SOC227H5 Study Guide - Summer 2018, Comprehensive Midterm Notes - Where We Are, Free Trade, Canada

SOC227H5
MIDTERM EXAM
STUDY GUIDE
Fall 2018
1
SOC 227—WORK AND OCCUPATIONS
Session #1: Culture, Models, History
Readings:
• Text: Introduction; Ch. 1: 1-10
• “A World without Work”
• “Automation and Job Loss in Canada
• We are receiving better jobs than our parents now
• Technology now available that can do jobs that were once available for humans
- for example, car factories (difference = dark because robots don’t need
overhead lights to see)
- things we thought machines couldn’t do… are happening (artificial intelligence)
- current fear = robot substitution on greater scale
- economists position = “it’s not as bad as we think”
• University students are having issues finding professional jobs when they leave
school
• 2009 – Great Recession = employment rate decreased dramatically
- since then “net trend” has been down
- Canadian economy does not provide as many paid jobs as it used to
JK MEDIA ITEM
INTRO to the COURSE
• ATTENDING CLASS IS IMPORTANT!
- LECTURE NOTES ARE NOT POSTED, ONLY OUTLINES
SOCIAL CULTURE
• Social entity: a grouping of individuals with some awareness that they are
members of the group
o Every social entity has social culture and social structure
o Could belong to country, religion, ethnic group or region (Quebec is most
aware province in Canada due to French speaking population; Alberta)
• Social structure: the relationships among the individual parts of the entity
o Friendship or status are examples
• Social culture: what people think and do that people believe to be relevant
find more resources at oneclass.com
find more resources at oneclass.com
2
1. Beliefs: broad ideas about the social entity and how the world works
o For example, religious beliefs (only 1 god)
2. Values: ideas about what’s important
o What’s right and wrong, how things should be
o For example; courses are easy to believe, families’ (social
structure) valuing their daughter to marry and have children, not
eating meat, etc.
3. Norms: commonly accepted and expected behaviors in the social
entity
4. Symbols: objects and behaviours that illustrate the beliefs & values
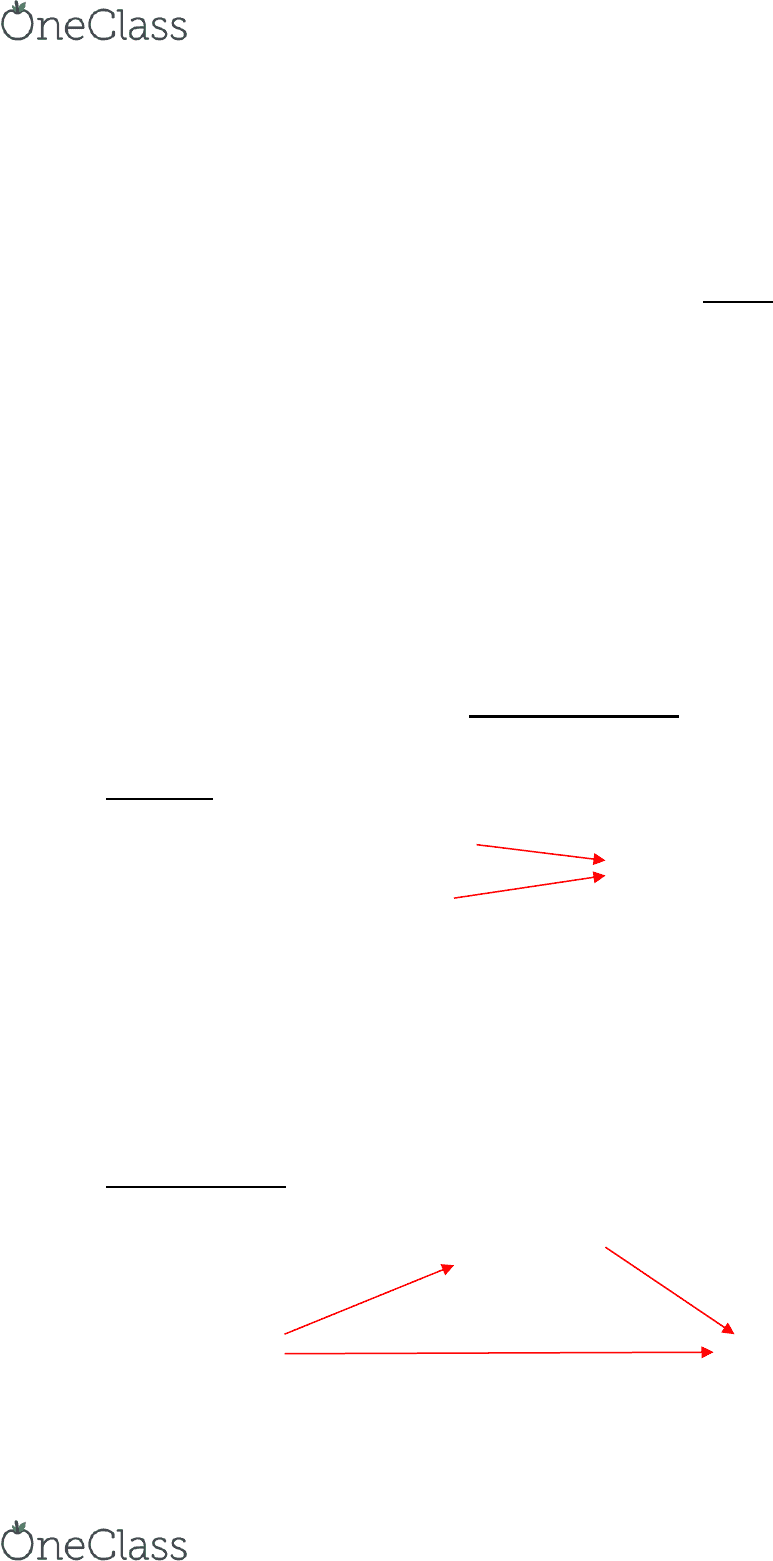
CAUSAL MODELS
1. Simple:
↓ M-F Power Difference
↑ Gender Harassment
↑ Proportion of M Ees
• Interpretation:
o The lower the male-female power difference = more gender
harassment
o Higher proportion of males = more gender harassment
2. Indirect Effect:
Job
Satisfaction
Pay Not
Quitting
find more resources at oneclass.com
find more resources at oneclass.com
Document Summary
Automation and job loss in canada: we are receiving better jobs than our parents now, technology now available that can do jobs that were once available for humans. For example, car factories (difference = dark because robots don"t need overhead lights to see) Things we thought machines couldn"t do are happening (artificial intelligence) Current fear = robot substitution on greater scale. Economists position = it"s not as bad as we think : university students are having issues finding professional jobs when they leave school, 2009 great recession = employment rate decreased dramatically. Since then net trend has been down. Canadian economy does not provide as many paid jobs as it used to. Intro to the course: attending class is important! Lecture notes are not posted, only outlines. Interpretation: the lower the male-female power difference = more gender harassment, higher proportion of males = more gender harassment, indirect effect: Eg #1: sex, dominance behaviours, and room size.

