L24 Math 233 Lecture Notes - Lecture 27: Cartesian Coordinate System, Polar Coordinate System, Polar Regions Of Earth
L24 Math 233 verified notes
27/34View all
Document Summary
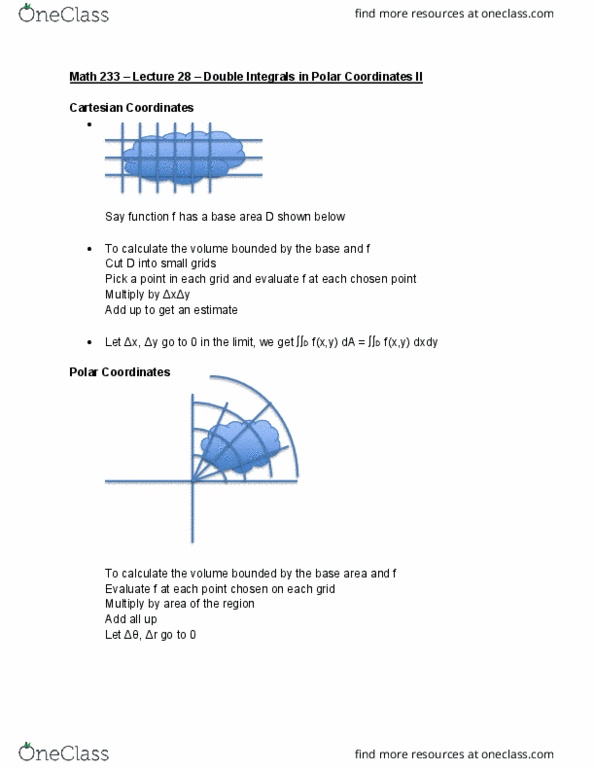
Math 233 lecture 27 double integrals in polar coordinates. D 0: d can be rectangles or areas bounded by two curves. Polar coordinates: we know in polar coordinates, x = rcos y = rsin r2 = x2+y2, polar rectangle is the region given by. Rpolar = {(r, )| a r b, : recall 0. R f(x,y) da = limit of f(rcos , rsin ) da as m and n approaches infinity. The idea here is that the definition of an integral is essentially calculating limit: however. For polar coordinates, da = r* r a r* b (normalization factor) If f is continuous on a polar rectangle rpolar given by 0 a r b, when 0 - 2 , then. R f(x,y) da = a f(rcos , rsin ) r drd . R (3x+4y2) da where r is the region in the upper half plane bounded by x2+y2=4 and x2+y2=1: define r.