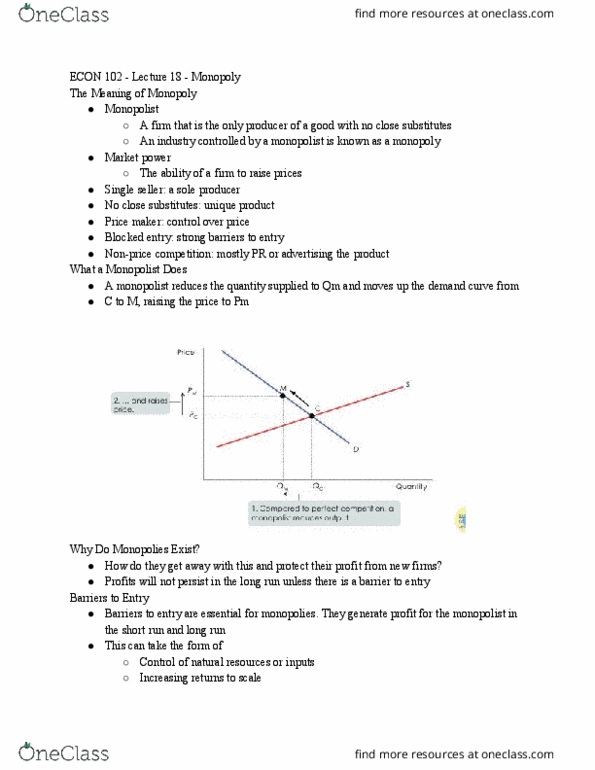
Q5. Table 5.5
Total Output Total Costs
0 10
1 18
2 21
3 23
4 24
5 26
6 29
7 33
8 38
9 44
10 51
In Table 5.5, the marginal cost of the third unit is
a. 2.
b. 4.
c. 3.
d. 1.
Q6. When marginal physical product begins to decline, marginal cost begins to increase.
a. true
b. false
Q7. It is possible for a firm to have positive fixed cost and zero total cost.
a. true
b. false
Q8. Which one of the following is TRUE?
a. Marginal cost increases as marginal physical product decreases.
b. Marginal cost decreases as marginal product decreases.
c. Total cost is the difference between marginal cost and total variable cost.
d. Total cost is the sum of marginal cost plus total variable cost.
Q9. The slope of the production function becomes negative when diminishing returns set in.
a. true
b. false
Q10. Table 5.7
Q Total Variable Cost Average Variable Cost Total Cost Average Total Cost
1 10 50
2 50 90
3 40
Refer to Table 5.7. What is the firm's total fixed cost?
a. 20
b. 40
c. 10
d. 30
Q11. When there are economic profits in a perfectly competitive industry
a. firms have no incentive to exit or enter the industry.
b. firms exit the industry.
c. firms enter the industry.
d. the high barriers to entry prevent further competition.
Q12. The market structure of perfect competition is defined by hundreds of firms producing an essential product, with barriers to the entry of new firms.
a. true
b. false
Q13. A single supplier of a good or service for which there is no close substitute is referred to as a(n)
a. monopolistic competitor.
b. strategic competitor.
c. monopoly.
d. oligopoly.
Q14. For the perfectly competitive firm the selling price of its product is determined by
a. the length of time it has been in business.
b. the amount it chooses to spend on marketing.
c. the interaction of market supply and demand.
d. the number of competing firms.
Q15. A company finds that at the MR = MC output level, its total cost is $500, total variable cost is $400, and total revenue is $450. Your advice to the firm is to
a. reduce output to reduce the cost of production.
b. continue to produce, as total revenue covers total variable cost.
c. increase output to reduce the per unit cost of production.
d. shut down immediately.
Q16. For a monopolist
a. P > MR.
b. P = MC.
c. P = ATC.
d. P = MR.
Q17. The perfect competitor
a. chooses the profit-maximizing quantity.
b. chooses the profit-maximizing price.
c. chooses a quantity that will make the most efficient use of his labor and capital resources.
d. produces what he thinks can be sold, regardless of cost.
Q18. In perfect competition, the larger firms will be able to charge a higher price than the smaller firms.
a. true
b. false
Q19. For the perfectly competitive firm, price equals marginal revenue.
a. true
b. false
Q20. For a monopolist, selling more units requires
a. allowing more firms to enter the industry.
b. hiring a more productive labor force.
c. forming a cartel.
d. lowering the selling price.
Q21. Monopolistic competition means
a. monopolies from several countries compete in the global market.
b. a large number of firms producing differentiated products.
c. a large number of firms producing homogeneous products.
d. few firms producing differentiated products.
Q22. Opportunistic behavior is discouraged by the desire to have repeat transactions.
a. true
b. false
Q23. By saying that firms in an oligopoly are interdependent, we mean that
a. actions by one will prompt reactions by others.
b. if one increases its profits, all others will increase profits as well.
c. all firms sell identical products.
d. if one increases its profits, all others will lose profits.
Q24. Price leadership is a form of
a. barrier to entry.
b. tacit collusion.
c. opportunistic behavior.
d. noncooperative behavior.
Q25. A monopolistically competitive firm in the long run
a. earns positive economic profits.
b. earns negative economic profits.
c. earns zero economic profits.
d. suffers economic losses.
Q26. Monopolistically competitive firms produce a product that is homogeneous.
a. true
b. false
Q27. Which of the following is a characteristic of both perfect competition and monopolistic competition?
a. In the long run, the firm will produce the output which minimizes average total cost.
b. Firms sell a homogeneous product.
c. In the long run, the firm will earn zero economic profit.
d. The firm seeks to differentiate its product from those of its competitors.
Q28. A monopolistically competitive firm uses advertising to
a. lower its costs.
b. differentiate its product.
c. signal its competitors that it is serious about staying in business.
d. motivate its work force.
Q29. For the monopolistic competitor, which is INCORRECT?
a. The profit maximizing rate of output is where the marginal cost curve intersects the marginal revenue curve.
b. The marginal revenue curve is downward sloping and lies below the demand curve.
c. Because the firm has some control over price, its demand curve slopes downward.
d. If the firm in a monopolistically competitive industry were making economic losses, firms would enter the industry.
Q30. Which of the following is TRUE?
a. In the model of price leadership, the dominant firm consistently charges the lowest price.
b. Opportunistic behavior is discouraged by the desire to have repeat transactions.
c. The strategic dependence that characterizes oligopoly means that no firms can earn positive accounting profits.
d. Price wars are most common in perfect competition.
Q31. Antitrust legislation seeks to correct market failure by ensuring that all firms in the industry earn an economic profit.
a. true
b. false
Q32. Market failures arise when
a. people look out for their own best interests.
b. there is a gap between the social and private costs of producing or consuming a good.
c. firms look out for their own best interests.
d. society seeks to operate at a point on the production possibilities curve.
Q33. Cases prosecuted under the Sherman Antitrust Act are intended to correct market failure arising from negative externalities.
a. true
b. false
Q34.
Figure 8.2
Refer to Figure 8.2. The market equilibrium is Q1. Point Q2 represents the optimal point of production. To reach Q2,
a. consumption of the good could be taxed.
b. a subsidy could be given to consumers.
c. production of the good could be taxed.
d. the industry producing the good should operate as a cartel.
Q35. What would happen in a free market system when production of a good generates negative externalities?
a. There would be a shortage of the good.
b. The equilibrium quantity of the good would be more than the efficient amount.
c. The equilibrium quantity of the good would be less than the efficient amount.
d. There would be a surplus of the good.
Q36. If providing a service results in negative external costs, then
a. the market price is below the true opportunity cost of resources used to provide the service.
b. the market price is above the true opportunity cost of resources used to provide the service.
c. the market quantity is too low.
d. market forces will always correct the problem.
Q37. The problem of positive externalities can be addressed by having some firms exit the industry.
a. true
b. false
Q38. The first case prosecuted under the Sherman Act was the antitrust case against Microsoft.
a. true
b. false
Q39. If your marginal tax rate is always higher than your average tax rate, then the tax system is a
a. proportional tax system.
b. regressive tax system.
c. fair tax system.
d. progressive tax system.
Q40. Private goods are characterized by the principle of rival consumption.
a. true
b. false
Q41. Collective bargaining is the process by which unions and employers negotiate the conditions of employment and wages.
a. true
b. false
Q42. The marginal physical product of labor is the addition to total revenue a firm experiences when it hires one additional worker.
a. true
b. false
Q43. A firm's marginal revenue product of labor curve is also
a. its labor demand curve.
b. its total revenue line.
c. its long-run input cost function.
d. its marginal cost curve.
Q44. An increase in the selling price of a product
a. increases the supply of labor to the industry.
b. increases the productivity of labor.
c. raises the firm's demand for labor.
d. decreases the supply of labor to the industry.
Q45. If unions succeed at restricting the supply of labor in any one area of the economy, wages in that sector will increase.
a. true
b. false
Q46. The fact that the labor supply curve slopes upward indicates that
a. workers seek to work more hours when the wage rises.
b. the income effect of a wage increases outweighs the substitution effect.
c. workers seek to work more hours when the wage decreases.
d. firms want to hire more workers when the wage rises.
Q47. The upward slope of the labor supply curve suggests that the income effect of a wage increase outweighs the substitution effect.
a. true
b. false
Q48. The number of strikes occurring in U. S. firms has steadily increased over the past 25 years.
a. true
b. false
Q49. Suppose a perfectly competitive firm faces a labor market in which the going wage rate is $480 per week. If the last worker hired has a marginal physical product of 12 units of output per week, what is the selling price of the firm's output?
a. $40 per unit
b. $480 per unit
c. $240 per unit
d. $12 per unit
Q50. If workers in an industry become less productive due to low employee morale, we would expect the
a. demand for workers to decrease.
b. wages in the industry to increase.
c. supply of workers to increase.
d. demand for workers to increase.