in memory
▪ Abstract knowledge, not episodic
1. Car
2. Train
3. Tractor
4. Elevator
5. Sled
1. Pants
2. Pajamas
3. Jacket
4. Mittens
5. Necklace
1. Orange
2. Pear
3. Grapefruit
4. Honeydew
5. Olive
Prototype Theory
• Categories are organized around a prototype: best exemplar
find more resources at oneclass.com
find more resources at oneclass.com
o Does not need to exist
• Items are related by family resemblance
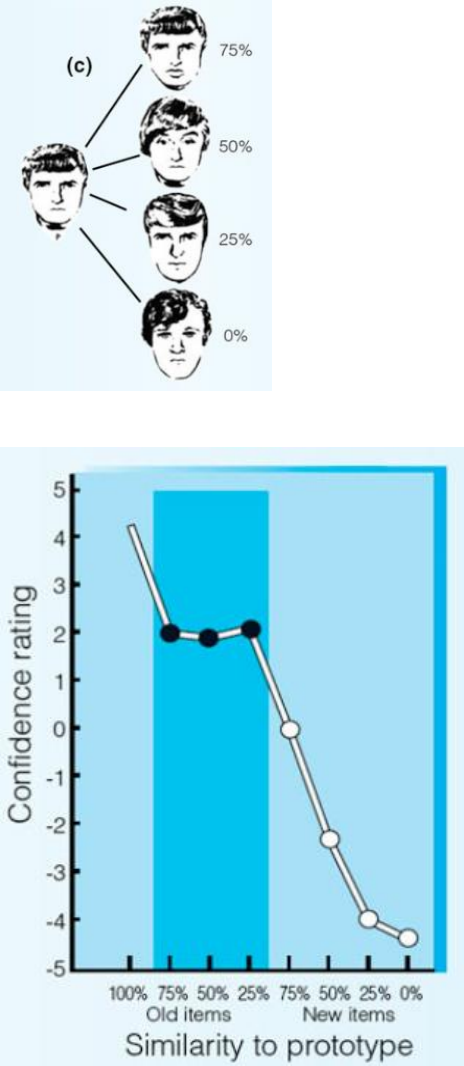
• Solso & McCarthy (1981)
o Participants were shown a series of faces
o Later, a recognition test was given with some old faces, a prototype face, and
some new faces that differed in degree from prototype
• The more similar to prototype it is, the more likely people confidently recognize it
(old, new, and prototype face)
o
• The more characteristic features an object has, the more likely we are to believe it is
part of the category
find more resources at oneclass.com
find more resources at oneclass.com
Document Summary
Prototype theory: categories are organized around a prototype: best exemplar, does not need to exist. Judged more quickly: generated more easily, more likely to be retrieved, errors more like prototype, basic level descriptions, description that does the best job of identifying similar items while excluding dissimilar items. Problems with prototype theory: problems, atypical features do not exclude category members (eg. , penguin as bird) Including all the typical features does not guarantee category membership. Problems with feature comparison model: lack of cognitive economy, how can it explain learning, how can it explain identification of weird variety of chairs, has to be designed to be sat in, chairs have no defining feature. Hierarchical model: semantic memory is organized as a hierarchical network of, units (nouns): animal, bird, robin, properties (verbs or adj): fly, yellow, pointers (relation between units): is a, can, has, has economy in space. If concepts are close to each other, will be fast.

