MAT 21D Lecture Notes - Lecture 1: Multiple Integral, Divergence Theorem, Riemann Sum
MAT 21D verified notes
1/32View all
Document Summary
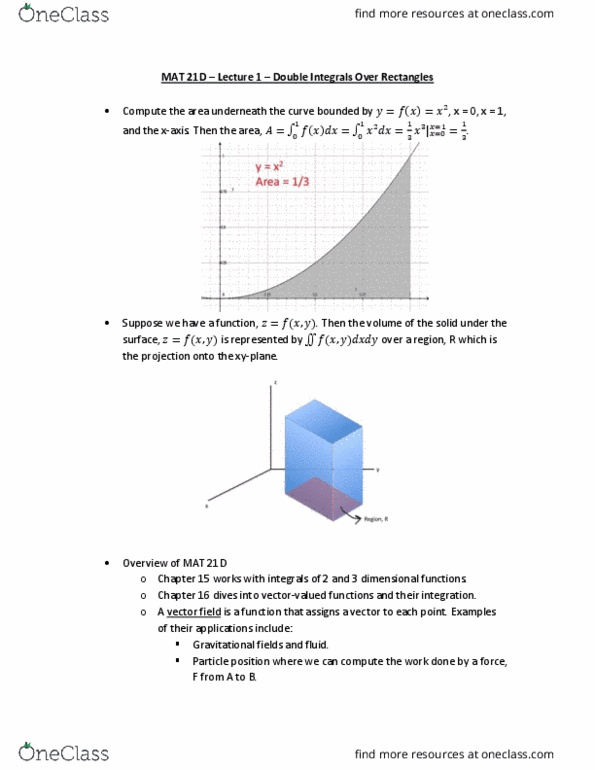
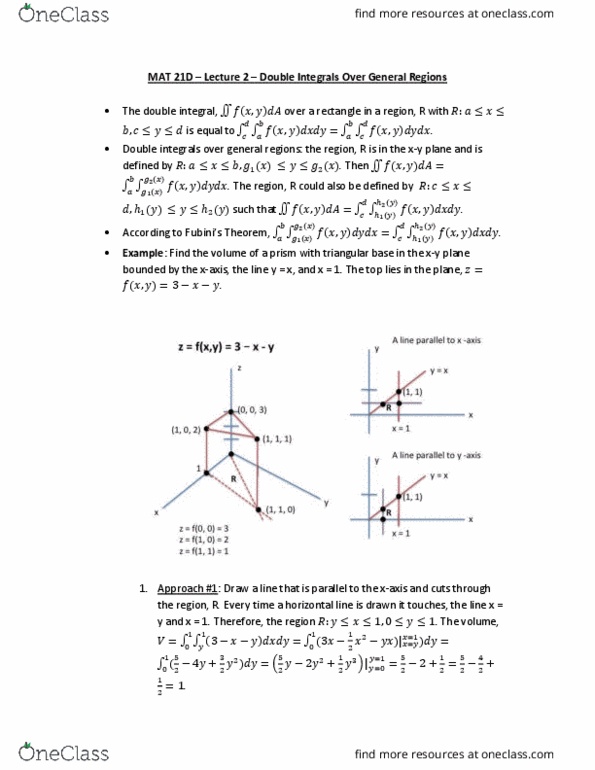
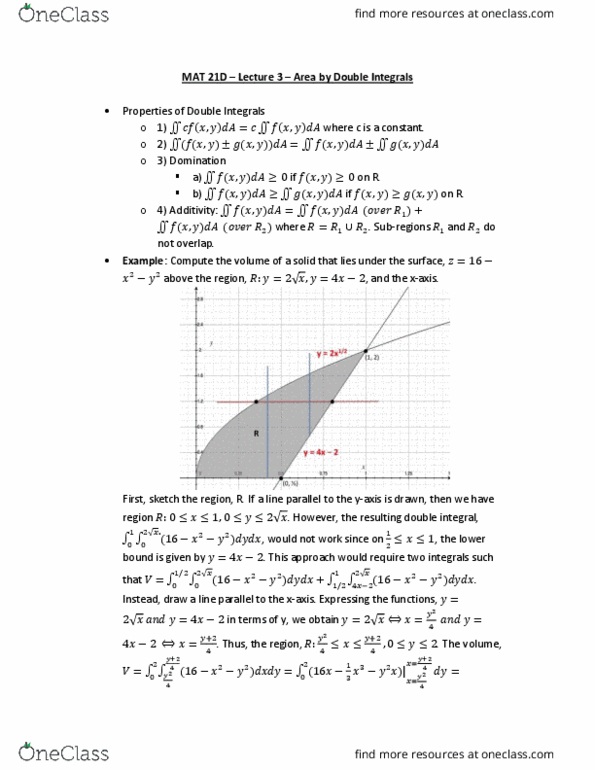
Mat 21d lecture 1 double integrals over rectangles: compute the area underneath the curve bounded by (cid:1877)=(cid:4666)(cid:1876)(cid:4667)=(cid:1876)(cid:2870), x = 0, x = 1, and the x-axis. =(cid:1516) (cid:1876)(cid:2870)(cid:1856)(cid:1876) (cid:2869)(cid:2868) (cid:2869)(cid:2868: suppose we have a function, (cid:1878)=(cid:4666)(cid:1876),(cid:1877)(cid:4667). Examples of their applications include: gravitational fields and fluid, particle position where we can compute the work done by a force, F from a to b: operators from physics: gradient, divergence (divergence, to integrate a function with one variable, we use a riemann sum to represent. If this limit exists, then the theore(cid:373)(cid:895), a(cid:374)d (cid:272)url (cid:894)stoke"s theore(cid:373)(cid:895): vectors contain both magnitude and direction. area underneath the curve, =lim integral of (cid:4666)(cid:1876)(cid:4667) exists. =(cid:2869) (cid:4666)(cid:1876)(cid:4667) (cid:1876: suppose we have a function of two variables, (cid:4666)(cid:1876),(cid:1877)(cid:4667) with :(cid:1853) (cid:1876) (cid:1854),(cid:1855) (cid:1877) (cid:1856). Then a riemann sum can be used to calculate the volume of a solid, = lim .