APK 2105C Study Guide - Quiz Guide: Endoplasmic Reticulum, Skeletal Muscle, Myocyte
Chapter 12 All Lectures
Muscle Physiology
Lecture 1
Chapter 12, Lecture 1
Muscle Physiology
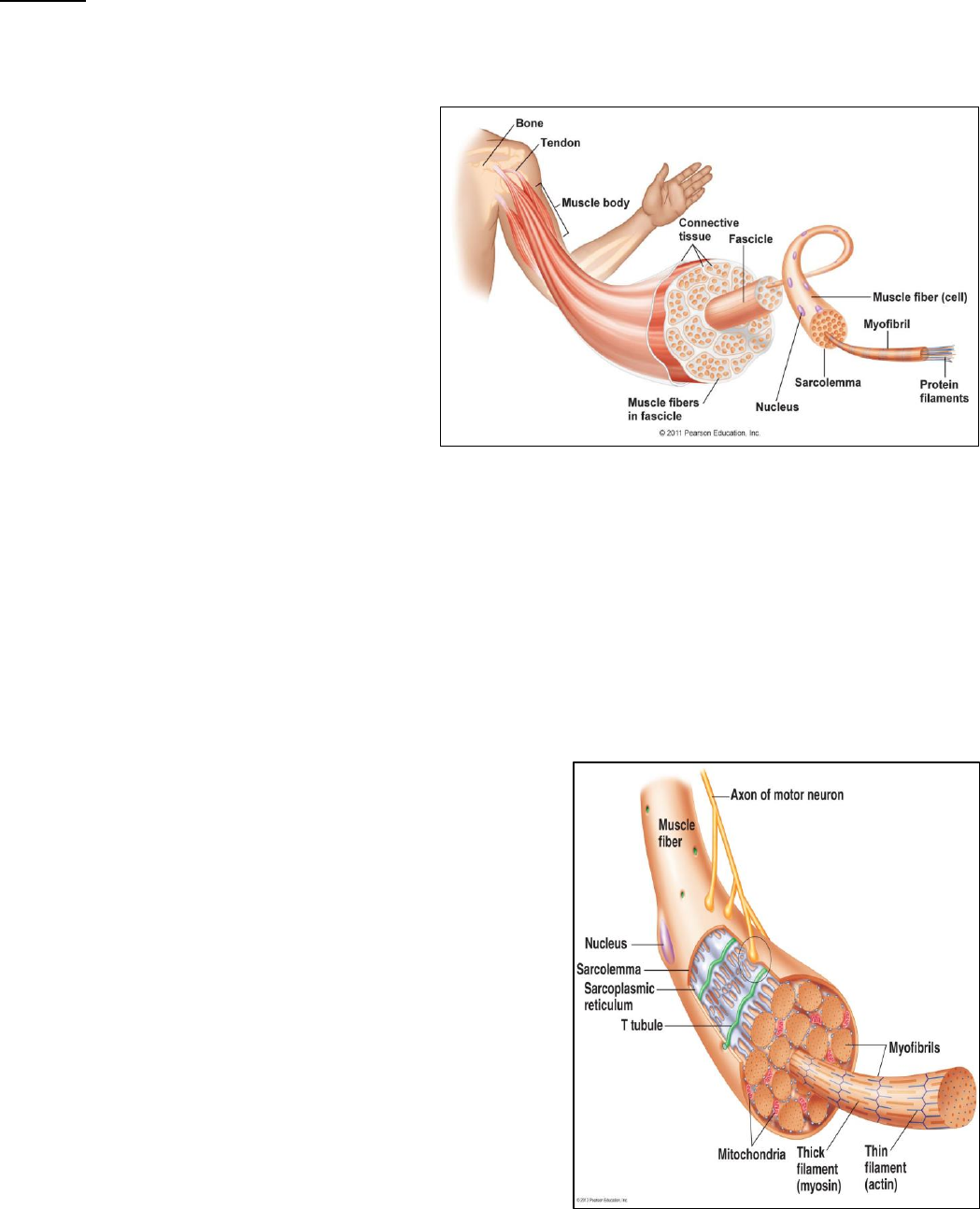
• Skeletal muscle structure
o CT covering the outside of the
muscle = epimysium
o Fascicles = bunches within the
muscle
▪ Paramysium =
surrounds the fascicles
and fills in gaps
between fascicle
o Myocyte = individual skeletal
muscle cell
▪ Extremely long—span
the length of the muscle
▪ Need multiple nuclei
▪ Endomysium =
surrounds the individual
myocyte
▪ Contains normal organelles and myofibrils—contractile organelle
• Myofibrils push other organelles to the edges of the cell
o Nuclei are on the outside of the cell
• Myofibrils are composed of protein filaments
o Actin
o Myosin
o Have dark and light stripes—causes striated appearance
o Blood vessels and nerves throughout each layer of cells
o Sarc = flesh
o Sarcolemma = plasma membrane of skeletal muscle cell
o Sarcoplasm = cytoplasm inside a skeletal muscle cell
• Myofibrils = contractile organelle that runs the length
of the myocyte
o Overlapping arrangement of myosin and actin
▪ Thick filament = myosin
▪ Thin filament = actin
• Actin fills up most of the
structure
o Lots of mitochondria in myocyte
o T (transverse) tubule
▪ Around and between the myofibrils
▪ Invaginations of the sarcolemma into
the cell’s interior
o Sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) = type of ER in
skeletal muscles
find more resources at oneclass.com
find more resources at oneclass.com
▪ Surrounds each myofibril and comes in contact with T tubule
▪ Membranous organelle that surrounds the myofibrils
▪ Terminal cisternae = enlarged regions of the SR that make contact with
the T tubules
• Have 2 of them around a T tuble
• Terminal cisternae + T tubule = triad
o 2 triads for every sarcomere
▪ Function = store Ca
• Normally, the muscle cell does not contain much Ca
• Motor neurons travel down sarcolemma as T tubule to trigger
release of Ca
• Ca is dumped into everything in the myofibrils
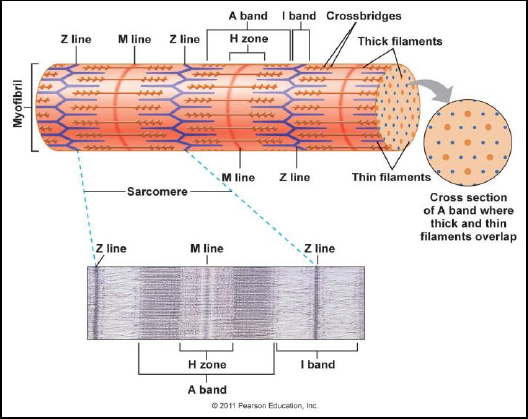
o Sarcomere = functional unit of
organization of the myofibril and its
overlapping arrangement of actin
and myosin to give the striated
appearance
▪ Myofibril is formed by a
series of sarcomeres
▪ Fills up the cells from end to
end
▪ Goes from one Z disk to
another Z disk (Z disk = Z
line)
▪ Myosin runs all the way
across the sarcomere
▪ Actin has space in between
them—allows for contraction
▪ M line
• Running down the middle of the sarcomere
• Midline
• Ends of myosin thick filaments are holding onto each other
o Heads on myosin are pointing towards the Z disk
▪ A band = length of myosin
• Darker than the I band
• Actin myofilaments overlapping the myosin give the dark color
▪ I band = only have actin myofilaments—mysosin myofilaments do not
encroach
• Surrounds either side of the Z disk
• Lighter than the A band
▪ H zone = bare zone
• No myosin heads—cannot attach to the actin myofilaments
• No actin myofilaments in a relaxed muscle
▪ 6 actin surround each myosin
• Contractile proteins
o Thin myofilaments = actin
▪ Double helix structure
▪ Each strand is made of individual protein structures = G actin
• Have specific spots on protein = myosin binding site
• Every G actin has a myosin binding site on it
find more resources at oneclass.com
find more resources at oneclass.com
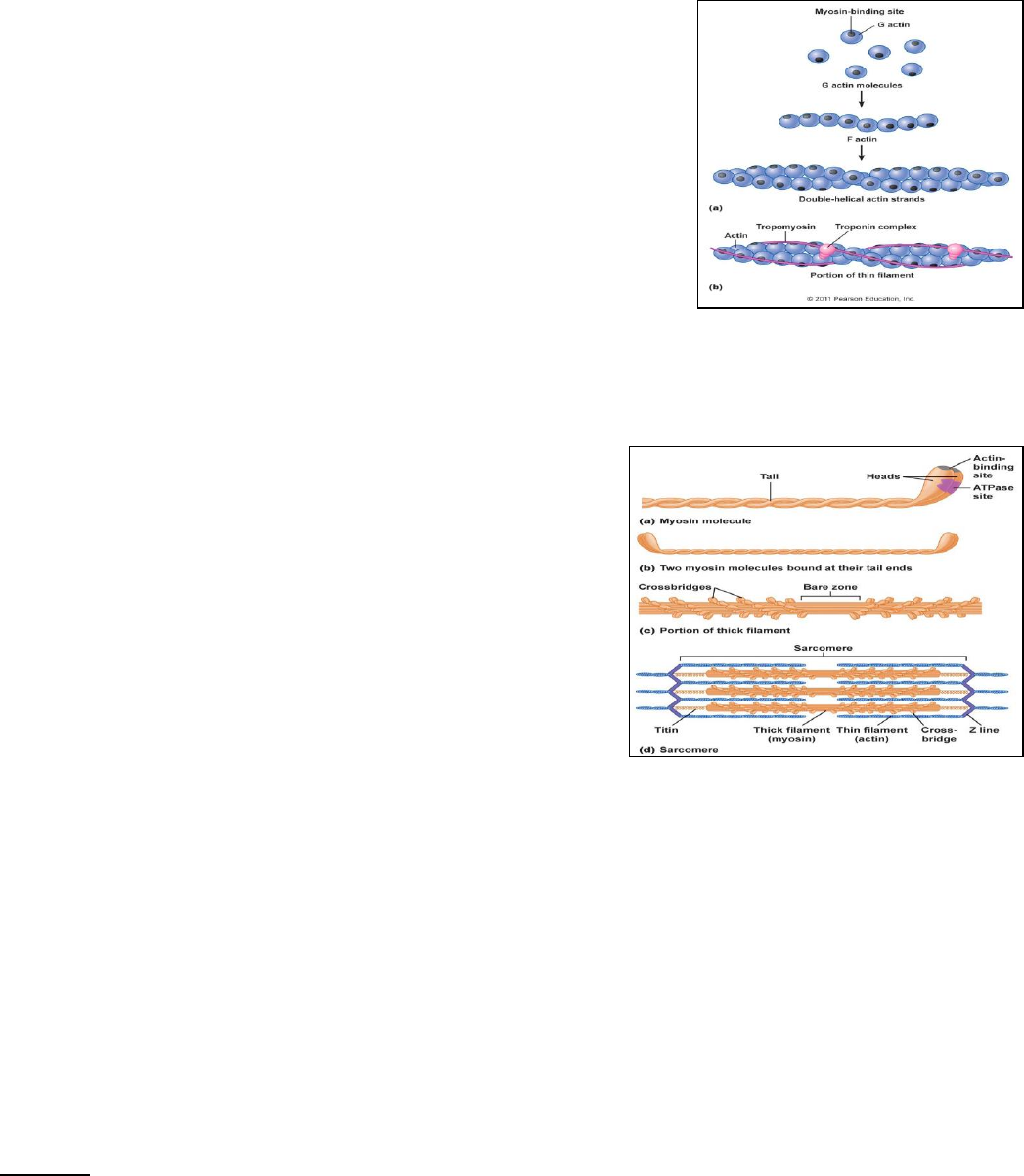
▪ Tropomyosin
• Long strand (longer name)
• Covers myosin binding site
o When myosin binding site is
exoposed—will ALWAYS have
contraction
• Troponin is associated with this protein
o Troponin
▪ Ca binds to a protein in
the troponin complex
▪ Ca causes shape change
in troponin to roll the
tropomyosin off of the binding site
▪ Binding site is exposed so contraction can occur
▪ Attached at the Z disks
o Thick myofilaments = myosin
▪ Has fibrous and globular structure
• Fibrous portion = double helix tail
o Bare zone = where the
tails all come together
• Globular structure = glob tail that
the tail terminates at
o Heads are evenly
distributed throughout the
filament
o Actin-binding site
▪ Connects to G
actin on the actin
myofilaments
o ATPase site
▪ Enzyme on the head of myosin that functions to
hydrolyze ATP (dephosphorylate)
• Releases energy to use in contractile
process
▪ Stretched across the middle of the sarcomere
▪ Actin and myosin overlap in outer region of A band
▪ Titin
• Coil at the end of myosin
• Attaches the myosin to the Z disk
• Very large protein
• Highly elastic
o Allows muscle to stretch
o Allows muscle to recoil—go back to resting length without
damage
Lecture 2
Chapter 12, Lecture 2
Muscle Physiology
• Sliding-filament mechanism of contraction
find more resources at oneclass.com
find more resources at oneclass.com
