PHYS 1C Lecture Notes - Lecture 16: Curved Mirror, Thin Lens

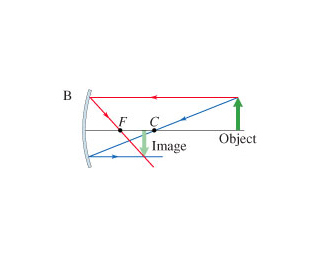
Convex mirror
-
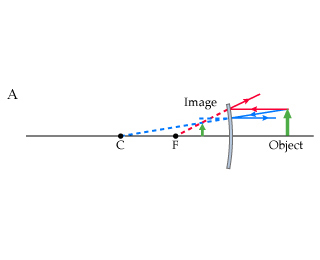
The object in front of the convex mirror
-
The image is virtual, upright, and smaller than the object (reduced)
-
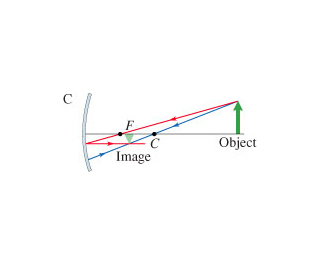
Spherical Mirrors
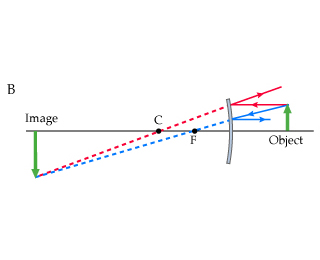
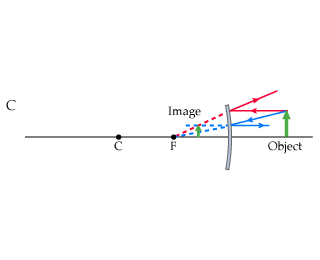
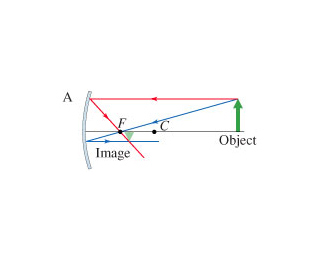
Ray 1: parallel to axis, ray diverted so it or its virtual ray goes
through focal point
-
Ray 2: directed to focal point, gets reflected parallel to axis
-
Ray 3: directed to center of curvature, reflected back
-
Ray Rules
A convex mirror is sometimes referred to a diverging mirror
-
The rays from any point on the object diverge after reflection as if
they were coming from some point behind the mirror
-
The image is virtual because it lies behind the mirror at the point
where the reflected rays appear to originate
-
In general, the image formed by a convex mirror is upright, virtual,
and diminished
-
Convex Mirrors
What if we wanted to use refraction to converge parallel light rays
to a single focal point? What type of shape should we use?
-
A parallel light ray was pushed downward
○
What happened when we flipped the prism?
○
A parallel light ray was pushed upward
○
Recall our prism example:
-
This is the basis behind constructing different types of lenses for
distorting light
-
This is known as a converging lens
○
It is a lens consisting of plastic or glass that refracts light
○
If focuses parallel light rays at a single point known as the
focal point
○
We can construct the following lens:
-
Converging Lenses
Converging lenses are thick in the middle and thin near the edges
-
They have positive focal lengths
-
A thin lens has two focal points, corresponding to parallel light rays from left or from the
right
-
This is known as a diverging lens
○
It is also a lens consisting of plastic or glass that refracts light
○
It defocuses parallel light rays to make it appear that it came from a single point
We can also construct the following lens
-
Diverging lenses
(16) Lecture 26B Converging and Diverging lenses
Monday, May 14, 2018
10:58 AM
week 6 Page 1
Document Summary
The object in front of the convex mirror. The image is virtual, upright, and smaller than the object (reduced) Ray 1: parallel to axis, ray diverted so it or its virtual ray goes through focal point. Ray 2: directed to focal point, gets reflected parallel to axis. Ray 3: directed to center of curvature, reflected back. A convex mirror is sometimes referred to a diverging mirror. The rays from any point on the object diverge after reflection as if they were coming from some point behind the mirror. The image is virtual because it lies behind the mirror at the point where the reflected rays appear to originate. In general, the image formed by a convex mirror is upright, virtual, and diminished. This is the basis behind constructing different types of lenses for distorting light. It is a lens consisting of plastic or glass that refracts light.