HUBS1107 Lecture Notes - Lecture 1: Orbicularis Oculi Muscle, Facial Muscles, Procerus Muscle
Identify the location of the parotid gland
•
Describe the general arrangement of the muscles of facial expression
•
Describe and identify the major muscles located around the eyes, the nose and the
mouth - those that close and open these openings
•
Describe which muscles of facial expression produce major expression in our face (frown,
smile, grimace, sucking, closing of eye etc)
•
Describe the sensory innervation of the face
•
Describe the motor innervation of the muscles of facial expression
•
Describe the course of the facial nerve and the potential for injury
•
Lecture and Lab Objectives:
Face provides individual identity
→
Anatomical variation contributes to human differences
→
Function of facial muscles critical to communication both in forming words
→
and in facial expression
Our facial expressions tell a lot about us
→
Facial muscles act as sphincters and dilators of openings of digestive,
→
respiratory and visual systems
Assist in keeping food between teeth to allow mastication
→
Facial Expression
Note the pattern present in the arrangement of facial muscles
→
Sphincters and muscles that oppose this - dilate or open
→
Facial muscles are subcutaneous
→
Most have a skeletal origin and a cutaneous insertion (under the skin)
→
The face lacks deep fascia present elsewhere in the body
→
Deep fascia is a connective tissue that wraps around muscles binding them into
compartments
→
This does not happen in the face
→
Why is there a difference?
→
Are also present around the ear and in the neck
○
Facial muscles control movement of the scalp by way of a 2 bellied muscle
(occipitofrontalis)
→
Arrangement of Facial Muscles
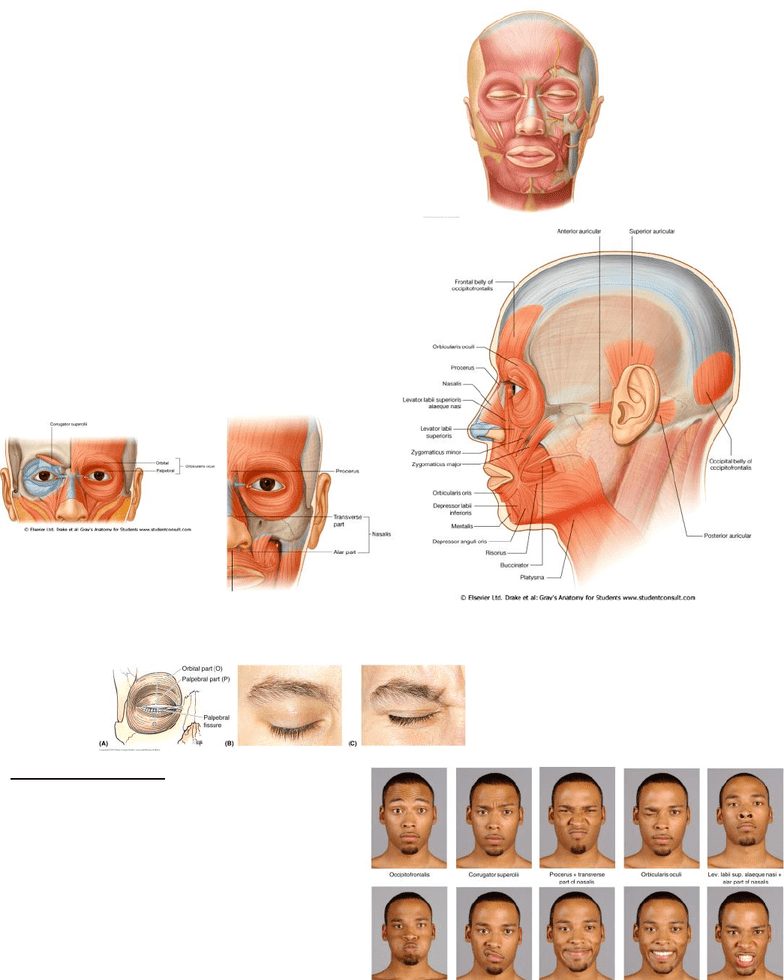
Note the sphincter like arrangement of orbicularis oculi and nasalis
→
Note the muscles that assist with frowning (procerus and corrigator supercilli)
→
Orbicularis oculi: this muscle has two parts, which are the orbital and palpebral (eyelid)
components
→
Frontalis is an elevator of the eyebrow as in the
○
expression of surprise or movement of eyebrow
(up and down motion)
Epicranius or Occipitofrontalis = surprise
→
Orbicularis oculi = closing eye and eye lid
→
Pulls the eyebrows together as in frowning
○
Corrugator supercilli = frowning
→
expression of surprise
Frontalis =an elevator of the eyebrow as in the
→
Procerus = depresses medial eyebrow, wrinkles nose in distain
→
Levator labii superioris alaeque nasi = raising upper
→
lip and dilating nostrils in a sneer
Nasalis = flaring of nostrils
→
Main muscles and their actions
Muscles of Facial Expression
Wednesday, 2 August 2017
8:29 PM
HUBS1107 Page 2.1
Document Summary
Describe the general arrangement of the muscles of facial expression. Describe and identify the major muscles located around the eyes, the nose and the mouth - those that close and open these openings. Describe which muscles of facial expression produce major expression in our face (frown, smile, grimace, sucking, closing of eye etc) Describe the motor innervation of the muscles of facial expression. Describe the course of the facial nerve and the potential for injury. Function of facial muscles critical to communication both in forming words and in facial expression. Our facial expressions tell a lot about us. Facial muscles act as sphincters and dilators of openings of digestive, respiratory and visual systems. Assist in keeping food between teeth to allow mastication. Note the pattern present in the arrangement of facial muscles. Sphincters and muscles that oppose this - dilate or open. Most have a skeletal origin and a cutaneous insertion (under the skin)

