PHYS 1110 Lecture 1: 02_Motion1D
Document Summary
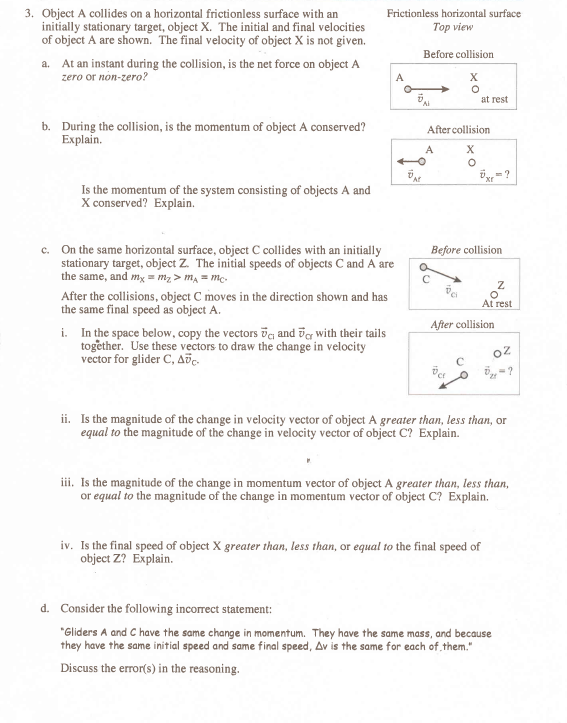
In this chapter, we study speed, velocity, and acceleration for motion in one-dimension. Things that have both a magnitude and a direction are called vectors. For 1d motion (motion along a straight line, like on an air track), we can represent the direction of motion with a +/ sign. = going left always! va = 10 m/s vb = +10 m/s. Objects a and b have the same speed s = |v| = +10 m/s, but they have different velocities. If the velocity of an object varies over time, then we must distinguish between the average velocity during a time interval and the instantaneous velocity at a particular time. X = xfinal xinitial = displacement (can be + or ) University of colorado at boulder distance traveleddspeed, s=,units are m/s or mph or km/hr ortime elapsedt change in positionxaverage velocity = v change in timet fi21fi21xxxxxvttttt .