ECN 001A Lecture Notes - Lecture 3: Comparative Advantage, Progressive Country, Opportunity Cost
ECN 001A verified notes
3/10View all
Document Summary
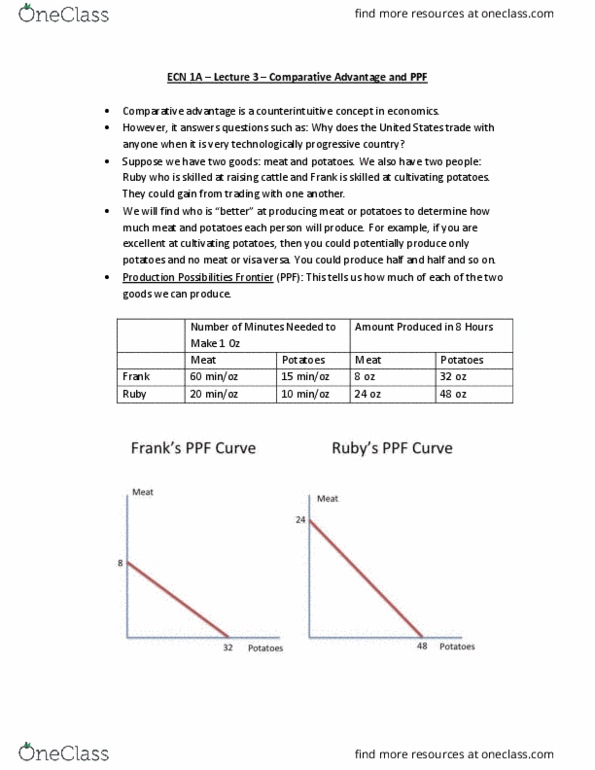
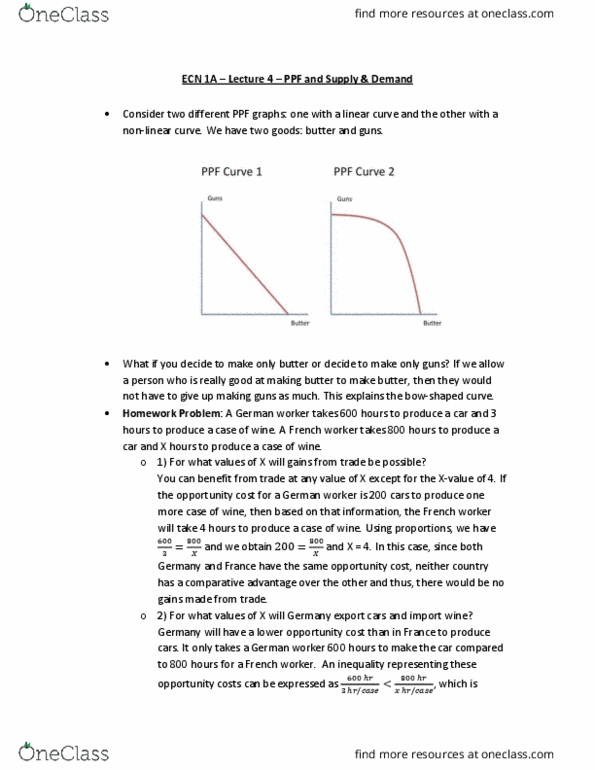
Ruby who is skilled at raising cattle and frank is skilled at cultivating potatoes. They could gain from trading with one another: we (cid:449)ill fi(cid:374)d (cid:449)ho is (cid:862)(cid:271)etter(cid:863) at produ(cid:272)i(cid:374)g (cid:373)eat or potatoes to determine how much meat and potatoes each person will produce. For example, if you are excellent at cultivating potatoes, then you could potentially produce only potatoes and no meat or visa versa. You could produce half and half and so on: production possibilities frontier (ppf): this tells us how much of each of the two goods we can produce. 48 oz: absolute advantage: the ability to produce a good with fewer inputs. This is because of comparative advantage: comparative advantage: this concept takes into consideration opportunity costs. I(cid:374) this s(cid:272)e(cid:374)ario, (cid:862)how much potatoes do you have to gi(cid:448)e up for a(cid:374) oz of (cid:373)eat? (cid:863: to produce 1 more ounce of meat, frank needs to give up 4 ounces of potatoes.