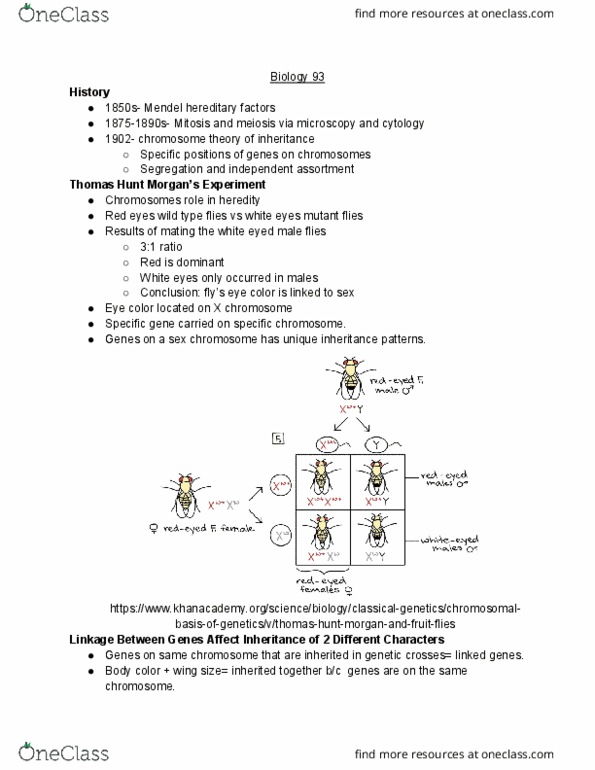
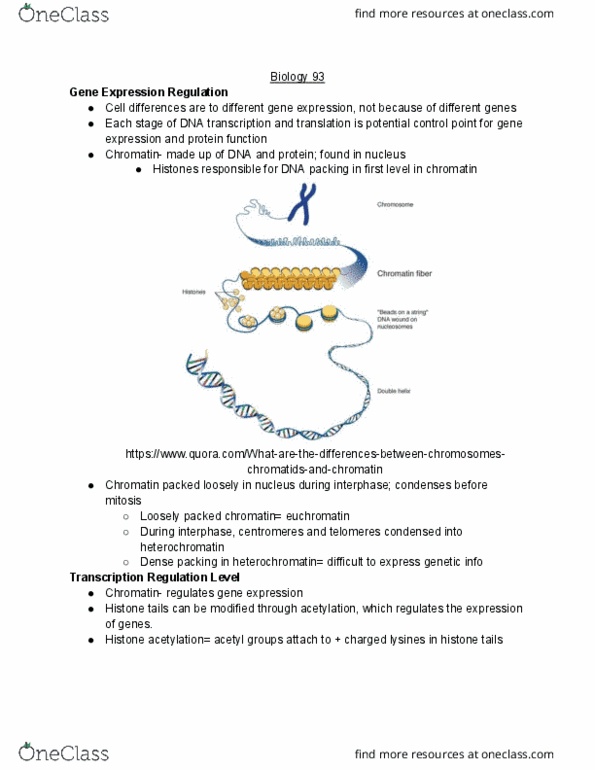
BIO SCI 93 Lecture Notes - Lecture 27: Heterochromatin, Chromatin, Euchromatin
Document Summary
Get access


Related textbook solutions
Related Documents
Related Questions
Chapter 10
1.Outline the history of our knowledge on DNA up to Watson and Crick. What were the main contributions made by each researcherâs key experiment?
2.Explain the setup of the Hershey and Chase experiment, what would the results have been if protein was the genetic material?
3.Draw the structure of a DNA nucleotide, labeling each main component correctly. How does an RNA nucleotide differ?
4.If a section of double stranded DNA contains 19% Adenine, how much Thymine is present?
5.You are a researcher studying the genetic basis of heart attacks and have been working to determine the expression levels of different genes that might contribute to cancer formation. You obtain the DNA methylation status of five genes of interest (the data are shown in the table below). The plus (+) sign indicates the level of DNA methylation; more plus signs correlates with increased methylation levels.Based on this information which genes would you predict to have the highest rate of transcription?
| Gene | Methylation levels |
| 1 | ++ |
| 2 | +++++ |
| 3 | +++ |
| 4 | ++ |
| 5 | + |
What are the characteristics of the 3 main DNA forms?
Chapter 11
What are the different types of chromatin?
What are the structures and important roles for telomeres and centromeres?
What are the differences found between eukaryotic chromosomes and mitochondrial?
Chapter 12
Explain each of the different models of replication.
If you grow a culture of bacteria in media with radioactive nucleotides so that all DNA in the cells include radioactive nucleotides and then place the bacteria in new non radioactive media. After two rounds of replication what proportion of the DNA molecules will contain radioactivity?
Summarize the similarities and differences between rolling-circle replication, theta replication and linear eukaryotic replication.
What are the functions of the different DNA polymerases found in eukaryotic cells?
Draw a replication fork and include all key components and orientations. (Leading/lagging strands, DNA helicase, RNA primer and DNA gyrase)
What is the Holliday model of recombination and what are the necessary steps?
Chapter 13
What are the different types of RNA and what roles do they play?
Describe the properties and functions of each of the RNA polymerases and how they differ depending on the organism.
Describe in detail the process and mechanisms of transcription in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Chapter 14
What are the primary purposes of each of the three post transcriptional modifications that occur in eukaryotic cells.
What is alternative splicing and what role does it play in the cell?
How is ribosomal RNA processed after transcription?
How do siRNA and miRNA work, describe/draw out the process in detail.
If an organismâs diploid chromosome number is 18, how many different possible combinations of homologous chromosomes lining up during meiosis exist for the eggs or sperm produced by that organism?
| A. | 512 | |
| B. | 9 | |
| C. | 18 | |
| D. | 128 | |
| E. | 36 |
At the end of metaphase I, _______________ separate.
| A. | sister chromatids | |
| B. | germ cells | |
| C. | homologous chromosomes | |
| D. | haploid chromatids | |
| E. | centrioles |
Mendel observed that dominant traits
| A. | are seen in all of the F1 hybrid pea plants in his experiments. | |
| B. | are expressed in all plants. | |
| C. | were absent in the F1 generation of pea plants that he used in his experiments. | |
| D. | were the only traits seen in the F2 generation of pea plants in his experiments. | |
| E. | are only expressed in hybrids. |
Cytokinesis in plant cells differs from cytokinesis in animal cells because
| A. | there is no difference. | |
| B. | in plant cells, the cell plate must also divide into two parts. | |
| C. | the contractile protein, actin, is important only in plant cells. | |
| D. | plant cells have a rigid cell wall. | |
| E. | a contractile ring forms only in plant cells. |
Sickle cell anemia is an example of what type of inheritance?
| A. | complete dominance | |
| B. | incomplete dominance | |
| C. | codominance | |
| D. | multiple alleles | |
| E. | recessive dominance |
Which of the following statements is true:
| A. | The dominant allele is masked in homozygous dominant individuals. | |
| B. | With recessive genetic disorders, if both parents are carriers, the offspring will all be affected. | |
| C. | In carriers, the recessive allele causes an intermediate phenotype. | |
| D. | In recessive genetic disorders, the mother and/or father of an affected individual must also be affected. | |
| E. | With dominant genetic disorders, the mother and/or father of an affected individual must also be affected. |
Skin cancers typically develop in the
| A. | upper layers of the epidermis. | |
| B. | lower layers of the dermis. | |
| C. | subcutaneous layer. | |
| D. | lower layers of the epidermis. | |
| E. | upper layers of the dermis. |
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (MD) is inherited from an X-linked recessive allele. What is the probability that a son with Duchenne MD inherited this disease from his biological father?
| A. | 1/2 | |
| B. | 0 | |
| C. | 1/16 | |
| D. | 1/4 | |
| E. | 1/8 |
The genetic makeup of a particular trait in an individual is its
| A. | genotype. | |
| B. | heterozygosity. | |
| C. | phenotype. | |
| D. | filial. | |
| E. | dominance. |
What structure holds the sister chromatids to the spindle fibers?
| A. | chromatin | |
| B. | kinetochore | |
| C. | MPF | |
| D. | centromere | |
| E. | cyclin |
If you view a cell in which the genetic material is beginning to be visible as separate bodies, and the nucleus has disappeared from view, you may surmise that the cells is in
| A. | telophase. | |
| B. | anaphase. | |
| C. | interphase. | |
| D. | metaphase. | |
| E. | prophase. |
Gregor Mendel was successful in his analysis of the genetics of pea plants because
| A. | he examined and analyzed both the F1 and F2 generations. | |
| B. | he studied the parental plants to determine their differences. | |
| C. | he decided to only look at his results in an objective manner. | |
| D. | he studied a trait that had a strange inheritance pattern. | |
| E. | pea plants have genetics different from other organisms. |
Tall corn plants (T) are dominant to dwarf plants (tt). Solid green leaves (G) are dominant to leaves with a white tip (gg). A cross between two corn plants yielded the following phenotypes: 51 tall plants with a white tip on their leaves; 43 dwarf plants with solid leaves; 48 dwarf plants with white tips on their leaves; 45 tall plants with solid leaves. What are the genotypes of the parents that produced these plants?
| A. | None of the above | |
| B. | TtGg x Ttgg | |
| C. | ttGG x TTgg | |
| D. | TtGg x TtGg | |
| E. | TtGg x ttgg |
In humans, a gene that has been identified as causing a type of skin cancer is the
| A. | superwoman echidna. | |
| B. | mutant superman. | |
| C. | sonic hedgehog. | |
| D. | mutant mole rat. | |
| E. | superhero aardvark. |
The segregation principle states that in sexually reproducing diploid organisms the two copies of each gene
| A. | segregate from each other during meiosis. | |
| B. | must always be the same allele. | |
| C. | separate from each other during mitosis. | |
| D. | will both wind up in either the sperm or egg. | |
| E. | move together as a unit during meiosis. |
In what phases is the genetic material in the cell correctly referred to as chromatids?
| A. | metaphase and telophase | |
| B. | anaphase and metaphase | |
| C. | interphase and telophase | |
| D. | interphase and prophase | |
| E. | metaphase and prophase |
Consider two traits for an organism, determined by two genes, each of which is governed by at least two alleles. In the case of a dihybrid individual, the gametes formed will be of either the parental type or the recombinant type. Recombinant type gametes are formed because of
| A. | the principle of dihybrids. | |
| B. | multiple alleles. | |
| C. | heterozygosity. | |
| D. | incomplete dominance. | |
| E. | independent assortment. |
An allele is
| A. | an alternate form of a gene. | |
| B. | always recessive. | |
| C. | the main factor determining a trait. | |
| D. | always one of a pair. | |
| E. | the dominant form of a gene. |
After the DNA is replicated, and it condenses in prophase, two identical rods of DNA are seen. These are
| A. | spindle fibers. | |
| B. | kinetochores. | |
| C. | chromatids. | |
| D. | chromatin. | |
| E. | centromeres. |
Special cells found in the gonads that give rise to gametes upon division are called
| A. | egg cells. | |
| B. | somatic cells. | |
| C. | germ cells. | |
| D. | stem cells. | |
| E. | basal cells. |
Q:
If an organismâs diploid chromosome number is 18, how many different possible combinations of homologous chromosomes lining up during meiosis exist for the eggs or sperm produced by that organism?
| A. | 512 | |
| B. | 9 | |
| C. | 18 | |
| D. | 128 | |
| E. | 36 |
At the end of metaphase I, _______________ separate.
| A. | sister chromatids | |
| B. | germ cells | |
| C. | homologous chromosomes | |
| D. | haploid chromatids | |
| E. | centrioles |
Mendel observed that dominant traits
| A. | are seen in all of the F1 hybrid pea plants in his experiments. | |
| B. | are expressed in all plants. | |
| C. | were absent in the F1 generation of pea plants that he used in his experiments. | |
| D. | were the only traits seen in the F2 generation of pea plants in his experiments. | |
| E. | are only expressed in hybrids. |
Cytokinesis in plant cells differs from cytokinesis in animal cells because
| A. | there is no difference. | |
| B. | in plant cells, the cell plate must also divide into two parts. | |
| C. | the contractile protein, actin, is important only in plant cells. | |
| D. | plant cells have a rigid cell wall. | |
| E. | a contractile ring forms only in plant cells. |
Sickle cell anemia is an example of what type of inheritance?
| A. | complete dominance | |
| B. | incomplete dominance | |
| C. | codominance | |
| D. | multiple alleles | |
| E. | recessive dominance |
Which of the following statements is true:
| A. | The dominant allele is masked in homozygous dominant individuals. | |
| B. | With recessive genetic disorders, if both parents are carriers, the offspring will all be affected. | |
| C. | In carriers, the recessive allele causes an intermediate phenotype. | |
| D. | In recessive genetic disorders, the mother and/or father of an affected individual must also be affected. | |
| E. | With dominant genetic disorders, the mother and/or father of an affected individual must also be affected. |
Skin cancers typically develop in the
| A. | upper layers of the epidermis. | |
| B. | lower layers of the dermis. | |
| C. | subcutaneous layer. | |
| D. | lower layers of the epidermis. | |
| E. | upper layers of the dermis. |
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (MD) is inherited from an X-linked recessive allele. What is the probability that a son with Duchenne MD inherited this disease from his biological father?
| A. | 1/2 | |
| B. | 0 | |
| C. | 1/16 | |
| D. | 1/4 | |
| E. | 1/8 |
The genetic makeup of a particular trait in an individual is its
| A. | genotype. | |
| B. | heterozygosity. | |
| C. | phenotype. | |
| D. | filial. | |
| E. | dominance. |
What structure holds the sister chromatids to the spindle fibers?
| A. | chromatin | |
| B. | kinetochore | |
| C. | MPF | |
| D. | centromere | |
| E. | cyclin |
If you view a cell in which the genetic material is beginning to be visible as separate bodies, and the nucleus has disappeared from view, you may surmise that the cells is in
| A. | telophase. | |
| B. | anaphase. | |
| C. | interphase. | |
| D. | metaphase. | |
| E. | prophase. |
Gregor Mendel was successful in his analysis of the genetics of pea plants because
| A. | he examined and analyzed both the F1 and F2 generations. | |
| B. | he studied the parental plants to determine their differences. | |
| C. | he decided to only look at his results in an objective manner. | |
| D. | he studied a trait that had a strange inheritance pattern. | |
| E. | pea plants have genetics different from other organisms. |
Tall corn plants (T) are dominant to dwarf plants (tt). Solid green leaves (G) are dominant to leaves with a white tip (gg). A cross between two corn plants yielded the following phenotypes: 51 tall plants with a white tip on their leaves; 43 dwarf plants with solid leaves; 48 dwarf plants with white tips on their leaves; 45 tall plants with solid leaves. What are the genotypes of the parents that produced these plants?
| A. | None of the above | |
| B. | TtGg x Ttgg | |
| C. | ttGG x TTgg | |
| D. | TtGg x TtGg | |
| E. | TtGg x ttgg |
In humans, a gene that has been identified as causing a type of skin cancer is the
| A. | superwoman echidna. | |
| B. | mutant superman. | |
| C. | sonic hedgehog. | |
| D. | mutant mole rat. | |
| E. | superhero aardvark. |
The segregation principle states that in sexually reproducing diploid organisms the two copies of each gene
| A. | segregate from each other during meiosis. | |
| B. | must always be the same allele. | |
| C. | separate from each other during mitosis. | |
| D. | will both wind up in either the sperm or egg. | |
| E. | move together as a unit during meiosis. |
In what phases is the genetic material in the cell correctly referred to as chromatids?
| A. | metaphase and telophase | |
| B. | anaphase and metaphase | |
| C. | interphase and telophase | |
| D. | interphase and prophase | |
| E. | metaphase and prophase |
Consider two traits for an organism, determined by two genes, each of which is governed by at least two alleles. In the case of a dihybrid individual, the gametes formed will be of either the parental type or the recombinant type. Recombinant type gametes are formed because of
| A. | the principle of dihybrids. | |
| B. | multiple alleles. | |
| C. | heterozygosity. | |
| D. | incomplete dominance. | |
| E. | independent assortment. |
An allele is
| A. | an alternate form of a gene. | |
| B. | always recessive. | |
| C. | the main factor determining a trait. | |
| D. | always one of a pair. | |
| E. | the dominant form of a gene. |
After the DNA is replicated, and it condenses in prophase, two identical rods of DNA are seen. These are
| A. | spindle fibers. | |
| B. | kinetochores. | |
| C. | chromatids. | |
| D. | chromatin. | |
| E. | centromeres. |
Special cells found in the gonads that give rise to gametes upon division are called
| A. | egg cells. | |
| B. | somatic cells. | |
| C. | germ cells. | |
| D. | stem cells. | |
| E. | basal cells. |