ECON 1 Lecture Notes - Lecture 6: Marginal Cost, Competitive Equilibrium, Economic Equilibrium
ECON 1 verified notes
6/31View all
Document Summary
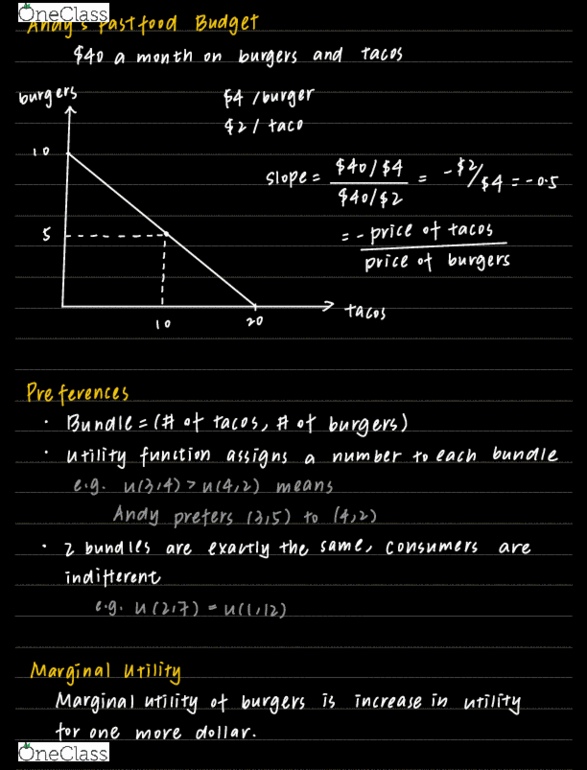
To maximize profit, create supply/demand graph and stop at the equilibrium. To maximize profitable trades, offshift by one to great max trades (equitable efficiency) Most equitable may be more costly than most profitable! Suppose pairs split profit when maximizing sales. Suppose competitive equilibrium price of 4 when maximizing profits. Competitive equilibrium is efficient, but it may not be equitable. Special characteristics of our experiments (assumptions in model) Can buy any amount of a good. Discrete units for some goods and services: pencils, haircuts. Continuous units for others: gasoline, time of econ 1 tutor. Can buy as often as we want. Quantity per period buyers willing to buy for each possible price. Quantity per period sellers willing to sell for each possible price. Price at which quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. Have no/minor control over price of good sold. Which quantity maximizes profits? (where revenue > cost) Total cost = fixed cost + variable cost.