ECON 1 Lecture Notes - Lecture 6: Average Variable Cost, Marginal Cost, Competitive Equilibrium
58 views2 pages
Verified Note
ECON 1 verified notes
6/31View all
Document Summary
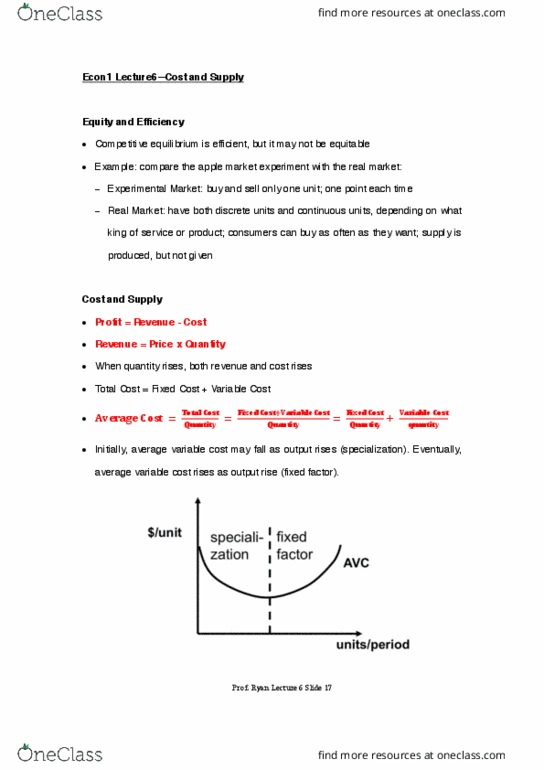
Equity and efficiency: competitive equilibrium is efficient, but it may not be equitable, example: compare the apple market experiment with the real market: Experimental market: buy and sell only one unit; one point each time. Real market: have both discrete units and continuous units, depending on what king of service or product; consumers can buy as often as they want; supply is produced, but not given. Cost and supply: profit = revenue - cost, revenue = price x quantity, when quantity rises, both revenue and cost rises, total cost = fixed cost + variable cost. Initially, average variable cost may fall as output rises (specialization). Eventually, average variable cost rises as output rise (fixed factor). Marginal cost: definition: the increase in cost from one more unit of output. If marginal cost > average cost, average cost is rising. If marginal cost < average cost, average cost is falling.
Get access
Grade+20% off
$8 USD/m$10 USD/m
Billed $96 USD annually

Homework Help
Study Guides
Textbook Solutions
Class Notes
Textbook Notes
Booster Class
40 Verified Answers
Class+
$8 USD/m
Billed $96 USD annually

Homework Help
Study Guides
Textbook Solutions
Class Notes
Textbook Notes
Booster Class
30 Verified Answers