ECON 2002.01 Lecture Notes - Lecture 16: Nominal Rigidity, Aggregate Demand, Exchange Rate
ECON 2002.01 verified notes
16/29View all
Document Summary
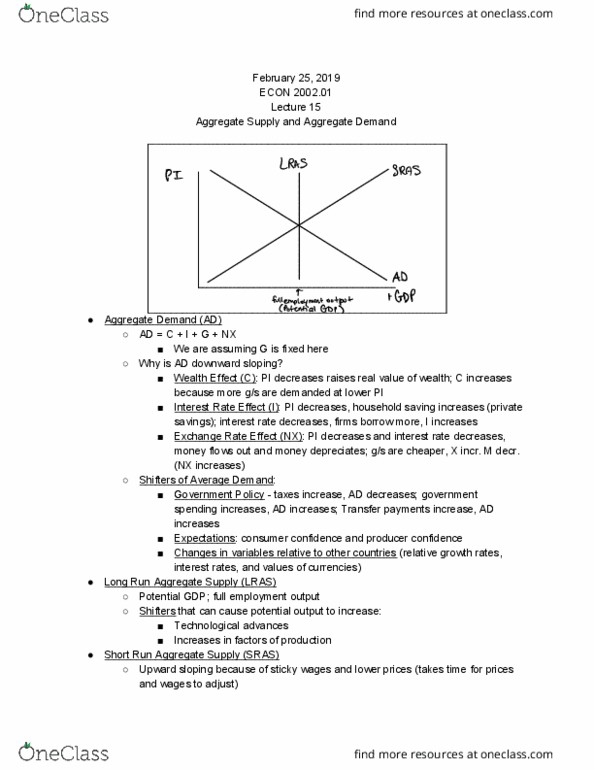
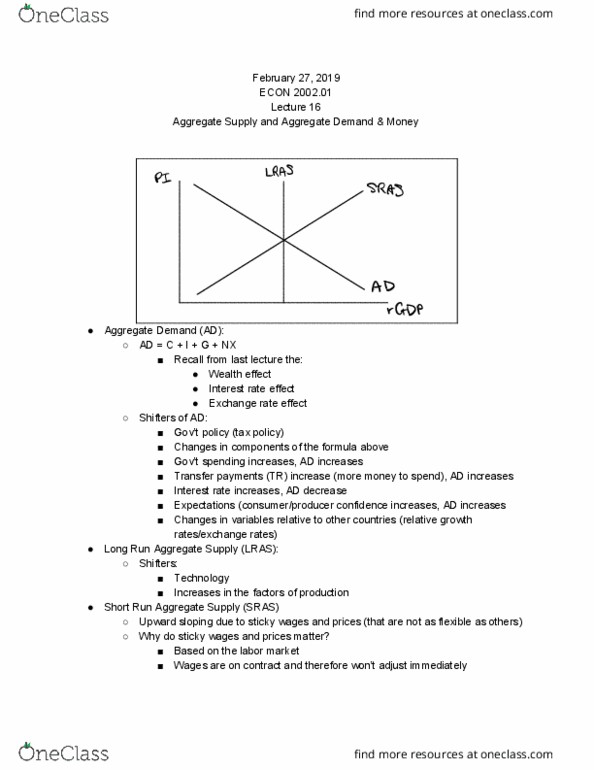
Changes in components of the formula above. Transfer payments (tr) increase (more money to spend), ad increases. Changes in variables relative to other countries (relative growth rates/exchange rates) Upward sloping due to sticky wages and prices (that are not as flexible as others) Wages are on contract and therefore won"t adjust immediately. Labor becomes cheaper, firms hire more, output increases. Firms build expected inflation into contracts, price of labor increases. Discourages production because profit (represented by symbol for pi) Workers accept lower wages, firms will accept lower prices - sras shifts. 3 scenarios - recession, expansion, supply shock. Ad decreases (rgdp drops below the potential gdp) Creates a recessionary gap which = potential gdp - actual gdp. Sras increases, then rgdp increases and pi and ur decrease. Producer confidence increases, ad decreases (rgdp increases, pi increases, ur decreases) Concerning because it creates an inflationary gap. Sras decreases, rgdp returns to potential, pi and ur increases inflationarygap vgdp.