MEDS12001 Lecture Notes - Lecture 9: Visual Artifact, Mirror Image, Turbulence
1 | P a g e
ARTIFACTS
• Artifacts in sonography occur as apparent
structures that are one of the following:
o Not real
o Missing
o Misplaced
o Of incorrect brightness, shape, or
size
ASSUMPTIONS OF ULTRASOUND SYSTEM
• Sound travels in a straight line
• Echoes originate only from objects located
on the beam axis
• The amplitude of the returning echoes is
related directly to the reflecting or
scattering properties of distant objects
• The distance to reflecting or scattering
objects is proportional to the round-trip
travel time
PROPAGATION ARTIFACTS
Slice thickness
• Third dimension
• Beam width perpendicular
to the scan plane
• Possible to resolve by
using tissue harmonic
imaging
Speckle
• Granular
appearance of
images that is
the result of
interference of
echoes from
the distribution of scatterers in tissue
• Echoes can combine constructively or
destructively
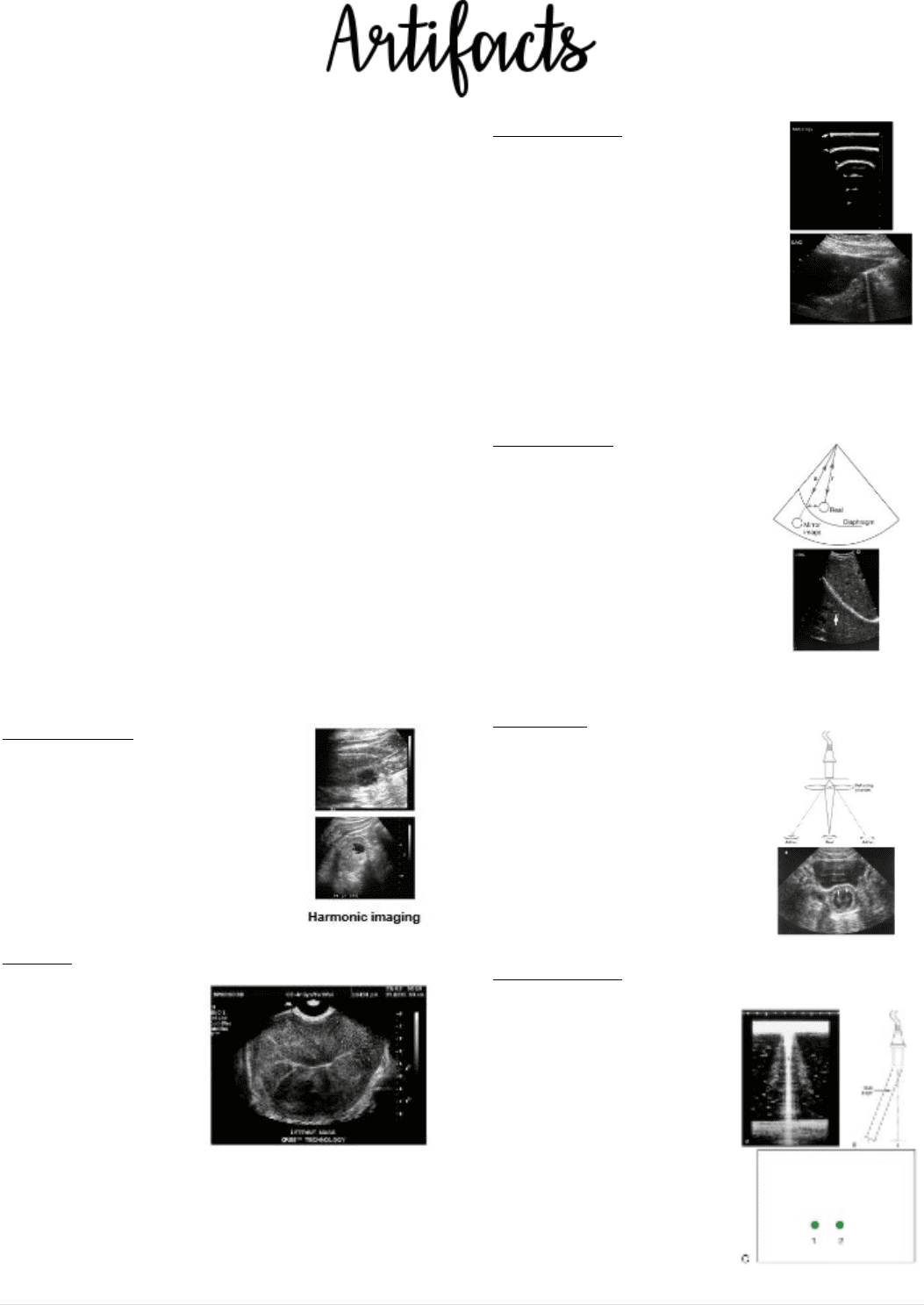
Reverberation
• Equally spaced
reflections of
diminishing amplitude
with increased imaging
depth
• Two or more strong
reflectors are
encountered in the sound path; multiple
reflections will occur
Mirror image
• Duplication of a
structure on the
opposite side of a
strong reflector
• Form of
reverberation
• Common around the
pleura and diaphragm
Refraction
• Change of direction of
the sound beam from
one medium to the
next
• Displaces structures
laterally from their
correct locations
Grafting lobes
• Additional weaker
beams emitted
from an array
transducer
• Duplicate
structures laterally
to the true ones
• Normally do not
produce displayed
echoes
find more resources at oneclass.com
find more resources at oneclass.com

2 | P a g e
Speed error
• Occurs when the speed of sound of soft
tissue is faster or slower than the assumed
1.54 mm/µs
• Slower speeds
place echoes
deeper
(position 2)
• Faster speeds
place echoes
closer
(position 3)
Range ambiguity
• All echoes are not
received before the
next pulse is emitted
• Places structures
much closer to the
surface than they
should be
ATTENUATION ARTIFACTS
Shadowing
• Weakening of echoes
distal to a strongly
attenuating or reflecting
structure or from the
edges of a refracting
structure
Enhancement
• Strengthening of
echoes distal to a
weakly attenuating
structure
• Increased
brightness behind
a weakly attenuating structure
DOPPLER ARTIFACTS
Nyquist limit
• The highest frequency in a sampled signal
represented unambiguously
• Equal to one half the pulse repetition
frequency
• The minimum number of samples required
to avoid aliasing
Aliasing
• Under sampling of the
Doppler shifts in a
pulsed Doppler system
• Appearance of Doppler
information (spectral or
colour) on the wrong
side of the baseline
Range ambiguity
• Pulse emitted before all the echoes from
the previous pulse
have been received
• Multiple sample
volumes will
appear as a result
Mirror image
• Duplication of a vessel or Doppler shift on
the opposite side of a strong reflector
• Mirror vessel will demonstrate colour and
spectral flow
find more resources at oneclass.com
find more resources at oneclass.com

3 | P a g e
Flash artefact
• Sudden burst of colour Doppler
• Typically caused by tissue or transducer in
motion
• Demonstrates an extension of colour
beyond the region of blood flow
SPECTRAL BROADENING
• Seen in turbulent flow conditions
• However incorrect settings or sampling
can mimic spectral broadening
EQUIPMENT CONTROLS
• Overall gain
• TGC
• Dynamic range
• Movement/blur
• Banding (multiple focal zones)
ARTIFACTS
ARTIFACTS
Any structure visible on an image that does
not accurately represent the true position or
presence or reflectivity of a corresponding
structure in tissue.
WHY DO ARTIFACTS OCCUR:
1. Ultrasound unit assumptions
2. Equipment failure/faulty
3. Equipment settings are inappropriate
4. Electrical interference
find more resources at oneclass.com
find more resources at oneclass.com
Document Summary
Reverberation: artifacts in sonography occur as apparent, equally spaced structures that are one of the following, not real, missing, misplaced, of incorrect brightness, shape, or size. Slice thickness: third dimension, beam width perpendicular to the scan plane, possible to resolve by using tissue harmonic imaging. Mirror image: duplication of a structure on the opposite side of a strong reflector, form of reverberation, common around the pleura and diaphragm. Refraction: change of direction of the sound beam from one medium to the next, displaces structures laterally from their correct locations. Grafting lobes: additional weaker beams emitted from an array transducer, duplicate structures laterally to the true ones, normally do not produce displayed echoes. Speed error: occurs when the speed of sound of soft tissue is faster or slower than the assumed. 1. 54 mm/ s: slower speeds place echoes deeper (position 2, faster speeds place echoes closer (position 3)

