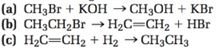CHM 2123 Lecture Notes - Lecture 3: Steric Effects, Potassium Bromide, Weak Base
Document Summary
The purpose of this lab was to analyze competing reaction pathways and the conditions that can be altered to favour one pathway over another. An alkyl halide can go through elimination and substitution reactions. In an e1 reaction, the halide leaves as the leaving group first, which is the rate determining step of the reaction. The weak base (usually is the solvent) then deprotonates a proton close to the carbon to form a double bond. E1 reactions favour secondary or tertiary carbocations in the intermediate state. It does not happen when the carbon is primary. In an e2 reaction, the strong base attacks a proton close to the carbon and the electrons move to make a double bond between the and adjacent carbon. The e2 reactions favour the most substituted alkene product if the base is small they favour the least substituted alkene if the base is bulky. In this reaction, e2 is favoured because of the strong base.