AGEC 2003 Chapter : Chapter 2 Lecture

7.10 Chapter Exercises 365
As for most statistical analyses, it is important to verify that the assumptions under-
lying the model are fulfilled. Of special importance are the assumptions of proper
model specification, homogeneous variance, and lack of outliers. In regression, this
can be accomplished by examining the residuals. Additional methods are provided
in Chapter 8.
7.10 CHAPTER EXERCISES
Concept Questions
For the following true/false statements regarding concepts and uses of simple linear
regression analysis, indicate whether the statement is true or false and specify what
will correct a false statement.
1. The need for a nonlinear regression can only be determined by
a lack of fit test.
2. The correlation coefficient indicates the change in yassociated
with a unit change in x.
3. To conduct a valid regression analysis, both xand ymust be
approximately normally distributed.
4. Rejecting the null hypothesis of no linear regression implies
that changes in xcause changes in y.
5. In linear regression we may extrapolate without danger.
6. If xand yare uncorrelated in the population, the expected value
of the estimated linear regression coefficient (slope) is zero.
7. If the true regression of yon xis curvilinear, a linear regression
still provides a good approximation to that relationship.
8. The xvalues must be randomly selected in order to use a
regression analysis.
9. The error or residual sum of squares is the numerator portion
of the formula for the variance of yabout the regression line.
10. The term ˆµy|xserves as the point estimate for estimating both
the mean and individual prediction of yfor a given x.
11. Useful prediction intervals for ycan be obtained from a regres-
sion analysis.
12. In a regression analysis, the estimated mean of the distribution
of yis the sample mean (¯
y).
13. All data points will fit the regression line exactly if the sample
correlation is either +1or −1.
14. The prediction interval for yis widest when xis at its mean.

366 CHAPTER 7: Linear Regression
15. The standard error of the estimated slope of a regression model
becomes larger as the dispersion of xincreases.
16. When there is no linear relationship between two variables, a
horizontal regression line best describes the relationship.
17. If r>0, then as xincreases, ytends to increase.
18. If a regression line is computed for data where xranges from 0
to 30, you may safely predict yfor x=40.
19. The correlation coefficient can be used to detect any relation-
ship between two variables.
20. If ris very close to either +1or −1, then there is a cause and
effect relationship between xand y.
Exercises
Note: Exercises 1 through 5 contain very few observations and are suitable for manual
computation, which can be checked against computer outputs. The remainder of the
problems are best performed by a computer.
1. The data of Table 7.14 represent the thickness of oxidation on a metal alloy for
different settings of temperature in a curing oven. The values of temperature
have been coded so that zero is the “normal” temperature, which makes manual
computation easier.
(a) Calculate the estimated regression line to predict oxidation based on tem-
perature. Explain the meaning of the coefficients and the variance of
residuals.
(b) Calculate the estimated oxidation thickness for each of the temperatures in
the experiment.
(c) Calculate the residuals and make a residual plot. Discuss the distribution of
residuals.
(d) Test the hypothesis that β1=0, using both the analysis of variance and t
tests.
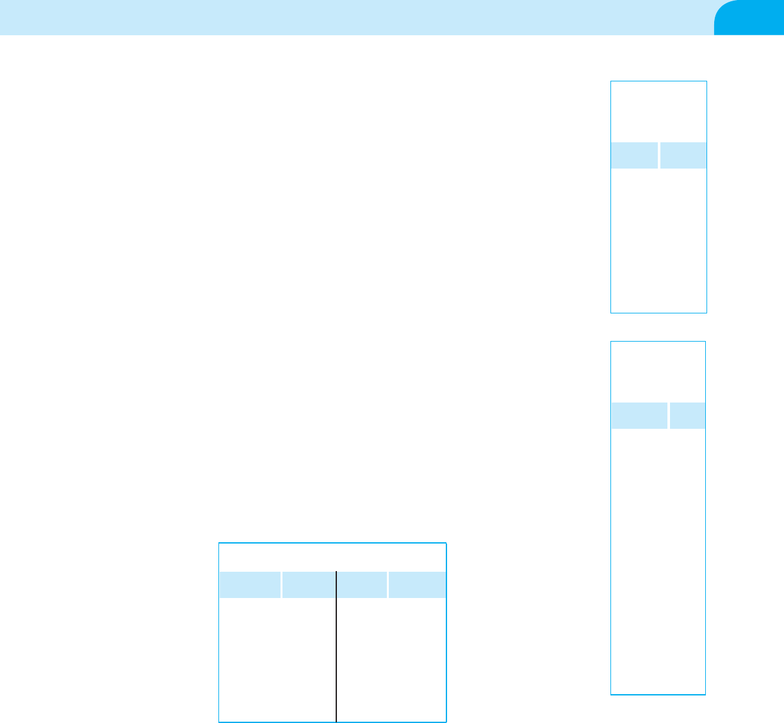
Table 7.14 Data for
Exercise 1
Oxidation Temperature
4−2
3−1
30
21
22
7.10 Chapter Exercises 367
2. The data of Table 7.15 show the sugar content of a fruit (Sugar) for different
numbers of days after picking (Days).
(a) Obtain the estimated regression line to predict sugar content based on the
number of days after picking.
(b) Calculate and plot the residuals against days. Do the residuals suggest a
fault in the model?
Table 7.15
Data for
Exercise 2
Days Sugar
07.9
1 12.0
39.5
4 11.3
5 11.8
6 11.3
74.2
80.4
Table 7.16
Data for
Exercise 3
Midterm Final
82 76
73 83
95 89
66 76
84 79
89 73
51 62
82 89
75 77
90 85
60 48
81 69
34 51
49 25
87 74
3. The grades for 15 students on midterm and final examinations in an English
course are given in Table 7.16.
(a) Obtain the least-squares regression to predict the score on the final exam-
ination from the midterm examination score. Test for significance of the
regression and interpret the results.
(b) It is suggested that if the regression is significant, there is no need to have
a final examination. Comment. (Hint: Compute one or two 95% prediction
intervals.)
(c) Plot the estimated line and the actual data points. Comment on these results.
(d) Predict the final score for a student who made a score of 82 on the midterm.
Check this calculation with the plot made in part (c).
(e) Compute rand r2and compare results with the partitioning of sums of
squares in part (a).
4. Given the values in Table 7.17 for the independent variable xand dependent
variable y:
(a) Perform the linear regression of yon x.TestH0:β1=0.
(b) Note that half of the observations have x=−1and the rest have x=1.
Does this suggest an alternate analysis? If so, perform such an analysis and
compare results with those of part (a).
Table 7.17 Data for Exercise 4
x y x y
−171 5
−131 8
−16112
−161 8
−171 6
−141 8
−121 9
5. It is generally believed that taller persons make better basketball players because
they are better able to put the ball into the basket. Table 7.18 lists the heights
of a sample of 25 nonbasketball athletes and the number of successful baskets
made in a 60-s time period.
(a) Perform a regression relating Goals to Height to ascertain whether there is
such a relationship and, if there is, estimate the nature of that relationship.
(b) Estimate the number of goals to be made by an athlete who is 60 in. tall.
How much confidence can be assigned to that estimate?
Document Summary
As for most statistical analyses, it is important to verify that the assumptions under- lying the model are ful lled. Of special importance are the assumptions of proper model speci cation, homogeneous variance, and lack of outliers. In regression, this can be accomplished by examining the residuals. For the following true/false statements regarding concepts and uses of simple linear regression analysis, indicate whether the statement is true or false and specify what will correct a false statement. The need for a nonlinear regression can only be determined by. The correlation coef cient indicates the change in y associated with a unit change in x. approximately normally distributed. To conduct a valid regression analysis, both x and y must be that changes in x cause changes in y. Rejecting the null hypothesis of no linear regression implies. In linear regression we may extrapolate without danger. of the estimated linear regression coef cient (slope) is zero.

