COMMERCE 2OC3 Study Guide - Final Guide: Standard Deviation, Service Level, Package Pilferage
Decouple/separate parts of the production process
•
Decouple/separate firm from demand fluctuations and provide stock with wide selection
•
To take advantage of quantity discounts and hedge against inflations
•
Inventory is a resource that a firm holds in stock with the intent of selling or transforming into a more valuable
state. The goal is to find balance between inventory investment and customer service. Inventory can:
Raw material is purchased but not processed and decouples suppliers from the production process
•
Cycle counting is the continued reconciliation of inventory with records through auditing
○
Work-in-process (WIP) have undergone some change but are not completed, exist due to cycle time (time
taken for product to be made) - reducing cycle time reduces inventory
•
MRO are maintenance, repair, and operating supplies that keep machinery productive
•
Finished-goods are complete products awaiting shipment
•
Types of Inventory
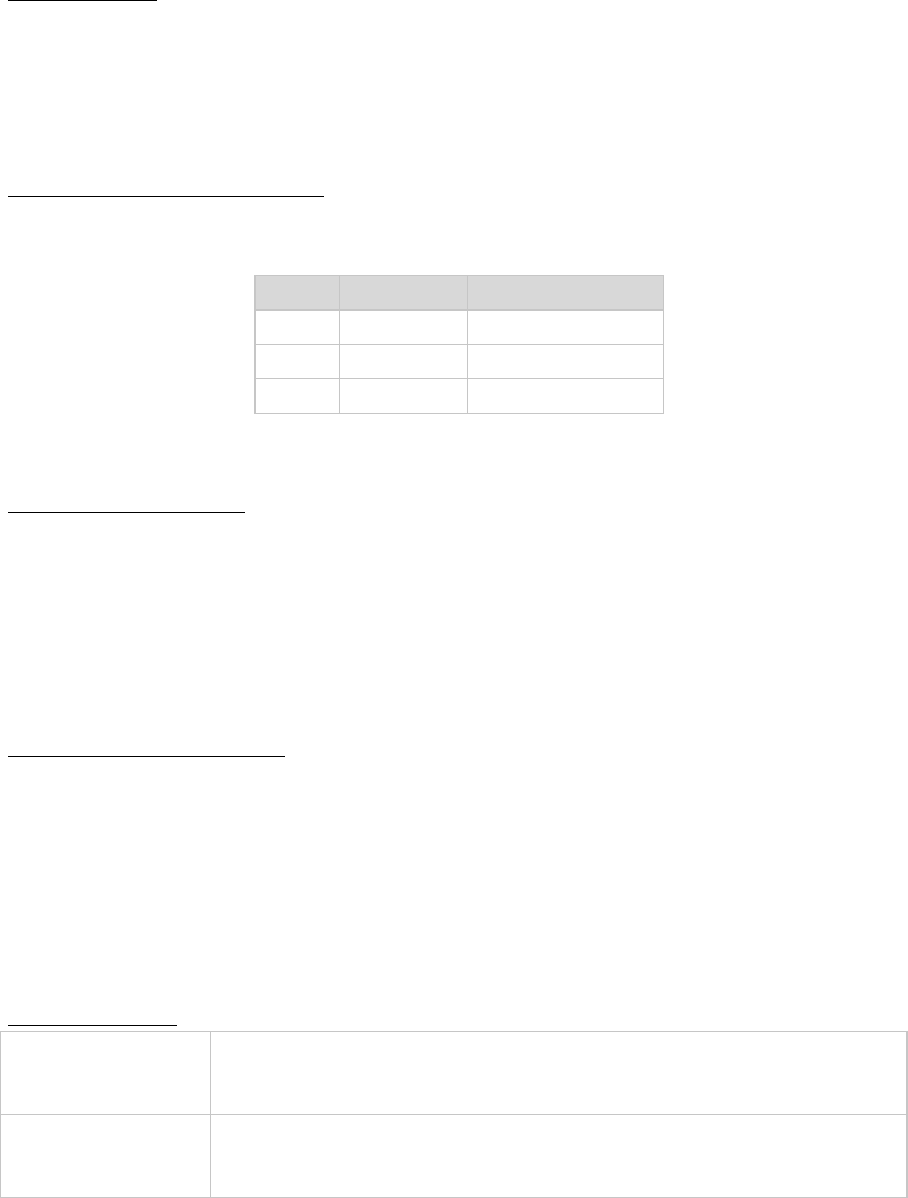
Managing Inventory Using ABC Analysis
ABC analysis divides on-hand inventory into three classifications based on annual dollar volume. It is motivated
by the Pareto principle and which describes the "critical few and trivial many" in terms of distribution of wealth
among society.
Class
% of inventory
% of total dollar usage
A
0.15
0.7 to 0.8
B
0.3
0.15 to 0.25
C
0.55
0.05
Leads to tighter inventory control on Class A items (secured storage, better demand forecasts, more frequent
orders).
Shrinkage is the inventory that is unaccounted for between receipt and sale
•
Pilferage is a small amount of inventory theft accounting between 1-3% in more retail stores
•
Control of Service Inventories
Good personnel selection, training, and discipline
•
Tight control of incoming shipments using bar-codes, radio frequency ID (RFID) and stock-keeping units
(SKU)
•
Effective control of all goods leaving facilities using direct observation, surveillance, or electronic
observation
•
Due to substantial impact on profitability, applicable techniques to control inventory include:
Four Categories of Inventory Costs
Ordering/setup costs are incurred as a result of work involved in placing purchase orders with suppliers or
configuring tools, equipment, fixed transport costs, machines to produce an item
•
Unit cost of the stock keeping-unit (SKU) is the price paid for purchased good or internal cost of producing
them
•
Holding/carrying costs are expenses associated with carrying inventory, consisting of storage, insurance,
working, transport, technology, works, security, averaging 30-35%
•
Backorders are from customers willing to wait while lost orders are from those unwilling to wait
○
Shortage/stockout costs are associated with SKU being unavailable when needed to meet demand
•
Goal is to minimize inventory costs and stockouts.
Performance Metrics
If too low, overstocking is occuring
•
Measures how many times inventory is used/sold in a year, computed annually.
= average inventory value for given period
= inventory investment = % total assets invested in inventory
Large percentages may be a risk, incurring extra storage costs or indicate an
ineffective supply chain.
Inventory Control Models
Inventory Management
March 6, 2018
2:36 PM
Operations Management Page 1
