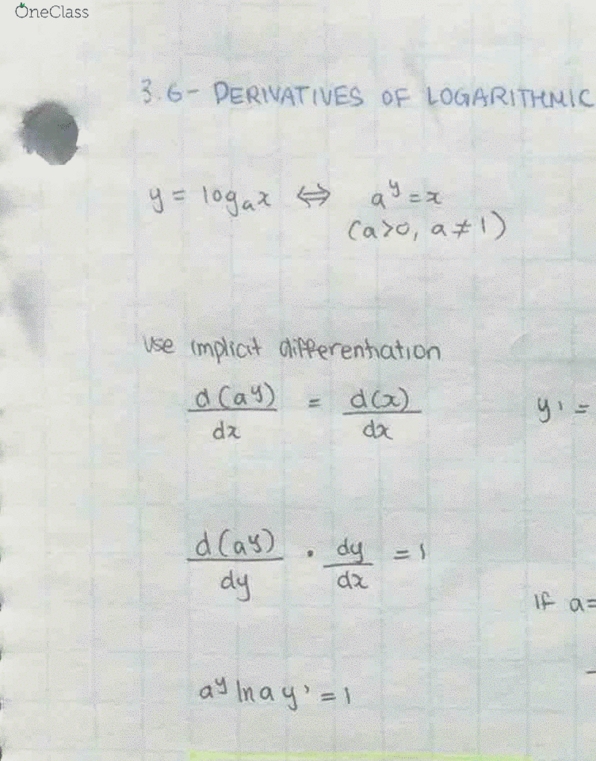Calculus 1000A/B Lecture Notes - Lecture 29: Inflection Point, Maxima And Minima, Inflection
CALC 1000A/B verified notes
29/49View all

Calculus 1000A – Lecture 29 – Section 4.3 Increasing and Decreasing Functions Continued
Prof: N. Kiriushcheva
01/1012018
Recall: The Concavity Test
a) If for all ‘x’ in an interval then the graph is concave upward on the interval
b) If for all ‘x’ in an interval then the graph is concave downward on the interval.
There is another element in concavity that can be a useful definition, which can contribute to our overall
analysis of functions:
The Second Derivative Test
Suppose that f’’ is continuous near ‘c’:
a) If and , then f has a local minimum at ‘c’
b) If and , then f has a local maximum at ‘c’
Example 1:
• Look at the first derivative: y’= 2x → thus there is a critical point y’(0)= 0
• Look at the second derivative: y’’= 2 → since this number is positive, the function has a local minimum
at f(0)= 0
o We can note that the concavity is concave upward for the entirety of the function-
Example 2:
• Look at the first derivative: y’= 3x2 → thus there is a critical point y’(0)= 0
• Look at the second derivative: y’’= 6x → when and when
o Since the sign of the second derivative changes, we know that the concavity changes
o Therefore, the point (0, 0) is an inflection point
Example 3:
• Looking at the graph above, we can determine that (0, 0) is a critical point, as f’(0) does not exist – recall
that derivatives do not exist at sharp edges
• This critical point is also an absolute minimum
Inflection Point:
A point ‘p’ on a curve y= f(x) is called an inflection point if a function is continuous there and the curve
changes from concave upward to concave downward, or from concave downward to concave upward.
Document Summary
Calculus 1000a lecture 29 section 4. 3 increasing and decreasing functions continued. Recall: the concavity test: if >(cid:882) for all (cid:858)(cid:454)(cid:859) in an interval then the graph is concave upward on the interval, if (cid:882), then f has a local minimum at (cid:858)c(cid:859, if (cid:4666)(cid:4667)=(cid:882) and (cid:4666)(cid:4667)