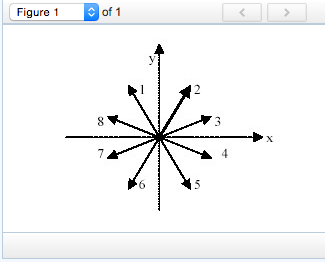
which of the vectors below best represents the direction of the impulse vector j⃗ ?
To learn about the impulse-momentum theorem and its applications in some common cases.
Using the concept of momentum, Newton's second law can be rewritten as
?F? =dp? dt, (1)
where ?F? is the net force F? net acting on the object, and dp? dt is the rate at which the object's momentum is changing.
If the object is observed during an interval of time between times t1 and t2, then integration of both sides of equation (1) gives
?t2t1?F? dt=?t2t1dp? dtdt. (2)
The right side of equation (2) is simply the change in the object's momentum p2??p1?. The left side is called the impulse of the net force and is denoted by J? . Then equation (2) can be rewritten as
J? =p2??p1?.
This equation is known as the impulse-momentum theorem. It states that the change in an object's momentum is equal to the impulse of the net force acting on the object. In the case of a constant net force F? net acting along the direction of motion, the impulse-momentum theorem can be written as
F(t2?t1)=mv2?mv1. (3)
Here F, v1, and v2 are the components of the corresponding vector quantities along the chosen coordinate axis. If the motion in question is two-dimensional, it is often useful to apply equation (3) to the x and y components of motion separately.
( The following questions will help you learn to apply the impulse-momentum theorem to the cases of constant and varying force acting along the direction of motion. First, let us consider a particle of mass m moving along the x-axis. The net force F is acting on the particle along the x-axis. F is a constant force.)
A) The particle starts from rest at t=0. What is the magnitude p of the momentum of the particle at time t? Assume that t>0.
B) The particle starts from rest at t=0. What is the magnitude v of the velocity of the particle at time t? Assume that t>0.
C) The particle has the momentum of magnitude p1 at a certain instant. What is p2, the magnitude of its momentum ?t seconds later?
D) The particle has the momentum of magnitude p1 at a certain instant. What is v2, the magnitude of its velocity ?t seconds later?
E) Find the magnitude of the impulse J delivered to the particle.
F) Which of the vectors below best represents the direction of the impulse vector J??
(Figure 1)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8





