COMMERCE 2OC3 Study Guide - Final Guide: Vendor-Managed Inventory, Longrun, Comparative Advantage
Supply Chain Management and Analytics
Supply chain management is the management of activities that procure materials and services, transform them in to
intermediate and final products, and deliver them in the distribution system
•
Supply chain analytics are set of quantitative tools used to manage, consisting of data analytics used to understand SC
patterns and performance optimization
•
Supply chain (SC) is a coordinated network of people, organizations, resources that move a product from suppliers to
consumers.
Supply Chain Strategy
Many suppliers strategy based on large supplier base that allows them to compete against one another - no desire to
create long-term relationships
•
Few suppliers strategy based on small supplier base and creating long-term relationships, reducing procurement costs
but increasing the cost of changing partners, and captive risk
•
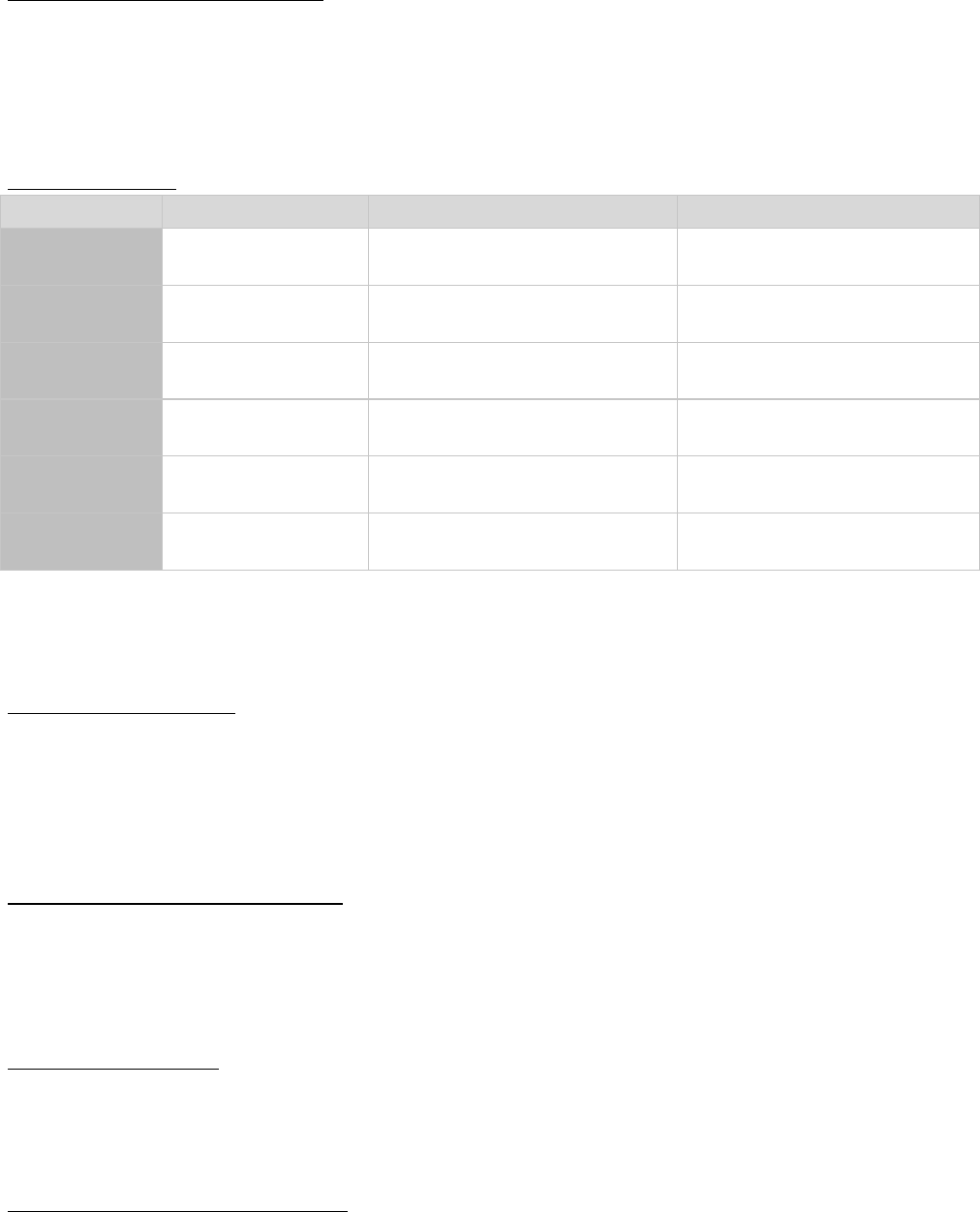
Low cost strategy
Response strategy
Differentiation strategy
Supplier goals
Demand at lowest cost
Quick response to changing demand
to minimize stockouts
Share market research, jointly
develop products
Decisions based on
Cost
Options that provide speed, capacity,
flexibility
Options that enhance product
development
Process
characteristics
High average utilization
Invest in excess capacity and flexible
processes
Use modular processes that lend
themselves to mass customization
Inventory
characteristics
Minimize inventory to
decreases costs
Develop responsive system with
buffer to ensure supply
Minimize inventory to avoid
obsolescence
Lead-time
characteristics
Shorten as long as costs
do not increase
Invest aggressively to reduce
production lead-time
Invest aggressively to reduce
development lead-time
Product-design
characteristics
Maximize performance
and minimize cost
Use product designs that lead to low
setup time and rapid production
Use modular design to postpone
product differentiation
Vertical integration forward and backward and joint ventures
•
Keiretsu networks consisting of company coalitions with share holding between members
•
Virtual companies provide services on-demand
•
Profit sharing where wholesaler and retailer set "integrated optimal retail price" and split profits
○
Revenue sharing where wholesaler and retailer set integrated optimal price and split revenue
○
Supply chain coordination contracts through profit sharing, revenue sharing, buy-back
•
Collaboration in Supply Chain
Reducing risk leads to mitigated disruption in: processes (material, quality, logistics), controls (management,
communications, designs, logistics scheduling), environment (duties, tariffs, security, natural disaster, currency
fluctuations, political issues)
•
Opportunity for personal, SC standard, and environmental ethic violations
•
Reducing SC costs increases profit by the same margin that a greater proportion of additional sales does
•
Supply Chain Risk, Ethics, and Sustainability
Local optimization sees greater fluctuations between optimal demand and supply - slight upturns and downturns are
overcompensated for
•
Incentives push merchandise into SC for sales that have not yet occurred
•
Large lots reduce unit costs but don't reflect actual sales and increase holding costs
•
Managing the Supply Chain
Pull data is accurate sales data that initiates transactions to pull products through the SC, generated by sharing point-
of-sale (POS) data and computer-assisted ordering (CAO)
•
Lot size reduction occurs with aggressive management that emphasizes economical shipments, discounts based on
volume rather than size, and reducing cost of ordering
•
Single-stage control of replication fixes responsibility on a member of the SC for monitoring inventory for the retailer
•
Opportunities in an Integrated Supply Chain
Supply Chain Management & Analytics
February 15, 2018
2:30 PM
Operations Management Page 1
Document Summary
Supply chain (sc) is a coordinated network of people, organizations, resources that move a product from suppliers to consumers. Supply chain management is the management of activities that procure materials and services, transform them in to intermediate and final products, and deliver them in the distribution system. Supply chain analytics are set of quantitative tools used to manage, consisting of data analytics used to understand sc patterns and performance optimization. Demand at lowest cost quick response to changing demand to minimize stockouts. Use modular processes that lend themselves to mass customization. Develop responsive system with buffer to ensure supply. Shorten as long as costs do not increase. Use product designs that lead to low setup time and rapid production. Many suppliers strategy based on large supplier base that allows them to compete against one another - no desire to create long-term relationships.
