AGR 2050 Lecture Notes - Lecture 24: Soil Health, Soil Respiration, Carbon Cycle
Wednesday, March 21, 2018
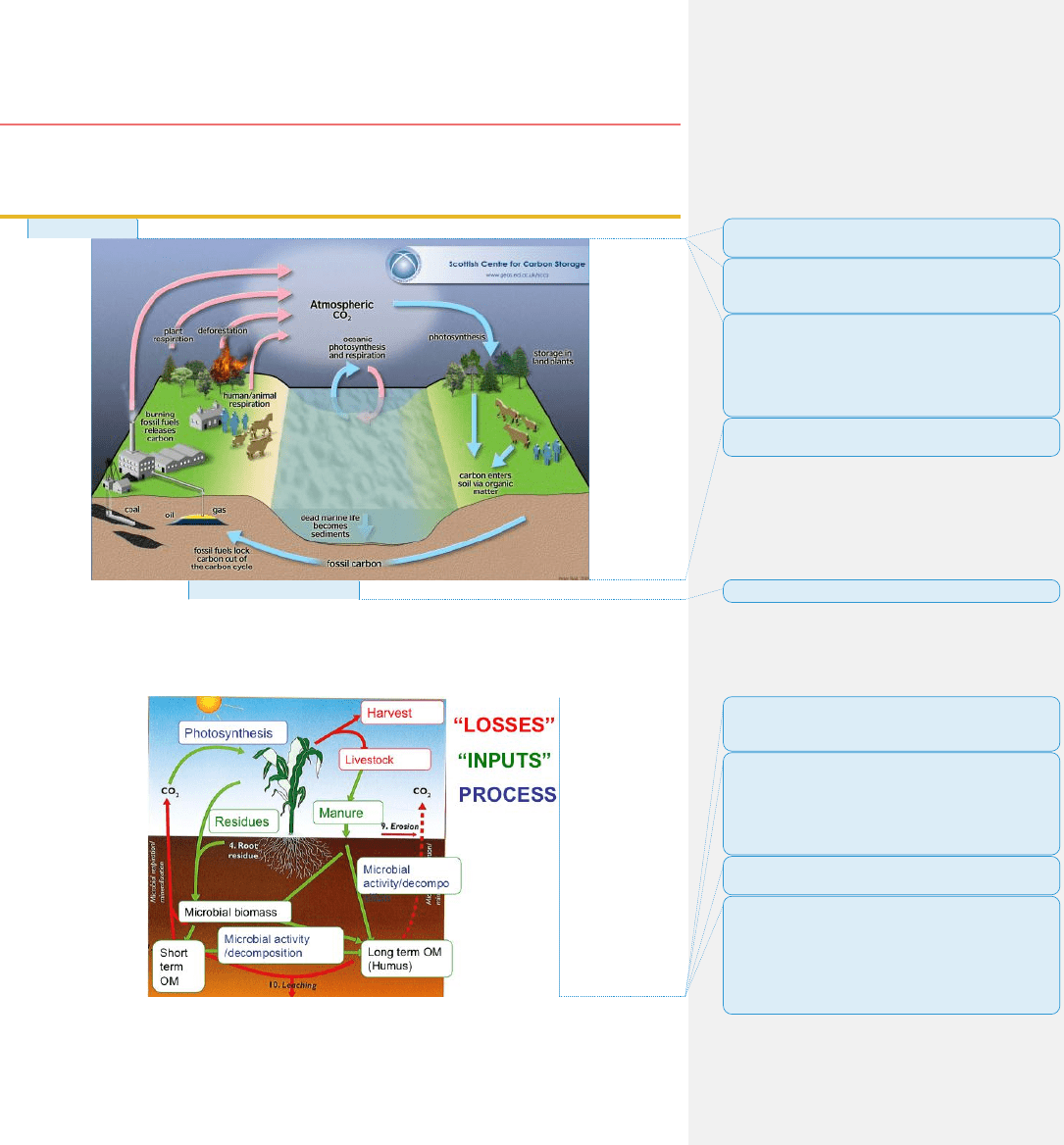
Carbon Cycling & SOM
Carbon Cycle
• Describes the movement of carbon as it is recycled & reused throughout the
biosphere
• Involves the incorporation of carbon dioxide into living tissue by
photosynthesis & its return to the atmosphere through respiration, the decay
of dead organisms, & the burning of fossil fuels
• The story of life
o Plant residue composition
Commented [A1]: Photosynthesis & the lifecycle
depend on this
Commented [A2]: When the carbon in the
atmosphere increases, what does this do to the
earth?
Commented [A3]: Influence the carbon cycle:
•OM
•Soil health
•pH
•Temperature
•Weather
Commented [A4]: Climate change: how will it
change? How will it affect our change to this?
Commented [A5]: Humans are a part of the cycle
Commented [A9]: Photosynthesis: transfer of solar
energy into useful plant energy
•Uses carbon dioxide (from the atmosphere) - to
ATP – to cellulose
•We eat the plants (absorption of energy)
•Expire & respire to put carbon dioxide back
into the atmosphere
Commented [A8]: Top: farm carbon cycle
(harvesting crops, etc.)
Commented [A7]: Residue on surface: how long it
takes to breakdown
•Proteins: do not decompose easily – more
complex
•Carbohydrates
•Different forms of carbon
Commented [A6]: If the cycle is slow or delayed
(something wrong below the ground) – there are
ways that we can help this process

Climate Change & Carbon
• Carbon cycle is an important part of the processes influencing atmospheric
carbon
• Current atmospheric level = 370 ppm
• CO2 levels in year 2100 estimated to be 500-1000ppm
• Year 2100 expect;
o Temperature change between 1.5 & 5.5 degrees
o Soil warming will decrease carbon storage
o Sea level change 0.1-0.9 m
• Largest Carbon Pool
• It’s not so much about averages
o As the extremes
Commented [A10]: No one truly knows where it is
going to be, at least a doubling
Commented [A11]: Talking about at the equator à
(2°C at the equator to 6°C at the pole)
Commented [A12]: Will make New York city sink
Commented [A13]: Biosphere connects: Atmosphere
(air), Hydropshere (water),
§ We have to adapt our production systems to maintain high
yields under those conditions
• Research is needed to understand the interaction of climate change &
carbon cycle
o At this time, the understanding of this interaction is incomplete
Soil Respiration & Global Carbon Cycle
• Soil respiration
o Is the primary path by which CO2 fixed by plants returns to the
atmosphere
o Increases with temperature
• Rising concentrations of CO2 in the atmosphere will increase the flux of CO2
from soils
• Soil carbon pool unlikely to moderate the rise in atmospheric CO2
• Flux of CO2 from soils tied to plant growth with supplies OM to decomposers
o Lower organic matter in the tropics (rainforests – decomposes faster)
than here
• Greatest rate of soil respiration is found in the tropics where plant growth is
luxuriant & conditions ideal for decomposers
• Greatest loss in soil carbon in tropics as temperature increases
• OM increase not from large biomass inputs but rather from other factors
(temperature) that limits decomposers
o That is why we have higher organic matter (more C within the soil)
• Tillage increases rate of OM decomposition because of soil aeration, moisture
content & higher rates of soil respiration
o Holland marsh is 70% organic matter, but every time they till, they loss a
little bit of their soil
• Tillage disrupts soil aggregates, exposing absorbed OM to decomposition
• Loss of OM lower in no-till
Document Summary
Commented [a1]: photosynthesis & the lifecycle depend on this. Commented [a3]: influence the carbon cycle: om, soil health, ph, temperature, weather. How will it affect our change to this: describes the movement of carbon as it is recycled & reused throughout the. Commented [a5]: humans are a part of the cycle biosphere. Involves the incorporation of carbon dioxide into living tissue by photosynthesis & its return to the atmosphere through respiration, the decay of dead organisms, & the burning of fossil fuels. The story of life: plant residue composition. Commented [a6]: if the cycle is slow or delayed (something wrong below the ground) there are ways that we can help this process. Commented [a7]: residue on surface: how long it takes to breakdown: proteins: do not decompose easily more complex, carbohydrates, different forms of carbon. Commented [a8]: top: farm carbon cycle (harvesting crops, etc. )

