HLTA02H3 Study Guide - Fall 2018, Comprehensive Midterm Notes - Medicine, Social Science, Sociology

HLTA02H3
MIDTERM EXAM
STUDY GUIDE
Fall 2018


HLTA02: lecture 1: What is Criticality?
Has many meanings:
• Ofod Eglish Ditioa: epessig o iolig itiis
• A reference to higher-order cognitive skills used to critically appraise
arguments and evidence – analytical
• A particular orientation or approach to knowledge-action: example a ritial
soial siee perspetive – rooted in social theory
▪ Wh soiet is the a it is politial, eooi…
• We eed to uestio ot the hat ut the h o ho
• In order to understand a problem, we need to understand multiple
perspectives.
Attributes of Critical Thinkers (assignments)
• Interest in context, power, social relations and fairness even when these
ideas and dialogues are challenging or uncomfortable.
• Problematize: ideas, evidence, conclusions, perspective, origins. Need
information to make a decision.
• Committed to humility, fairness, collaboration, reflexivity.
• Reflective: thinking about a concept.
• Reflectiveness: putting yourself in the problem and the impact you will have
on others.
• Creative: open to thinking outside the box. You cannot treat an affluenza
outbreak the same as an obesity outbreak.
• Knowledge-power nexus and epistemic communities: committed to rigorous
application of theory to practice
• Value and purpose: social justice, solidarity, social transformation.
Epistemic Communities:
• a etok of people ith eogized epetise ho possess a shaed set of…
principled beliefs, common practices, and a conviction that human welfare
will be enhanced as a oseuee.
• 3 types of beliefs
What is critical Health studies?
Health sciences:
• A collection of disciplines that support and constitute medicine:
▪ Disiplies ased aoud edial ategoies ad asi siees suh
as nursing, occupational therapy, pharmacy.
▪ Disciplines based around edial ategories ad asi siees such
as anesthesiology, micro-biology, toxicology, genetics, and
immunology.
▪ Disciplines based around clinical specialties such as geriatrics,
pediatrics, family practice, critical care, and mental health care.
Health studies:
find more resources at oneclass.com
find more resources at oneclass.com
• Can look from a multiple perspectives.]
• Ideology is not something theoretical, in fact it forms decisions
• What ideologies underpin health and social care systems?
• Well-fare, child care benefits, OD+, etc.
• Canada is the only country in the world that offers Universal healthcare
without pharma-care
(Critical) Health Studies:
• Knowing together: questions posted by the Health Studies Epistemic
Community
• What constitutes health, illness, and care?
• What ideologies underpin health and social care systems?
• What health challenges do individuals and communities face?
• What historic conditions and emerging dynamics are shifting our experience
of health and illness?
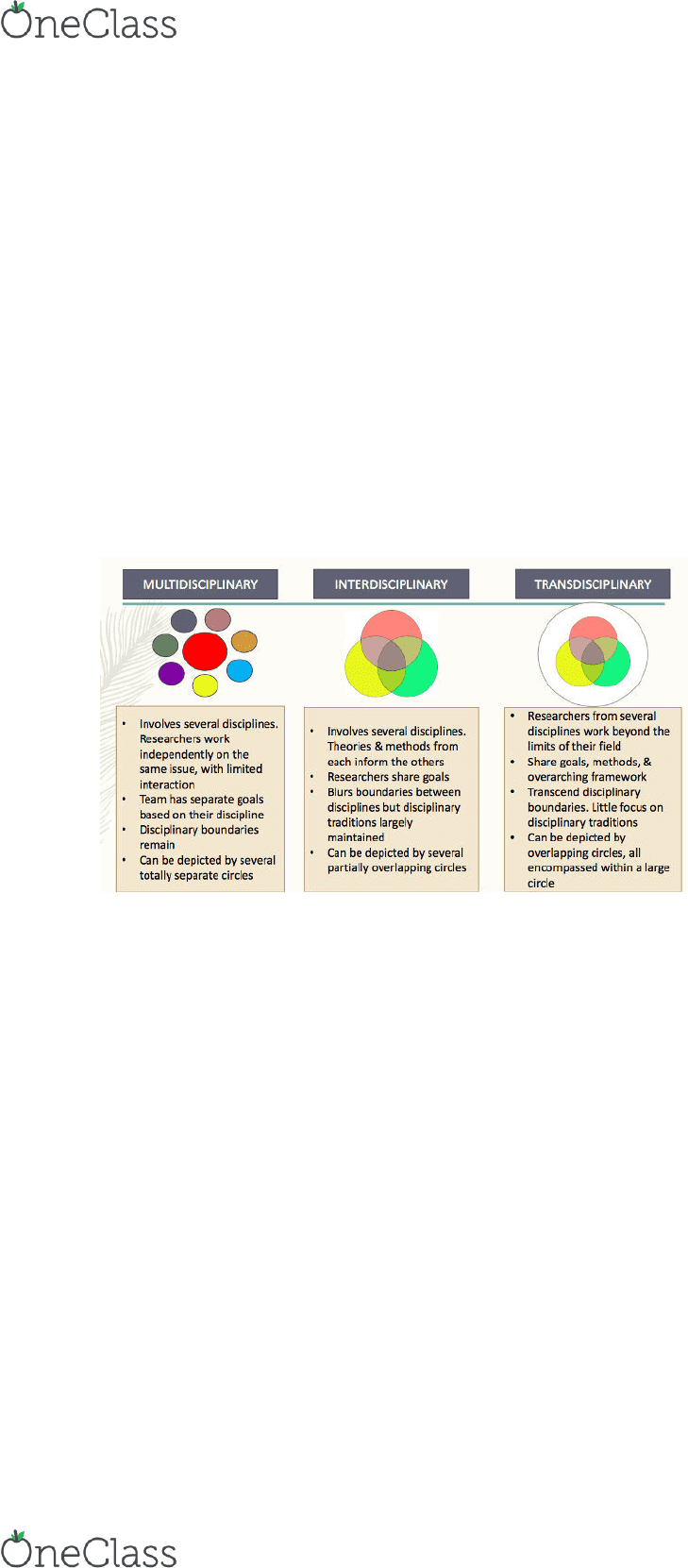
Disciplinary in Health Studies- what are they?
• Multi: interaction is very limited. Example: salad bowl, you can see the tomatoes,
cucumbers, and lettuce.
• Inter: sharing of knowledge, practices and theories. Shared perspective. Do not really
know where the boundaries are. Public health falls in this segment.
• Trans: collaborative work that addresses the work. Mixes quantitative and
qualitative. You do not see the ingredients in the cake (egg, sugar, etc.)
Transdisciplinary in Health
• An epistemic community forms around a common conceptual framework that:
▪ Combines disciplinary knowledge
▪ Combines knowledge from different conceptual fields (caring studies,
cultural studies, etc.)
▪ Combines knowledge from different professional domains
▪ Rigorous use of mixed-methods: quantitative and qualitative
▪ Collaborative and often participation from multiple stakeholders
Why Disciplinarily approaches?
• Resolve a real world problem
• Resolve complex problems
• Offer multiple perspectives
find more resources at oneclass.com
find more resources at oneclass.com
Document Summary
In order to understand a problem, we need to understand multiple perspectives. Interest in context, power, social relations and fairness even when these ideas and dialogues are challenging or uncomfortable: problematize: ideas, evidence, conclusions, perspective, origins. Need information to make a decision: committed to humility, fairness, collaboration, reflexivity, reflective: thinking about a concept, reflectiveness: putting yourself in the problem and the impact you will have on others, creative: open to thinking outside the box. You cannot treat an affluenza outbreak the same as an obesity outbreak: knowledge-power nexus and epistemic communities: committed to rigorous application of theory to practice, value and purpose: social justice, solidarity, social transformation. Epistemic communities: (cid:862)a (cid:374)et(cid:449)o(cid:396)k of people (cid:449)ith (cid:396)e(cid:272)og(cid:374)ized e(cid:454)pe(cid:396)tise (cid:449)ho possess a sha(cid:396)ed set of principled beliefs, common practices, and a conviction that human welfare will be enhanced as a (cid:272)o(cid:374)se(cid:395)ue(cid:374)(cid:272)e. (cid:863, 3 types of beliefs. Disciplinary in health studies- what are they: multi: interaction is very limited.
