ECON 2 Lecture Notes - Lecture 18: Real Interest Rate, Comparative Advantage, Autarky
ECON 2 verified notes
18/19View all

ECON 2 Lecture 18: Trade and Exchange Rates
The Terms of Trade
● Benefits of international trade come from comparative advantages and specialization
○ Comparative Advantage: one party can produce a product at a lower opportunity
cost than the other party
○ Increased returns of scale allow for greater specialization and reduced prices for
goods
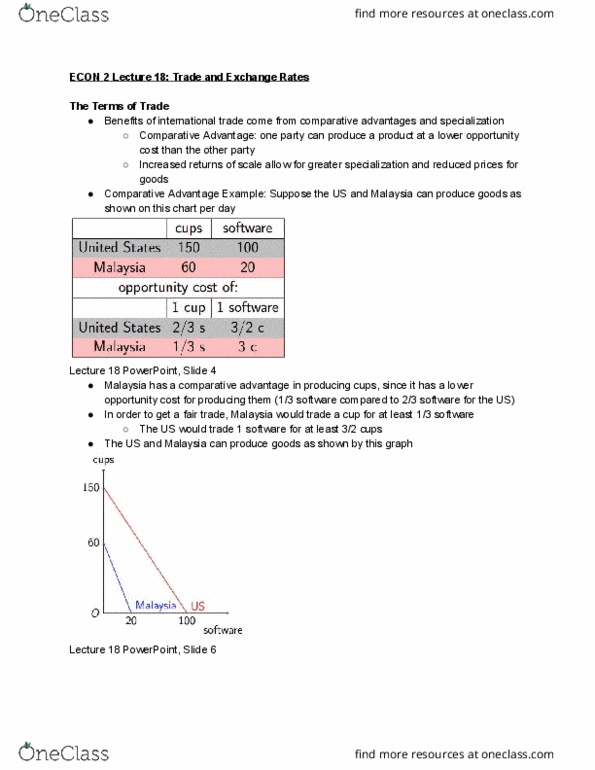
● Comparative Advantage Example: Suppose the US and Malaysia can produce goods as
shown on this chart per day
Lecture 18 PowerPoint, Slide 4
● Malaysia has a comparative advantage in producing cups, since it has a lower
opportunity cost for producing them (1/3 software compared to 2/3 software for the US)
● In order to get a fair trade, Malaysia would trade a cup for at least 1/3 software
○ The US would trade 1 software for at least 3/2 cups
● The US and Malaysia can produce goods as shown by this graph
Lecture 18 PowerPoint, Slide 6

● Suppose the world market price for 1 cup was 1/2 software. If Malaysia only produced
cups, they could trade whichever cups they didn't need for software and end up with
more goods than if they didn't trade anything.
Lecture 18 PowerPoint, Slide 11
Microeconomics of Tariffs
● Tariffs: taxes on imported goods
● Here is what the supply and demand curve looks like in a closed economy (no
exports/imports)
○ CS: Consumer Surplus; how much value the consumers gain
○ PS: Producer Surplus; how much value the producers profit
● Here is what the supply and demand curve looks like in a open economy
(exports/imports)
○ Pw: The world market's price
Document Summary
Econ 2 lecture 18: trade and exchange rates. Benefits of international trade come from comparative advantages and specialization. Comparative advantage: one party can produce a product at a lower opportunity cost than the other party. Increased returns of scale allow for greater specialization and reduced prices for goods. Comparative advantage example: suppose the us and malaysia can produce goods as shown on this chart per day. Malaysia has a comparative advantage in producing cups, since it has a lower opportunity cost for producing them (1/3 software compared to 2/3 software for the us) In order to get a fair trade, malaysia would trade a cup for at least 1/3 software. The us would trade 1 software for at least 3/2 cups. The us and malaysia can produce goods as shown by this graph. Suppose the world market price for 1 cup was 1/2 software.