ENGR 1A Lecture Notes - Lecture 16: Uncertainty Principle
ENGR 1A verified notes
16/31View all
Document Summary
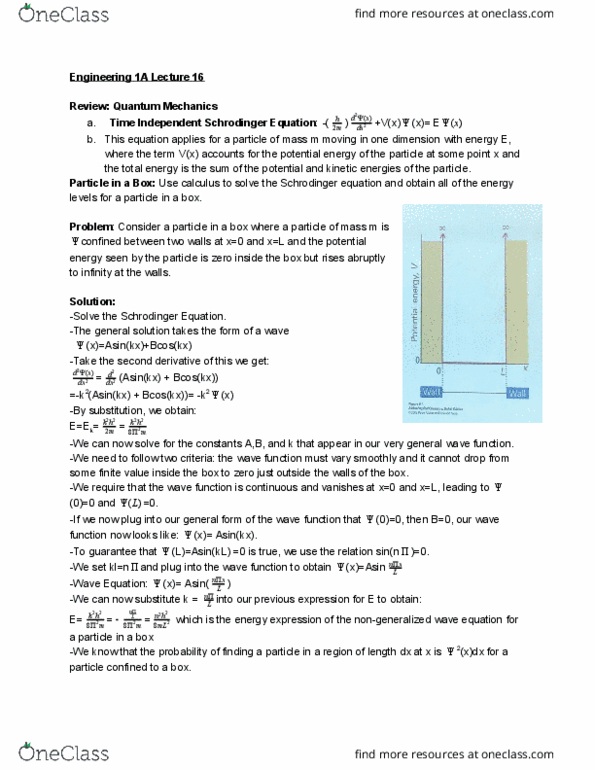
Time independent schrodinger equation a: this equation applies for a particle of mass m moving in one dimension with energy e, (x)= e. 2 d (x) dx2 where the term v(x) accounts for the potential energy of the particle at some point x and the total energy is the sum of the potential and kinetic energies of the particle. Use calculus to solve the schrodinger equation and obtain all of the energy confined between two walls at x=0 and x=l and the potential. : consider a particle in a box where a particle of mass m is. Particle in a box: levels for a particle in a box. Problem energy seen by the particle is zero inside the box but rises abruptly to infinity at the walls. The general solution takes the form of a wave. Take the second derivative of this we get: 2 d (x) dx2 (x)=asin(kx)+bcos(kx) d2 dx2 (l) .