ECON101 Lecture Notes - Lecture 15: Indifference Curve, Equilibrium Point, Substitute Good
ECON101 verified notes
15/25View all
Document Summary
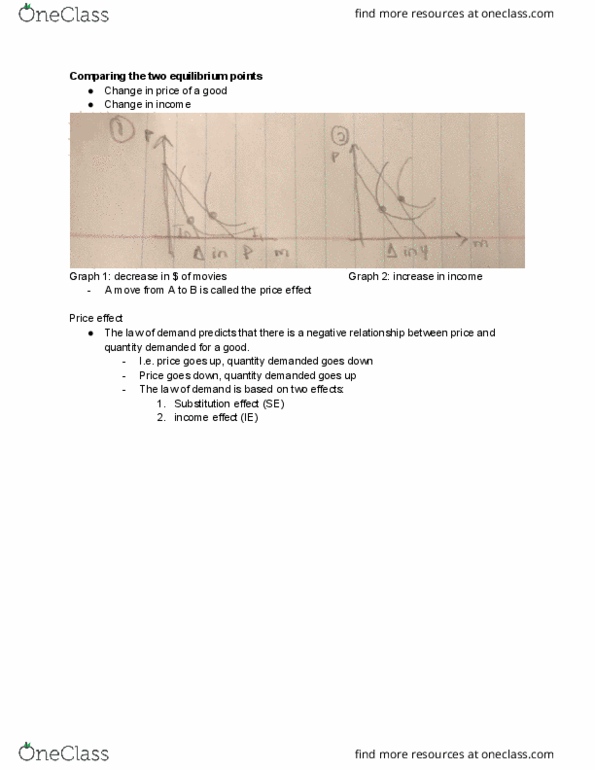
Chapter 8, the theory of consumer choice (a recap): Hypothetical consumer: lisa (rational and self interested) Two prices: pm and pp income : y. S. t. s = pmqm + ppqp = y. Pick the bundle from affordable set that maximizes combined total utility or where marginal utility per $ spent on both goods are equal. Mum divided by pm = mup divided by pp. A rational consumer chooses between bundles of goods by ranking them according to pleasure/satisfaction he/she gets from consuming these bundles. Set of all bundles of goods that a consumer views as being equally desirable. All combinations of the goods that provide the consumer with the same level of utility or satisfaction. Marginal rate of substitution (mrs) is what the diagram above the preference map is called. The rate at which consumer is willing to trade one good for another. Mrs decrease when there"s more of one good. Higher indifference curve is always preferred to lower indifference curves.