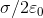PHYS 212 Lecture 4: Conductors and Gauss's Law 1/30/17
Document Summary
Electric fields and conductors if an external e-field is applied, these electrons move. Electric field opposite to external field free charges stop moving when their field cancels external in general, for conductor in electrostatic equilibrium, e-field is zero inside the conductor. A +3 nc charge resides within a cavity in a conductor, find the total charge on the cavity surface. Net field inside a conductor must be zero the electric field of a conductor has both parallel and perpendicular components. Parallel components rearrange charges on the surface until an induced field cancels it out. So, the total field must be perpendicular to surface at equilibriumo, the total field must be perpendicular to surface at equilibrium. (cid:1831) = 9 if net charge is inside conductor, it repels to surface. Even if there is an inner cavity, so long as it is empty. Charge density of a conductor is higher near points far away from the center.