PHYS201 Lecture Notes - Lecture 12: Net Force, Acceleration
Document Summary
Get access


Related textbook solutions
Related Documents
Related Questions
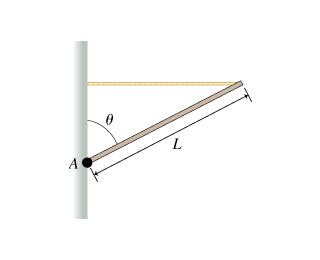
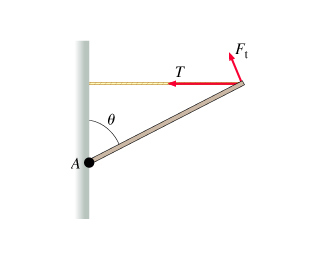
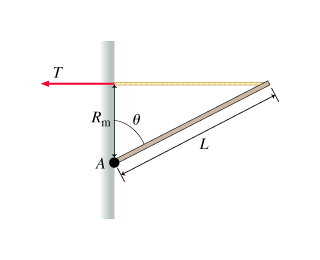
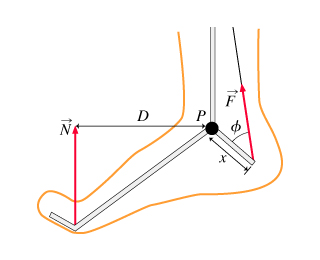
A force F⃗ of magnitude F making an angle θ with the x-axis is applied to a particle located along the axis of rotation A, at Cartesian coordinates (0,0) in the figure. The vector F⃗ lies in the XY plane, and the four axes of rotation A, B, C, and D all lie perpendicular to the XY plane. (Figure 1)
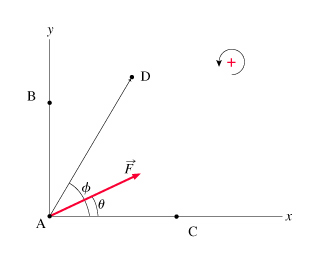
A particle is located at a vector position r⃗ with respect to an axis of rotation (thus r⃗ points from the axis to the point at which the particle is located). The magnitude of the torque τ about this axis due to a force F⃗ acting on the particle is given by
τ=rFsin(α)=(moment arm)⋅F=rF⊥,
where α is the angle between r⃗ and F⃗ , r is the magnitude of r⃗ , F is the magnitude of F⃗ , the component of r⃗ that is perpendicular to F⃗ is the moment arm, and F⊥ is the component of the force that is perpendicular to r⃗ .
Sign convention: You will need to determine the sign by analyzing the direction of the rotation that the torque would tend to produce. Recall that negative torque about an axis corresponds to clockwise rotation.
In this problem, you must express the angle α in the above equation in terms of θ, ϕ, and/or π when entering your answers. Keep in mind that π=180degrees and (π/2)=90 degrees.
Part A
What is the torque τA about axis A due to the force F⃗ ?
Express the torque about axis A at Cartesian coordinates (0,0).
|
|
|||
| τA = |
SubmitHintsMy AnswersGive UpReview Part
Part B
What is the torque τB about axis B due to the force F⃗ ? (B is the point at Cartesian coordinates (0,b), located a distance b from the origin along the y axis.)
Express the torque about axis B in terms of F, θ, ϕ, π, and/or other given coordinate data.
|
|
|||
| τB = |
SubmitHintsMy AnswersGive UpReview Part
Part C
What is the torque τC about axis C due to F⃗ ? (C is the point at Cartesian coordinates (c,0), a distance c along the x axis.)
Express the torque about axis C in terms of F, θ, ϕ, π, and/or other given coordinate data.
|
|
|||
| τC = |
SubmitHintsMy AnswersGive UpReview Part
Part D
What is the torque τD about axis D due to F⃗ ? (D is the point located at a distance d from the origin and making an angle ϕ with the x axis.)
Express the torque about axis D in terms of F, θ, ϕ, π, and/or other given coordinate data.