Kinesiology 2241A/B Chapter Notes -Buoyancy
74 views2 pages
19 Apr 2013
School
Department
Course
Professor
Document Summary
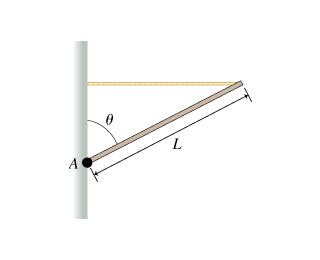
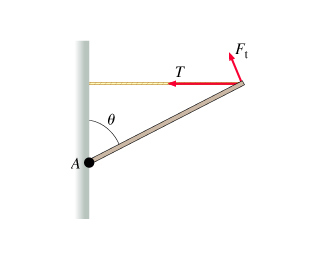
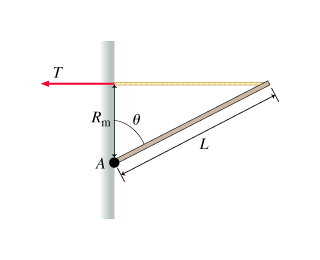
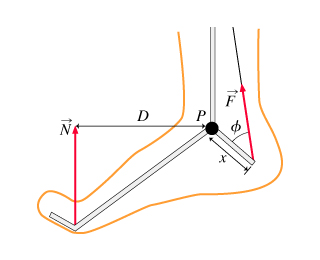
When a force is applied to an object, it moves the object"s c of g in a linear path. When the object is restricted to movement about an axis, the force causes the object to rotate: except when the force is applied directly at the axis of rotation. Eccentric force off-center force that causes torque. Four properties of torque-producing forces: magnitude, direction, line of action, point of application. Torque is produced by muscles when they pull on bones, and the result is rotary motion of the body segments about an axis. The stronger the muscle contraction, the greater torque on the bone. The longer the force arm, the greater the torque. Teeter-totter: if the weight is less (ie. a child), it creates less torque, if the weight is placed closer to the axis it creates less torque. If many torques are applied to a system, the sum of the torques tells the movement direction (net torque)
Get access
Grade+20% off
$8 USD/m$10 USD/m
Billed $96 USD annually

Homework Help
Study Guides
Textbook Solutions
Class Notes
Textbook Notes
Booster Class
40 Verified Answers
Class+
$8 USD/m
Billed $96 USD annually

Homework Help
Study Guides
Textbook Solutions
Class Notes
Textbook Notes
Booster Class
30 Verified Answers