PHYSICS 7E Lecture Notes - Lecture 3: Perfect Fluid, Daniel Bernoulli, Buoyancy

14
PHYSICS 7E Full Course Notes
Verified Note
14 documents
Document Summary
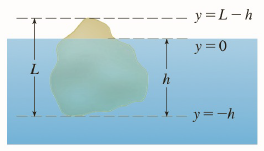
Physics 7e - lecture 3 - fluid mechanics. The buoyant force is the upward force exerted by fluid on any immersed object. The buoyant force is the resultant force due to all forces applied by the fluid due to all forces applied by the fluid surrounding the object. The liquid in dashed circle is in equilibrium. The upward force, b , must equal (in magnitude) the downward gravitational force. The magnitude of the buoyant force always equals the weight of the fluid displaced by the object, and is independent of the composition the object. Archimedes" principle, crown example mcrown in ar = t 1 = 7. Archimedes was (supposedly) asked, is the crown gold? . Weight in water (submerged) = 6. 84 n. Buoyant force will equal the apparent weight loss. Difference in scale readings will be the buoyant force gv. B = v = ( 1 t 2. Then to find the material of the crown,