ECON 1201 Lecture Notes - Lecture 20: Marginal Utility, Marginal Cost, Externality
Document Summary
Get access


Related Documents
Related Questions
Question 1
An externality
|
enhances market efficiency. |
||
|
is a private cost or benefit that results from the production or consumption of a good or service that is external to a market. |
||
|
is a benefit or cost that affects someone who is not directly involved in the production or consumption of a good or service. |
||
|
refers to production or consumption that occurs outdoors. |
5 points
Question 2
Externalities can be produced by:
|
the high price of goods and services |
||
|
individuals; firms |
||
|
market prices; market incomes |
||
|
oceans; streams |
5 points
Question 3
When an external cost exists that is NOT taken into account in the production of a product,
|
the level of output is too high, and the supply curve should shift to the left to account for the externality. |
||
|
the price of the product is too high, and production should be expanded to lower the price. |
||
|
the level of output is optimal, and there should be no change in the supply curve. |
||
|
the level of output is too low, and the supply curve should shift to the right to account for the externality. |
5 points
Question 4
Which of the following is correct?
|
MSC = MPC - MD |
||
|
MPC = MSC + MD |
||
|
MSC = MPC + MD |
||
|
MD = MSC + MPC |
5 points
Question 5
If external costs (costs of cleaning up) are included and added to a firm's private costs, then
|
the demand curve will shift to the left. |
||
|
the supply curve will shift to the right. |
||
|
the demand curve will shift to the right |
||
|
the supply curve will shift to the left. |
5 points
Question 6
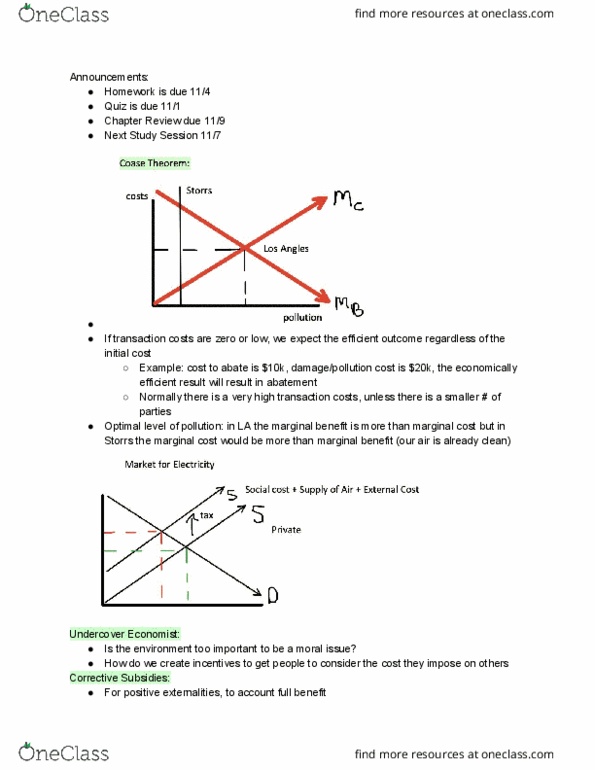
The Coase Theorem states that
|
government intervention is always needed if externalities are present. |
||
|
assigning property rights is the only thing the government should do in a market economy. |
||
|
if transaction costs are low, private bargaining will result in an efficient solution to the problem of externalities. |
||
|
a free-market equilibrium is the best solution to address externalities. |
5 points
Question 7
Buffalo in the United States almost became extinct while cattle, an animal that provides similar products, never have been close to extinction. The difference is due to
|
the use of private property rights on cattle and common property rights on buffalo. |
||
|
the greater marginal value of a head of cattle relative to buffalo, leading to over-hunting of buffalo. |
||
|
cattle existing in Europe also while buffalo were specific to North America. |
||
|
the greater marginal value of a buffalo relative to a steer, leading to the overharvesting of buffalo. |
5 points
Question 8
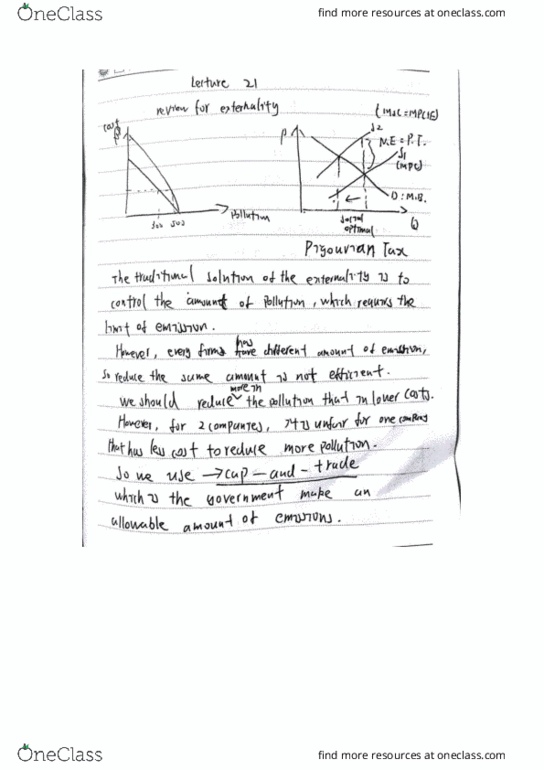
In theory, the Emissions Fee would
|
cause firms to generate less pollution than their allowed limits. |
||
|
raise the production costs of all firms. |
||
|
cause firms to generate more pollution than their allowed limits. |
||
|
lower the production costs of all firms. |
5 points
Question 9
A cap-and-trade policy
|
has a set number of permits. |
||
|
allows polluters to trade permits. |
||
|
caps the total level of pollution allowed. |
||
|
all of the above. |
Question 10
A Pigouvian tax corrects for
|
market congestion. |
||
|
market losses. |
||
|
inefficient sales. |
||
|
low market prices. |
Question 1
Which compensation method helps to explain the large difference between the salaries of top-level managers and mid-level managers in a firm?
| A. | Tournaments | |
| B. | New blood | |
| C. | Piece rate | |
| D. | Backloaded compensation |
3 points
Question 2
Please consider the information provided under Question 19 in Chapter 3 (page 54). Based on the stated information, the optimal number of bees kept if the externality is ignored by Yung is 5,000. Is the socially optimal number of bees higher or lower than 5,000?
| A. | We do not have enough information to answer this question | |
| B. | Same | |
| C. | Lower | |
| D. | Higher |
3 points
Question 3
Which of the following factors contribute to the existence of firms?
| A. | All of these factors contribute to firm existence | |
| B. | Risks associated with specialization | |
| C. | Incomplete contracts | |
| D. | Willingness of some people to take on risk in exchange for residual income |
3 points
Question 4
Public goods are often subject to free-rider problems because these goods are:
| A. | Non-rival and non-excludable | |
| B. | Rival and non-excludable | |
| C. | Non-rival and excludable | |
| D. | Rival and excludable |
3 points
Question 5
Which of the following is the most efficient mechanism for allocating scarce goods?
| A. | Government allocation system | |
| B. | First-come-first-served system | |
| C. | Market system | |
| D. | Random allocation system |
3 points
Question 6
Many years ago, most of the major Hollywood movie studios also owned chains of local movie theaters across the US. Today, most of the local movie theaters are owned by other companies. What has happened to the degree of integration in the movie industry over time?
| A. | Less horizontally integrated | |
| B. | Less vertically integrated | |
| C. | More horizontally integrated | |
| D. | More vertically integrated |
3 points
Question 7
Your firm produces replacement parts for the nuclear submarines operated by the US Navy. Which one of Porter's Five Forces will be most prominent in determining your strategies and profitability?
| A. | Bargaining Power of Suppliers | |
| B. | Bargaining Power of Customers | |
| C. | Threat of New Entrants | |
| D. | Threat of Substitutes |
3 points
Question 8
Which of the following statements is NOT true?
| A. | The market mechanism for allocating resources is most efficient due to the incentives it creates. | |
| B. | Markets are always the most efficient way to allocate goods, even if the market is not perfectly competitive. | |
| C. | The random allocation mechanism provides no incentives at all. | |
| D. | The government allocation mechanism provides no incentive for the economy to grow. |
3 points
Question 9
Suppose a firm's cost structure exhibits economies of scope. Which of the following actions is compatible with this cost structure?
| A. | Diversify into other product lines | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| B. | Focus on core competencies and reduce production | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| C. | Focus on core competencies and maintain constant production | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| D. | Focus on core competencies and expand production Question 10 Please refer to Table 8.3 on page 132 in the book. Suppose we change the payoffs in the "low price, low price" cell to 0, 25 from 0, 0. Does this change the Nash equilibrium for the game, and is the game still a Prisoner's Dilemma?
3 points Question 11 Which of the following statements about restricting entry to markets is NOT true?
3 points Question 12 Your firm earns $2 million per quarter in total revenue, and your accounting profits are $100,000 per quarter. You do not charge the firm for the use of an old building that you own because it is 50 years old and fully depreciated. However, another firm has offered you $200,000 per quarter to use the facility, and this is the market rental rate for similar facilities. In this case, we know that your:
3 points Question 13 Please refer to Question 13 in Chapter 1 (page 17). What is the marginal cost of reducing global warming by 0.017 degrees?
3 points Question 14 In Chapter 6, Boyes focuses on negative externalities such as the various types of pollution. However, as we discussed during our online session, we can also observe positive externalities in which external benefits are generated for people. Which of the following is NOT an example of a positive externality?
3 points Question 15 Common property resources are:
3 points Question 16 The free-rider problem arises in markets for common property resources.
3 points Question 17 Firms that set their product price below the actual cost of production may be engaging in:
3 points Question 18 Under a cap-and-trade mechanism to control air pollution, what happens to the price of pollution rights if the supply of righs is reduced (i.e., the supply of rights is reduced)?
|